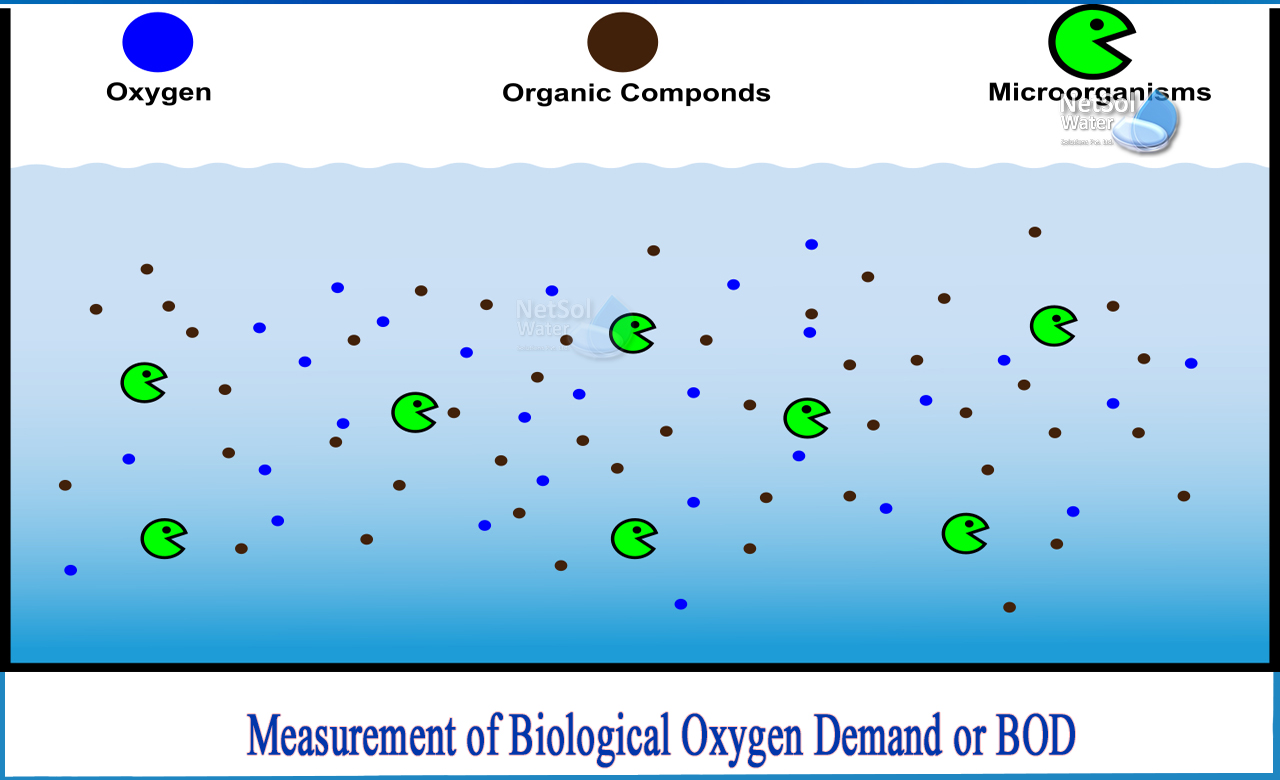
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is an important parameter used to measure the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms in wastewater treatment plants. It is measured as mg/L or mg/l.
BOD is a procedure for determining the amount of dissolved oxygen required by aerobic biological organisms in a body of water to break down organic material present in a given water sample at a specific temperature over a specific time period.
Sources of biochemical oxygen demand
Top soil, leaves, and woody debris; animal manure; effluents from pulp and paper mills, wastewater treatment plants, feedlots, and food-processing plants; failing septic systems; and urban stormwater runoff are all sources of biochemical oxygen demand.
How to Calculate Biological Oxygen Demand?
BOD is a measure of how much oxygen is required by wastewater treatment plants to remove organic matter. It is measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L), which equals parts per million (ppm). The higher the number, the greater the amount of oxygen needed to treat the waste stream.
The most common method of measuring BOD is through the use of a colorimetric reagent called dichromatic acid. We add this reagent to the sample and wait until the reaction occurs. Then, we read the absorbance of the solution on a spectrophotometer and determine the BOD value.
Although it is not a precise quantitative test, it is widely used to indicate the organic quality of water. It is most commonly expressed in milligrams of oxygen consumed per litre of sample during 5 days of incubation at 20°C (BOD-5) and is frequently used as a reliable surrogate for the degree of organic pollution in water.
The amount of dissolved oxygen in rivers and streams is directly affected by biological oxygen demand. Temperature, pH, the presence of certain microorganisms, and the type of organic and inorganic material in the water all influence the rate of oxygen consumption.
The higher the value, the faster oxygen is depleted in the stream. This means that higher forms of aquatic life have less oxygen available to them. High BOD levels have the same consequences as low dissolved oxygen levels: aquatic organisms become stressed, suffocate, and die.
The same factors that influence dissolved oxygen also influence biological oxygen demand. Measuring biochemical oxygen demand necessitates the collection of two measurements. The first is measured for dissolved oxygen immediately (initial), and the second is incubated in the lab for 5 days before being tested for the amount of dissolved oxygen remaining (final). This is the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms during the incubation period to break down the organic matter in the sample.
Problems related to BOD measurement
When there is a problem with your values, most operators first blame the instrument or probe. After all, it is the source of your values!
Many factors can contribute to the problem, including dirty bottles, DI water, bad seed, bubbles, non-linearity, and so on.
Warm-Up Time: Polarographic probes require a 5-15 minute warm-up period before calibrating and using the probe. Inadequate warm-up time can easily result in data drifting due to inaccurate calibration. Warm-up time is not required for optical probes.
Probe Care: Polarographic sensors require fresh electrolyte and membranes, as well as a well-maintained anode and cathode, to perform optimally. Optical sensors will require a visual inspection of the paint layer on the sensor cap on a regular basis.
Calibration: Irrespective of technology, it is suggested that the instrument be calibrated only once a day before taking readings. Before calibrating, ensure that there are no water droplets on the probe tip and that the probe is in a totally and utterly water-saturated. All that is required is a BOD bottle with a little water in the bottom. When not in use, return the probe to this bottle.
Conclusion
The operator must be acquainted with standard methods as well as technical literature on the subject. When used correctly, the test provides a dependable characterization of wastewater. Although its use as a control tool is limited by the 3 or 5 day wait required for the test (and sometimes 20 days!), it is expected to be a standard for regulatory agencies for many years.
BOD Calculation Formula
- Metabolic Rate = Number of Organisms x 0.039 mg O2 / L
- For example, if you have 1 million bacteria in a sample, and each consumes 0.039 mg of oxygen per hour, then the BOD would be:
- BOD = 1,000,000 * 0.039 = 39,000 mg/L