Sewage treatment plants are crucial for ensuring that wastewater is treated and disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner. One of the most popular and effective technologies for sewage treatment is the Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology.
In this blog, we will explore the design of a sewage treatment plant based on MBBR technology, along with the functions of each equipment in detail, supported by relevant image.
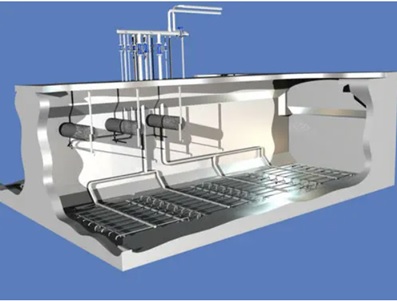
Design of an STP based on MBBR technology
- Raw Wastewater Inlet: The first stage in the sewage treatment plant design is the inlet, where the raw wastewater is collected and fed into the treatment plant. The incoming wastewater is first screened and de-gritted to remove any large debris and solid particles that could damage the downstream equipment.
- Primary Treatment: In the primary treatment stage, the wastewater is separated into three layers: scum, sludge, and clarified water. The scum layer, consisting of fats, oils, and grease, is skimmed off the top of the wastewater, while the heavier sludge layer is collected at the bottom of the tank. The clarified water layer, located between the scum and sludge layers, is then fed into the next stage of treatment.
- MBBR Tank: In the MBBR tank, the wastewater is further treated using a biofilm process. The MBBR system uses plastic media that is suspended in the wastewater, providing a surface area for the growth of bacteria that break down organic matter and pollutants in the water. The MBBR tank consists of multiple layers of plastic media, where the wastewater flows through each layer to provide maximum contact time with the biofilm.
- Secondary Clarifier: After passing through the MBBR tank, the wastewater is directed to the secondary clarifier, where the biofilm and suspended solids are allowed to settle. The clarified water is then collected at the top of the clarifier and directed to the next stage of treatment.
- Tertiary Treatment: In the tertiary treatment stage, the wastewater is further treated to remove any remaining organic matter, nutrients, and pathogens that may still be present. This stage involves several processes such as sand filtration, disinfection, and chemical dosing.
- Effluent Discharge: The final stage in the sewage treatment plant design is the discharge of treated water into the environment. The treated water is discharged through a dedicated line, which is monitored for compliance with environmental regulations.
Equipment Functions in an MBBR Sewage Treatment Plant
- Screens and Grit Removal: The screens and grit removal equipment are used to remove large debris, such as stones, plastics, and rags, from the raw wastewater before it enters the treatment plant. The equipment also removes grit, such as sand and gravel, which could damage downstream equipment.
- Primary Clarifier: The primary clarifier separates the raw wastewater into three layers: scum, sludge, and clarified water. This stage helps to reduce the load on downstream equipment, and the collected sludge can be further treated and processed for disposal or reuse.
- MBBR Tank: The MBBR tank is the heart of the sewage treatment plant, where the wastewater is treated using the biofilm process. The plastic media in the tank provides a surface area for the growth of bacteria that break down organic matter and pollutants in the water.
- Secondary Clarifier: The secondary clarifier is used to separate the biofilm and suspended solids from the treated water. The clarified water is then collected at the top of the clarifier and directed to the next stage of treatment.
- Tertiary Treatment Equipment: The tertiary treatment equipment includes processes such as sand filtration, disinfection, and chemical dosing. These processes further treat the wastewater to remove any remaining impurities, ensuring that the treated water meets the environmental regulations for discharge.
- Disinfection Equipment: Disinfection equipment is used to remove any remaining pathogens or bacteria in the treated water. Common disinfection methods include chlorine dosing, ultraviolet (UV) treatment, and ozone treatment.
- Sludge Handling Equipment: Sludge handling equipment is used to manage the collected sludge from the primary and secondary clarifiers. This equipment includes sludge pumps, sludge thickeners, and sludge dewatering systems.
- Effluent Monitoring Equipment: Effluent monitoring equipment is used to monitor the quality of treated water before it is discharged into the environment. This equipment includes pH sensors, turbidity meters, and dissolved oxygen meters, among others.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sewage treatment plants based on MBBR technology play a critical role in protecting the environment and public health by treating wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. Each equipment in the sewage treatment plant plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and effective treatment of wastewater. Proper operation and maintenance of the equipment can help ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the treatment plant.
For any other support, inquiries, or product purchases, call on +91-9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com



