Design of UASBR Technology for Organic India with Layout
Organic wastewater is a common by product of industrial and agricultural activities, and its disposal can pose a significant environmental challenge. The untreated wastewater can contain high levels of organic pollutants that can cause pollution, harm aquatic life, and even pose a threat to human health. Therefore, the treatment of organic wastewater is critical to protect the environment and public health.
To ensure the optimal performance of UASBR technology, it is important to design the reactor properly. The design involves several steps, including determining the organic loading rate, hydraulic retention time, reactor size, influent COD concentration, biogas production rate, gas retention time, sludge volume index, sludge concentration, and sedimentation time. By following these steps, the UASBR technology can be designed to be efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable.
To design the UASBR technology for organic India, the following steps are recommended:
-
Determine the organic loading rate (OLR) of the wastewater:
OLR (kg COD/m3/day) = influent COD (kg/day) / reactor volume (m3)
-
Determine the hydraulic retention time (HRT) of the wastewater:
HRT (days) = reactor volume (m3) / influent flow rate (m3/day)
-
Determine the reactor size:
Reactor volume (m3) = OLR (kg COD/m3/day) x HRT (days)
-
Determine the influent COD concentration:
Influent COD (kg/day) = influent flow rate (m3/day) x influent COD concentration (kg COD/m3)
-
Determine the biogas production rate:
Biogas production rate (m3/day) = influent COD (kg/day) x biogas yield (m3/kg COD)
-
Determine the gas retention time (GRT):
GRT (days) = gas volume (m3) / biogas production rate (m3/day)
-
Determine the gas volume:
Gas volume (m3) = reactor volume (m3) x gas hold-up (dimensionless)
-
Determine the sludge volume index (SVI):
SVI (ml/g) = sludge volume (ml) / sludge concentration (g/L)
-
Determine the sludge concentration:
Sludge concentration (g/L) = sedimentation time (h) x sludge volume index (SVI) / 1000
-
Determine the sedimentation time:
Sedimentation time (h) = reactor height (m) / surface overflow rate (m/h)
These steps are crucial in determining the design of the UASBR technology, ensuring that it is optimized for the treatment of organic wastewater.
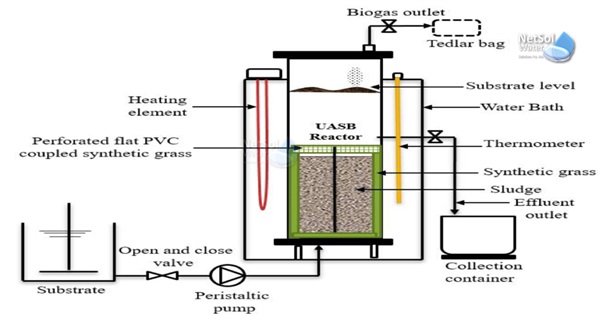
UASBR Technology Layout
The UASBR technology layout includes the placement of the reactor, the biogas collection system, and the sludge storage tank. The layout must be designed to ensure easy access to the reactor and the biogas collection system for maintenance purposes.
The reactor is placed in a designated area with adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases. The biogas collection system is placed adjacent to the reactor to allow for easy collection of the biogas.
The sludge storage tank is placed near the reactor to allow for easy transfer of the stabilized sludge. The sludge can be used as a fertilizer, contributing to Organic India's sustainability goals.
Conclusion
UASBR technology is an effective method for treating organic wastewater, and its design plays a crucial role in ensuring its effectiveness. The design involves several steps, including determining the organic loading rate, hydraulic retention time, reactor size, influent COD concentration, biogas production rate, gas retention time, sludge volume index, sludge concentration, and sedimentation time. By following these steps, the UASBR technology can be designed to be efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable.
To get in touch with us and to relish the benefits of our services, call us at +91-9650608473 or send an email to enquiry@netsolwater.com



