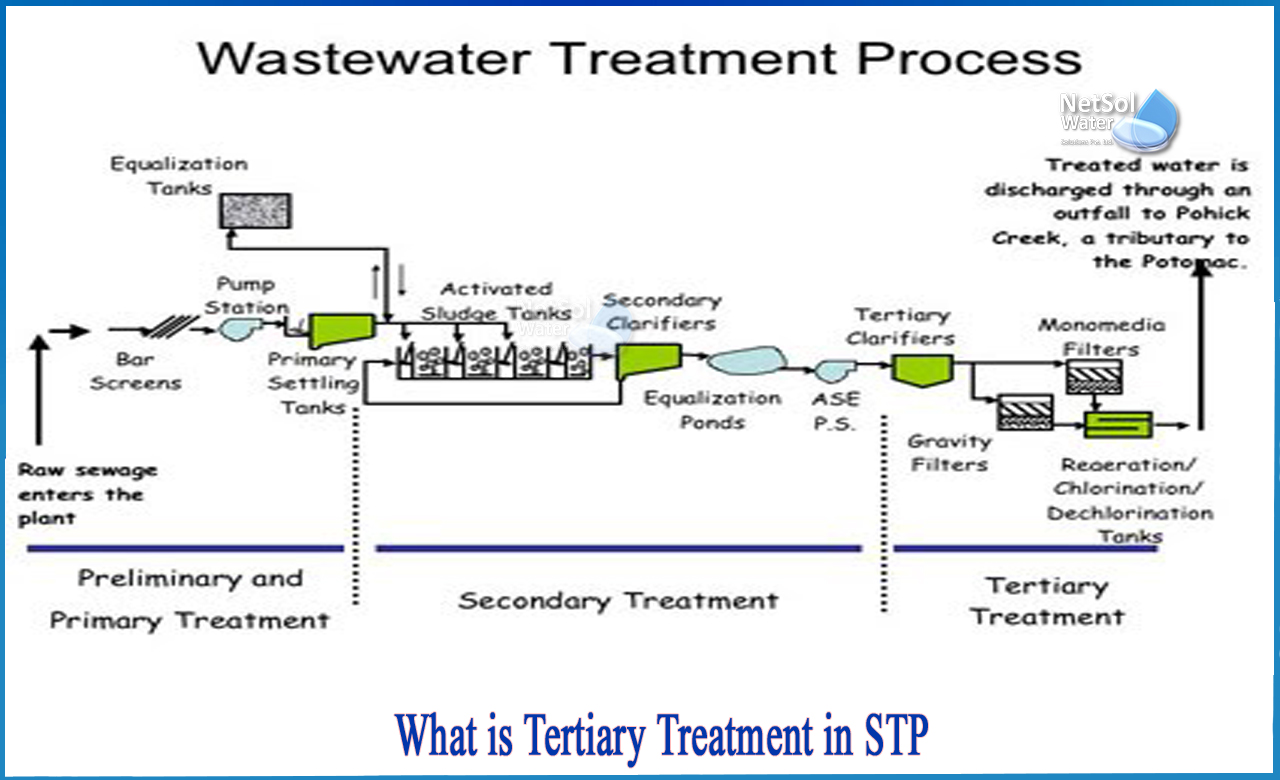
What is Tertiary Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant?
The last stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process is tertiary water treatment. Inorganic chemicals, bacteria, viruses, and parasites are all removed during the third stage of therapy. After these dangerous compounds have been removed, the treated water is safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
Waste water preparation for Tertiary treatment:
Primary wastewater treatment entails screening out large solid pollutants. The wastewater is then purified further by secondary treatment, which includes bio-filtration, aeration, and oxidation. All of these methods aid in the removal of silt from water.
NETSOL's municipal water treatment solutions can assist you in carrying out the three phases of wastewater treatment. We safeguard both humans and the natural environment from the detrimental impacts of untreated wastewater with this responsible three-stage water treatment procedure.
Methods of Tertiary treatment:
Tertiary wastewater treatment often entails final filtering of the treated effluent. When necessary, alum is used to eliminate phosphorus particles from the water. Alum also causes any particles that were not removed by primary and secondary wastewater treatment to clump together, allowing them to be removed by filters.
When necessary, the filters are backwashed to reduce floc build-up, allowing the filters to continue performing efficiently.
1. Disinfection: The addition of chlorine to the final effluent before disposal is an essential aspect of wastewater treatment. In this procedure, chlorine is injected into the headworks of a serpentine effluent detention chamber. Chlorination in wastewater treatment destroys bacteria and viruses, as well as parasites like Giardia and Cryptosporidium, which may cause severe disease. To summarise, this technique disinfects water so that it may be reused or recycled safely.
2. Dis-chlorination: The last stage of tertiary wastewater treatment involves eliminating the chlorine used to disinfect the water. This procedure is critical since chlorine is toxic to aquatic life. When present at high amounts, chlorine also degrades biological water quality.
A chemical called sodium bisulphite is added to the water to eliminate the chlorine. Water chloride ions react with this chemical and are eliminated.
Once the chlorine content has been decreased to a safe level, the treated water is deemed safe to discharge into the environment.
Technologies applied in Tertiary care:
Tertiary treatment removes the nitrogen and phosphate burdens from the water. Some of the processes involved are filtration, ion exchange, activated carbon adsorption, electro dialysis, nitrification, and de-nitrification.
Filtration process: The filtration process eliminates particulate particles from water by passing it through porous medium. The filtering process employs many types of media, which are often composed of sand, gravel, and charcoal. Slow sand filtration and fast sand filtration are the two forms of sand filtration.
Membrane process: Membrane technology is used to handle a wide range of wastes such as sewage, organic and inorganic debris, and water-soluble oil wastes. Membrane processes are categorised according to their driving force and separation mechanism, such as Multi Filtration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nano-filtration (NF), Reverse Osmosis (RO), and Forward Osmosis (FO).
Advanced oxidation system: Ozone is added to the process to kill bacteria and breakdown organic pollutants. By transporting oxygen via a high voltage electric field, ozone gas (O3) is generated. After chlorine, ozone is now the most extensively used disinfectant.
Conclusion
Netsol water is India's leading manufacturer of water treatment and sewage treatment systems. We are the leading service provider for waste and waste water solutions, including solutions, testing and monitoring, analysis, and recommended corrective steps, based on our many years of expertise.
We are the leading provider of solutions for treating sludge and industrial wastewater in order to protect water and the environment.