The amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in the water is the simplest definition of water hardness. Dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium, are abundant in hard water. The last time you washed your hands, you may have felt the impacts of hard water. Depending on the hardness of your water, you may have noticed a film of residue on your hands after washing with soap. Soap reacts with calcium (which is relatively high in hard water) to generate "soap scum" in hard water.When you use hard water, you'll need more soap or detergent to get things clean, whether it's your hands, hair, or laundry.
Have you ever taken out glasses from the dishwasher after a load of dishes and seen stains or film on them? This is more hard-water residue, which isn't harmful but is unsightly. The hardness of water is a concern for many industrial and domestic water users. Solid calcium carbonate deposits can form when hard water is heated, such as in a residential water heater.This scale can shorten equipment life, increase water heating expenses, diminish the effectiveness of electric water heaters, and clog pipes.
Mineral buildup can also form in your home coffee makers, which is why some people pour vinegar (an acid) through it on occasion. By making mineral particles charged, vinegar's acidity aids in their dissolution. These newly charged particles are easily washed away due to their attraction to the positive and negative charges in water. However, there are some advantages to hard water.
HARDWATER AND RO MEMBRANES! DO THEY GO HAND IN HAND?
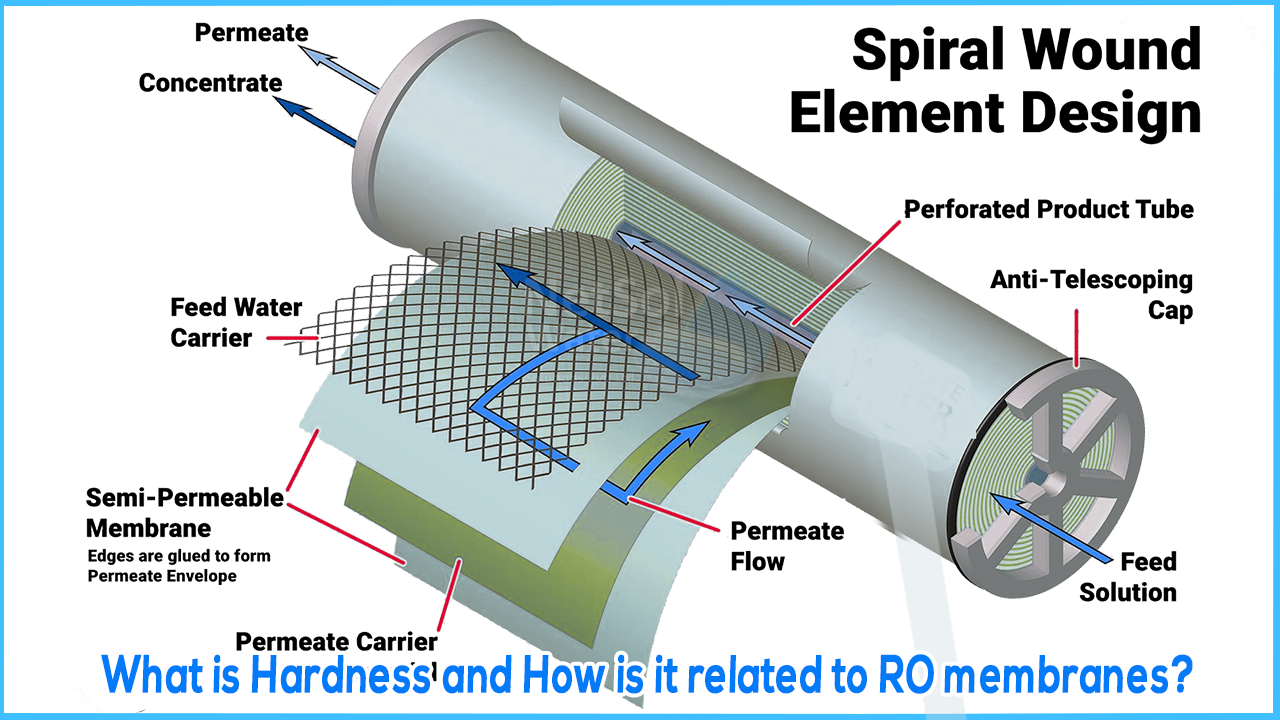
Reverse Osmosis is the only pressure driven membrane process that can protect equipment from mineral scale. This is because only RO membranes have small enough openings to hold back calcium and magnesium from crossing the membrane into the permeate.
Hard water poses a number of difficulties. Hard water can develop scale during the filtration process, making it extremely difficult for the RO membrane to function, resulting in poor water quality. Hard water is caused by a high mineral concentration, which is typically calcium and magnesium ions. Scale is caused by dissolved rock, which has been proven to impede appliance function, resulting in energy inefficiency and higher utility expenditures.
Hardness can cause membrane scaling, which reduces the membrane's production. It lowers the quality of the water that the membrane produces and, in effect, kills the membrane over time. The calcium molecules that attach to each other are the ones that have the most impact on a RO system. Calcium in the water behaves similarly to cholesterol in the blood, adhering to everything and thickening and hardening as more accumulates. Calcium molecules clog the membrane of a RO membrane, necessitating constant backwashing.
Ion exchange is a popular method for softening water. Hard water is fed through a cylinder packed with sodium-saturated resin beads during the ion exchange process. Hardness ions are drawn to the resin and sodium ions are released when this happens. One of the most significant disadvantages of hard water is its inefficiency in terms of energy efficiency. Minerals that clog the RO and induce scaling make the unit work harder, waste water, and increase utility expenses.
There are ways to avoid this and benefit the environment at the same time. The problem is serious enough that the water treatment sector is focusing on reducing discharge, conserving water, and being more environmentally friendly.
There's no denying that RO has been a reliable filtration technique for decades. While it has waste and energy downsides, for domestic and light business use, there are few more efficient and practical inventions available. Companies will become more concerned of end users, the environment, and the business line as they continue to go green with solutions for hard water and scale reduction.