Nutrient Removal from Effluent with MBR Technology
Excess nitrogen and phosphorus in effluent can lead to eutrophication and hypoxic conditions in receiving waters. Conventional activated sludge processes provide inconsistent nutrient reduction. However, advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology can offer reliable enhanced nutrient removal for sustainable effluent quality.
Nutrient Removal Mechanisms
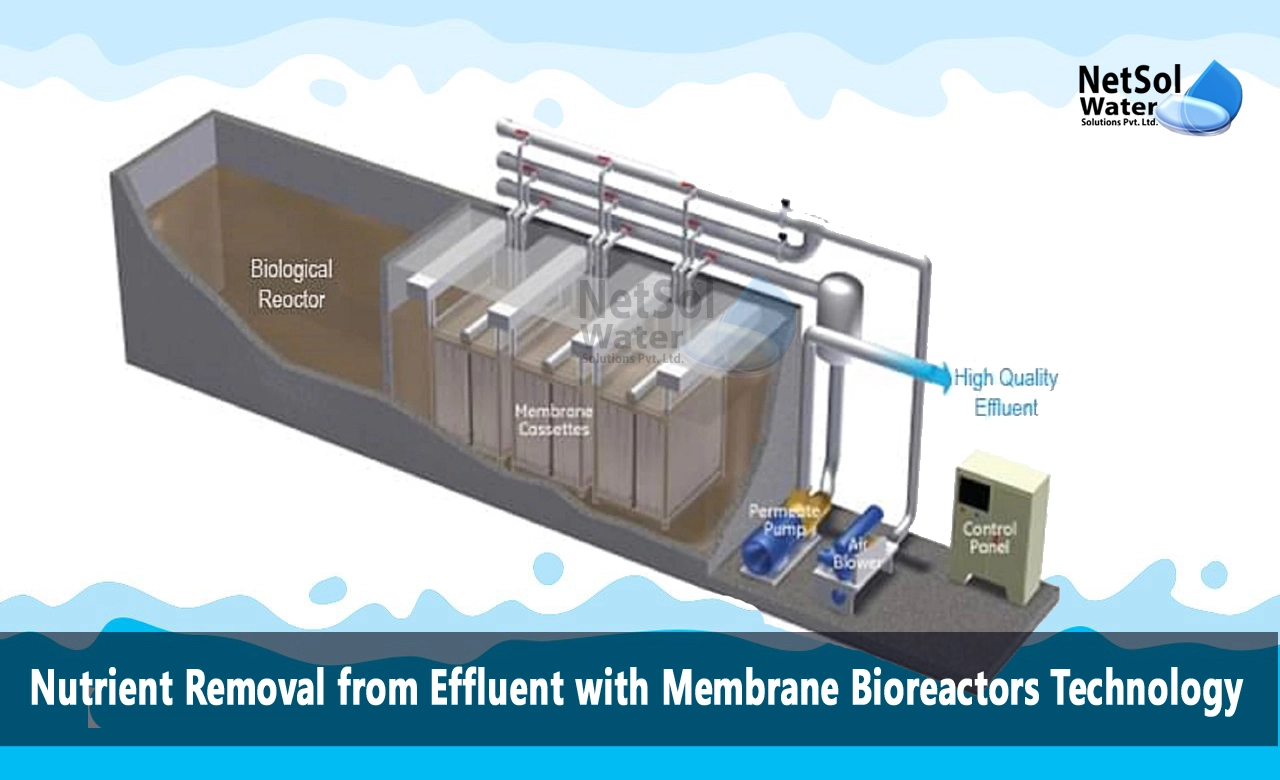
MBRs integrate biological treatment with low-pressure membrane filtration. This combines activated sludge and secondary clarification in a single step. The membrane component uses microfiltration or ultrafiltration to produce an exceptionally clear permeate stream. For nutrient removal, the MBR may incorporate configurations. This involves anoxic and aerobic zones to facilitate nitrification and denitrification by regulating oxygen levels and recycling flows. Phosphorus can be biologically removed by organisms called polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) through anaerobic and aerobic cycles. The membrane provides excellent solids separation to retain PAOs.
Configurations for Nutrient Control
Several MBR configurations canoptimise nutrient removal:
1- Pre-anoxic MBRs route the influent through an initial anoxic zone to begin denitrification prior to aeration. This anoxic-aerobic setup enhances nitrogen removal.
2- A2O MBRs using anaerobic, anoxic and aerobic zones in sequence encourage PAO biology and maximise phosphorus uptake in the anaerobic stage. Recycle streams between zones facilitate denitrification.
3- SBR MBRs utilise sequencing batch reactors with defined periodic cycles of anaerobic, anoxic and aerobic conditions in the same tank to promote PAO biology and nitrogen removal.
4- Hybrid MBRs combine fixed film and suspended growth bioreactors. The attached growth on fixed media provides extensive surfaces for PAOs to prosper.
Benefits of Nutrient Control
MBRs offer several advantages for nutrient reduction:
1- Complete solids retention by the membrane enables higher mixed liquor suspension solids and sludge age, optimising PAO growth.
2- The membrane effluent quality provides superior total nitrogen and phosphorus removal to simple clarification.
3- Low hydraulic retention times still allow sufficient biological reactions for nutrients thanks to uncoupled solids retention.
4- Smaller reactor volumes are possible compared to conventional nutrient removal processes.
5- Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification can be achieved in a single unit with proper cycling.
Challenges for Nutrient MBRs
While promising for enhanced nutrient control, MBRs also pose some challenges:
1- Fouling caused by extracellular polymeric substances can impact nutrient removal performance and require extensive cleaning.
2- Chemical addition may be needed to target phosphorus precipitation if biological removal is not sufficient.
3- Energy demands for aeration and permeate pumping are higher for MBR systems.
4- Nutrient limitations and improper environmental conditions can hinder PAO and nitrifier kinetics.
5- Costs are greater than conventional nutrient removal, though a smaller footprint and superior effluent quality may offset this.
Bioaugmentation
The addition of specific compounds and cultured bacteria has shown a potential to boost nutrient removal for MBRs. For example:
1- Powdered activated carbon provides a surface area to stabilise nitrification and adsorb recalcitrant organics.
2- Adding silica can aid phosphorous removal through absorption.
3- Commercial nutrient-removing bacteria products may enhance PAO populations.
4- Hydrogen peroxide and microbubbles can increase oxygen transfer for nitrification.
Operational Optimization
Proper operational optimisation is key to maintaining excellent MBR nutrient removal:
1- Adjusting sludge age and DO setpoints based on frequent SVI monitoring and kinetics testing.
2- Using online nutrient analysersto adjust redox conditions continuously.
3- Scheduling membrane cleaning around nitrification cycles.
4- Coordinating recycle flows and waste pumping to sustain the desired biology.
5- Tracking trends in nutrient removal to catch issues early.
Conclusion
With tightening regulations worldwide, wastewater plants need advanced solutions for complete nutrient control. While challenging to implement, MBR technology provides unmatched effluent quality along with smaller spatial requirements. MBRs capable of simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal down to ultra-low levels help wastewater facilities consistently meet or exceed discharge limits now and into the future. However, optimised design and diligent operation are crucial to translate the technical potential into day-to-day plant reliability and sustainability.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.