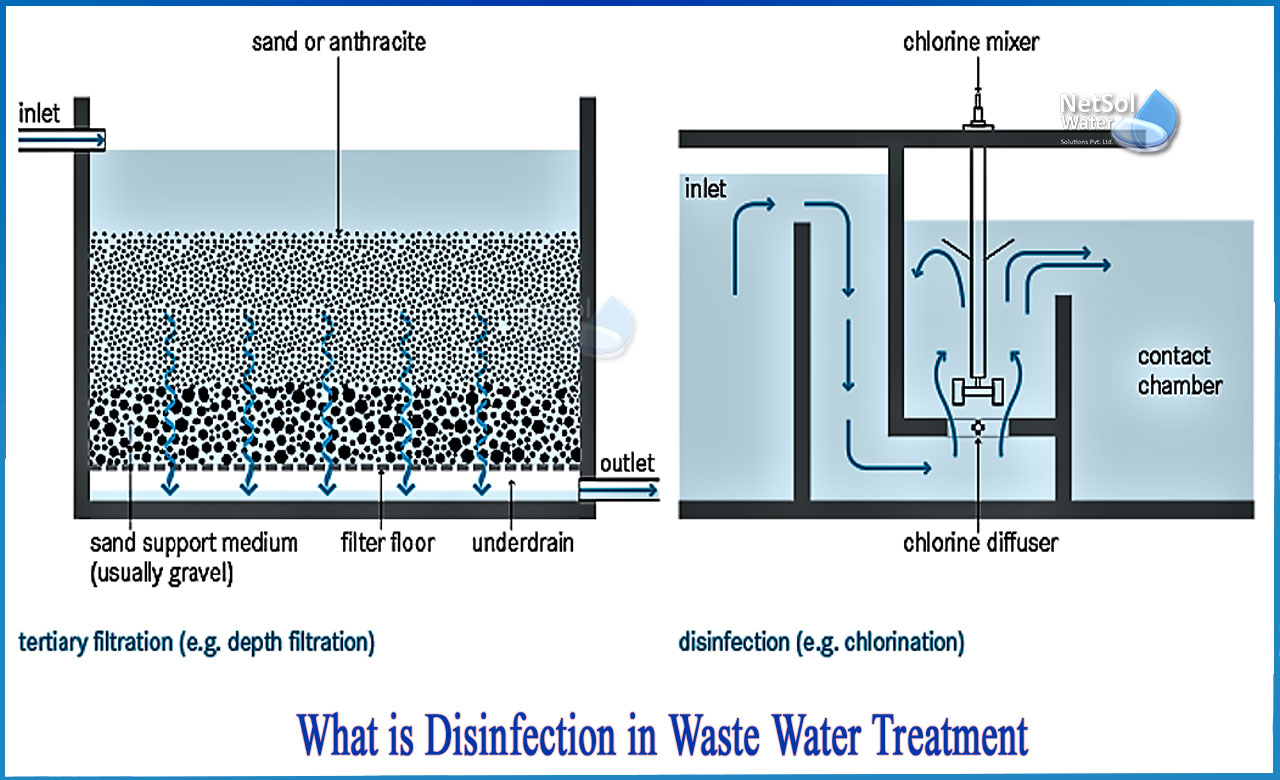
What is Disinfection in waste water treatment?
Depending on the quality of the water entering the treatment facility, water may be treated differently in various areas. Because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more silt and pollutants and are more likely to be polluted than ground water, surface water often requires more treatment and filtration than ground water.
Disinfection refers to the process of removing many or all harmful germs from inanimate items, excluding bacterial spores. Objects in health-care settings are often disinfected using liquid chemicals or wet pasteurisation. Each of the different parameters that impact disinfection efficacy might invalidate or restrict the process's efficacy.
The disinfection of water:
The purpose of disinfection of public water supply is to eliminate germs that cause waterborne infections. Diseases such as typhoid and paratyphoid fevers, cholera, salmonellosis, and shigellosis can be prevented by using treatments that significantly lower the overall amount of live bacteria in the water.
In the United States, chlorination is the most often used method for cleaning water sources. The ease of this approach, as well as its extremely satisfying performance as a disinfectant, which has been proven through decades of usage, can be ascribed to its near universal adoption. It has been so successful that the absence of waterborne disease outbreaks is now almost taken for granted. "Chlorination is the benchmark of disinfection against which others are measured," according to Drinking Water and Health (National Academy of Sciences, 1977).
However, the finding that chlorination can result in the creation of trihalomethanes (THMs) and other halogenated hydrocarbons has motivated a re-examination of existing disinfection techniques to identify alternate agents or processes.
The method used to disinfect water for human consumption is determined by a number of variables.
These are some examples:
- its effectiveness against pathogens found in water (bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and helminths);
- the degree of precision with which the process can be monitored and controlled;
- its capacity to generate a residue that provides further protection against probable posttreatment contamination caused by distribution system defects;
- the treated water's aesthetic qualities; and
- the availability of technology enabling the method's implementation on the scale necessary for public water suppliers.
Chlorine disinfection:
The technique of adding chlorine to drinking water to eliminate parasites, germs, and viruses is known as chlorination. To produce acceptable amounts of chlorine in drinking water, many techniques can be utilised. Drinking water with trace levels of chlorine has no negative health consequences and protects against waterborne illness epidemics.
Chloramine disinfection:
Chloramination is the technique of disinfecting and killing bacteria by adding chloramine to drinking water. It is occasionally used instead of chlorination. Chloramines are a class of chemical compounds containing both chlorine and ammonia. Monochloramine, a kind of chloramine used in drinking water disinfection, is added into water at levels that kill bacteria while being safe to consume.
Disinfection process in waste water treatment is an advanced step to purify water before discharging it into water resources.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.