A granular activated carbon filter (GAC) is a tried-and-true method for removing pollutants from water. Additionally, GAC filters can be used to get rid of pollutants like chlorine and hydrogen sulphide, which give water unpleasant taste or aroma like rotten eggs.
Other pollutants, such as iron and nitrate, are not drawn to the carbon and are not eliminated, necessitating the use of another type of filter, like reverse osmosis (RO) or sand filters. Some organic compounds are also be eliminated by RO Plants.
In this blog, we will review how the activated carbon’s capacity is affected by its particle size.
Raw materials for granular activated carbon filters
Raw organic resources that are high in carbon, such as coal or coconut shells, are used to make granular activated carbon. These filters are sometimes referred to as "charcoal" filters, since heat is employed to raise or activate the surface area of the carbon, in the absence of oxygen. Certain compounds like chlorine, dissolved in water that is going through a filter that contains GAC are removed by the activated carbon, by trapping (adsorbing) the chemicals in the GAC.
How is the activated carbon’s capacity affected by the particle size of carbon molecules?
An activated carbon's capacity does not increase with decreasing particle size. This is due to the fact that a carbon's surface area is essentially unchanged when it is fine, regardless of how finely the surface area is at a molecular level.
However, as the carbon particle size drops, the kinetics (speed of adsorption) does significantly increase. This implies that less bedding will be needed to obtain a given performance, by the smaller particle size of the carbon.
When should you select activated carbon with smaller particle size?
An activated carbons pressure drop increases with decreasing particle size, which raises the cost of attaining flow through it. It may be inferred that the smallest size of carbon should always be employed, provided that the benefit of needing a small bed outweighs the expense of pumping fluid through it.
The equation below can be used to predict the change in adsorption kinetics of activated carbon particles:
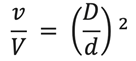
Where,
D = the biggest carbon's typical particle diameter.
V = the biggest carbon's fastest rate of adsorption.
D = the average size of the smallest carbon particle.
v = the smallest carbon's adsorption velocity.
Replacing activated carbon filters
Water use and pollutant levels should be used to determine how frequently the GAC should be changed. If pollutant levels or water use are low, some filters may endure for several years, but if these factors are higher, they may need to be changed more frequently.
To choose the proper system size and components of activated carbon filter, it is crucial to know the kind and concentration of contaminants, as well as the normal water usage. Thus the treatment system needs to be installed correctly and should be maintained on a regular basis.
How can we assist?
Netsol Water, a well-known manufacturer of water treatment plants, are able to provide a broad selection of industrial water filters that can be tailored, to the specifications and needs of any given project.
We also offer high-quality activated carbon filters and commercial and industrial RO Plants, which are appropriate for any application in tertiary water treatment and water purification. With manufacturing and supply all over the world, we maintain exclusive contracts that enable us to offer products of unrivalled quality, at incredibly affordable prices.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.



