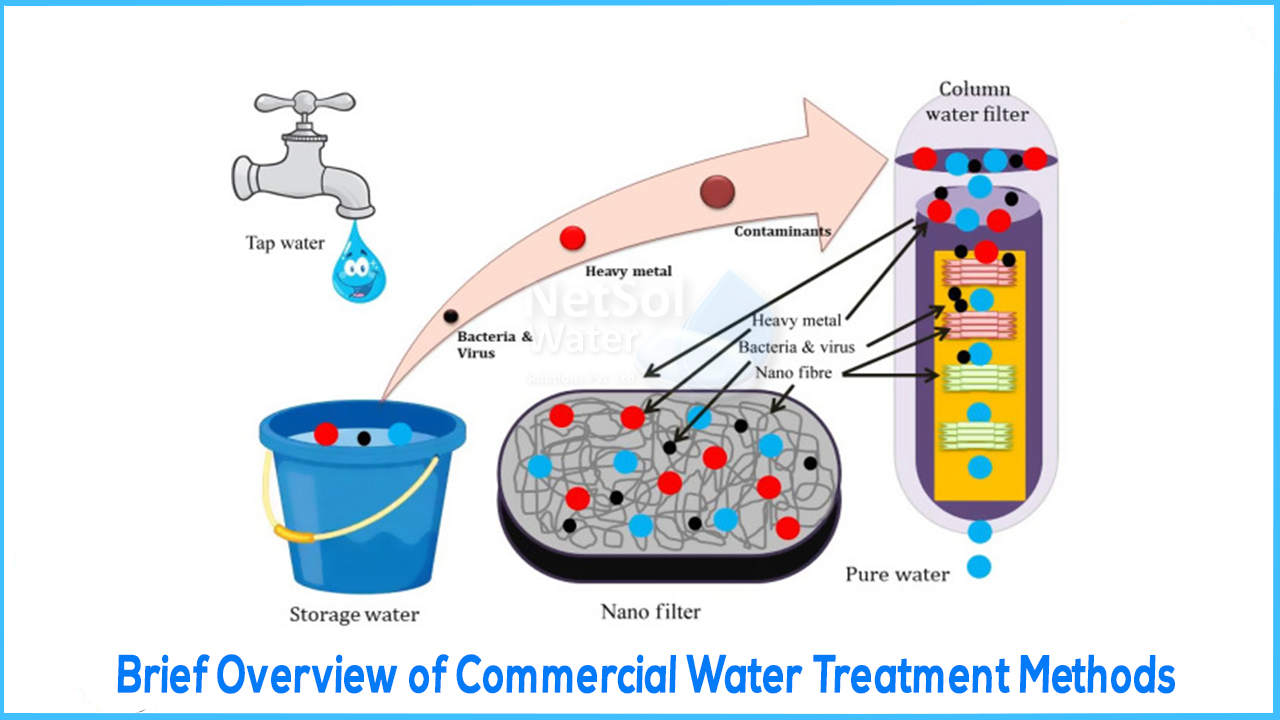
WATER TREATMENT
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it suitable for a specific end use. The end use can be drinking water, industrial water supply, irrigation, river maintenance, water recreation, or many other uses. This treatment is vital to human health and allows people to benefit from both drinking water and irrigation.
Treatment to produce drinking water involves the removal of contaminants and/ or the inactivation of potentially harmful microbes from raw water to produce water that is pure enough for human consumption. Generally, the greatest microbial risks are associated with ingesting water contaminated with human or animal (including bird) faeces. The elimination or destruction of microbial pathogens is essential and generally involves the use of reactive chemicals, suchas suspended solids, to eliminate bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi, and minerals, including iron and manganese.
Water quality maintenance is not just dependent upon water treatment but also on its conveyance and delivery.Therefore, it is common practice to leave disinfectant residue in treated water to remove bacterial contamination during distribution and to keep pipes clean.
PROCESSES INVOLVED IN WATER TREATMENT
Main processes of water treatment are boiler water treatment and cooling water treatment-
- 1. Boiler Water Treatment
This treatment system employs such systems so they prevent scaling, corrosion etc. that are caused due to dissolved calcium and other metals and minerals in water, which in the long run harm the boiler too much that it becomes a loss. Different treatment methods are used at different points to prevent scale, corrosion or foaming.
- 2. Cooling Water Treatment
Water cooling is a process for the dissipation of heat from components of machines and industrial plants. Water cooling is commonly used to cool internal combustion engines of automobiles and large industrial plants, such as nuclear and steam power plants, hydroelectric generators, oil refineries, and chemical plants.
TECHNOLOGIES INVOLVED
The technologies employed in water treatment plants are as follows-
- 1. Chemical treatment
Chemical treatments are techniques used to make domestic water suitable for use or discharge. These include chemical precipitation, chemical disinfection, chemical oxidation, advanced oxidation, ion exchange, and chemical neutralization. Ion- exchange or zeolite process is the most commonly used method of water treatment. It reduces or removes the hardness of water, makes water soft and pleasant to use.
- 2. Physical treatment
Filtration removes particles from the water by passing them throughrapid sandfilters, or in a mechanical filter. Dissolved air flotation removes suspended matter from water.For filtration, different sizes of sieves are used and their mesh size vary according to needs.
- 3. Biological treatment
Biological filters use microbes to treat water and make it usable.Slow sand filters use a biological process to purify water.They work with a complex biological film that grows naturally on the surface of the sand. This gelatinous biofilm, known as the hypogeal or ground cover layer, is found in the upper few millimetres of the sand layer. The surface biofilm cleanses the water as it flows through the layer.
- 4. Physical-chemical treatment
Chemical flocculants are used to create a floc in the water that traps suspended solids. Then these suspended solid settle down in the sedimentation chamber and clean water is flown for the next step in treatment.
All of these above treatment methods are employed in any commercial or industrial setting in accordance to the need of the industry.