How is RO Water Used in RMC Plant?
Reverse osmosis water plays a clear role in modern ready mix concrete plants. This water moves through a filter system to remove salts, particles and other dissolved matter. Plants use this water to protect concrete quality and to meet strict project standards. When a plant uses clean water it controls setting time and avoids unwanted reactions. Many projects require water that meets precise chemical limits. Using regular water can cause problems with admixtures, cement hydration and long-term durability. By partnering with a trusted Commercial RO Plant Manufacturer, facilities ensure they have a high-capacity system tailored to these industrial needs. RO water gives a steady source of clean water. It helps plants make consistent concrete batch after batch. Here we are going to explain how is RO water used in RMC plant and why it matters in daily plant work.
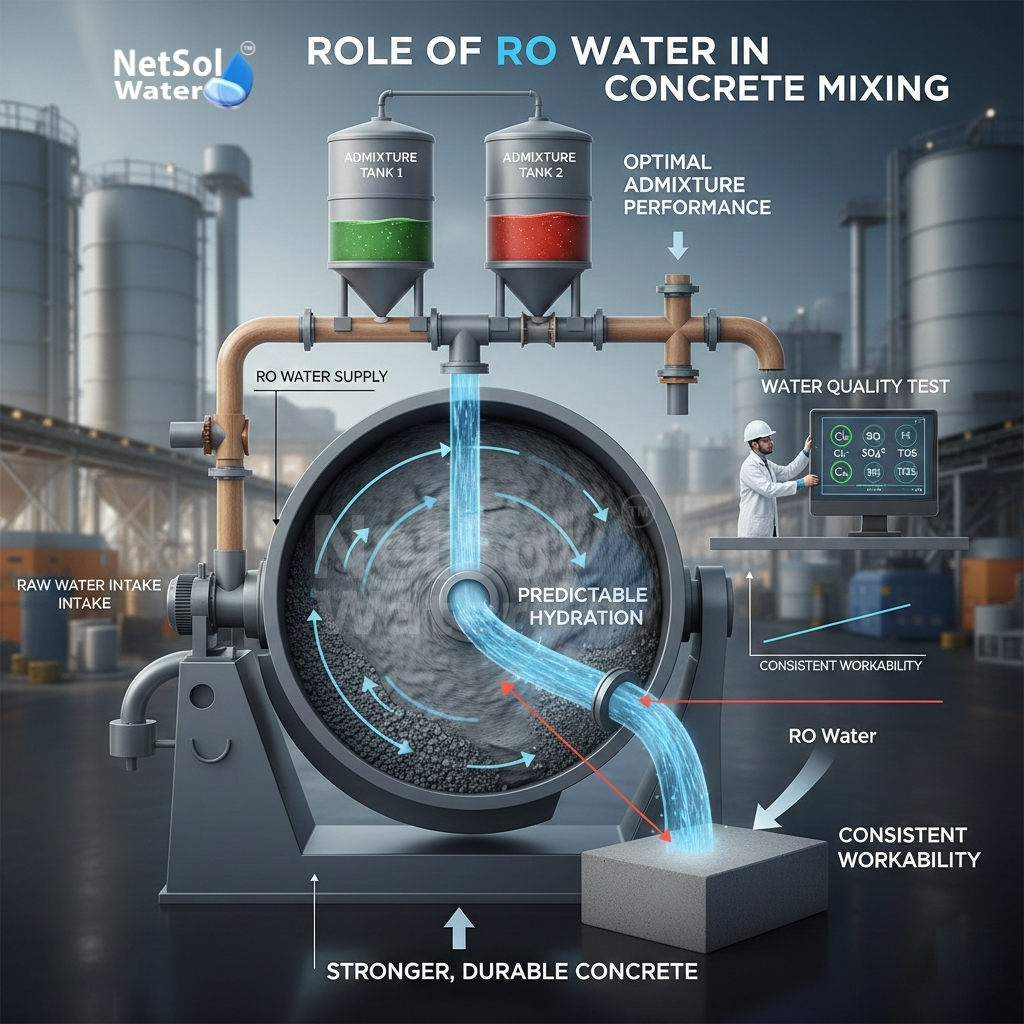
Role of RO water in concrete mixing
Water controls the chemical processes that form concrete strength. Hard particles and salts can change these reactions and reduce final strength. Clean water helps control the mix and ensures that the cement hydrates as expected. Let us have a look on some key points and how plants use RO water in mixing.
1: Water quality and cement hydration
Water participates in cement chemistry. If water carries extra salts or ions then it can speed or slow hydration. Plants that use Reverse Osmosis water remove those unwanted ions. This action makes hydration more predictable. A predictable hydration path lets the plant hit strength targets and timing goals.
2: Consistent water demand and workability
Workability depends on water content and water quality. When water quality changes, the same mix can feel different. That difference forces operators to change water amounts or change admixture doses. RO water keeps the mix feel steady. The plant can set mix designs and then follow them without surprise.
3: Admixture performance
Many admixtures react with salts or with specific ions in raw water. If water contains those ions then admixture action can weaken. RO water has low ion content. This low ion level lets admixtures work as the maker expects. When admixtures work correctly mixes keep pumping strength and finish targets.
Quality control and testing for RO water
Testing confirms that water meets the limits for a project. Plants must record results and follow a clear testing routine. Let us have a look on some main tests and how they support plant control.
1: Chemical tests and thresholds
Plants test for chloride, sulfate and total dissolved solids among other items. These tests show if water can harm steel or speed corrosion. Plants follow standards from codes and from project specs. Reverse Osmosis water usually passes these tests but plants still test it at intake and after storage.
2: Microbial and physical checks
Water can host microbes or suspended particles. Both can change mix performance or affect admixtures. Plants use simple filters and UV units and then test water on a schedule. When a test fails the plant isolates that water and uses an alternate source until the problem clears.
3: Record keeping and traceability
Plants keep records of each test result. These records link to specific batches and to delivery times. Traceability helps respond to field complaints and to quality audits. RO water systems must show consistent tests to keep plant records complete.

Storage, handling and distribution of RO water
Storage affects water quality and the risk of contamination. Plants design tanks, piping and pumps to protect water quality. Let us have a look on some storage and handling steps and how they fit into day to day work.
1: Tank materials and layout
Tanks must not add contaminants to RO water. Plants choose materials that do not leach salts or metals. A good layout keeps the RO tank near the plant to cut pipe length. Short pipes reduce the time water sits unused and reduce contamination risk.
2: Avoiding stagnation
Water that stands still can change quality. Plants avoid long hold times by running recirculation lines or by scheduling batches around RO output. Operators label tanks with fill times and run checks before each shift. This work keeps water fresh and ready for mixing.
3: Distribution and metering
Plants use closed pipes and metered pumps to feed mixers. Meters show how much RO water goes into each batch. This control helps maintain the exact water cement ratio. When a plant uses metering it keeps the batch record accurate and consistent.

Dosage and proportioning with RO water
Clean water may alter the performance of admixtures and the effect of cement. Plants must adjust proportioning and dose admixtures with care. Let us have a look on some dosing practices and how they keep mixes steady.
1: Setting water cement ratios
Plants set the water cement ratio based on mix needs. RO water does not change the ratio in a direct way. It changes how the mix performs at that ratio. Operators test trial mixes to confirm that the chosen ratio gives the needed workability and strength.
2: Admixture dosing strategies
Admixtures need trial dosing to match RO water. Plants run small mixes and then adjust the dose for slump set time and compressive strength. This step prevents overdosing and underdosing. It also avoids costly rework on site.
3: Automated controls and manual checks
Some plants use automated systems that add RO water and admixtures by weight or volume. Automation gives repeatable dosing. Manual checks still matter. Operators watch for mix feel and for any signs of segregation or poor set.
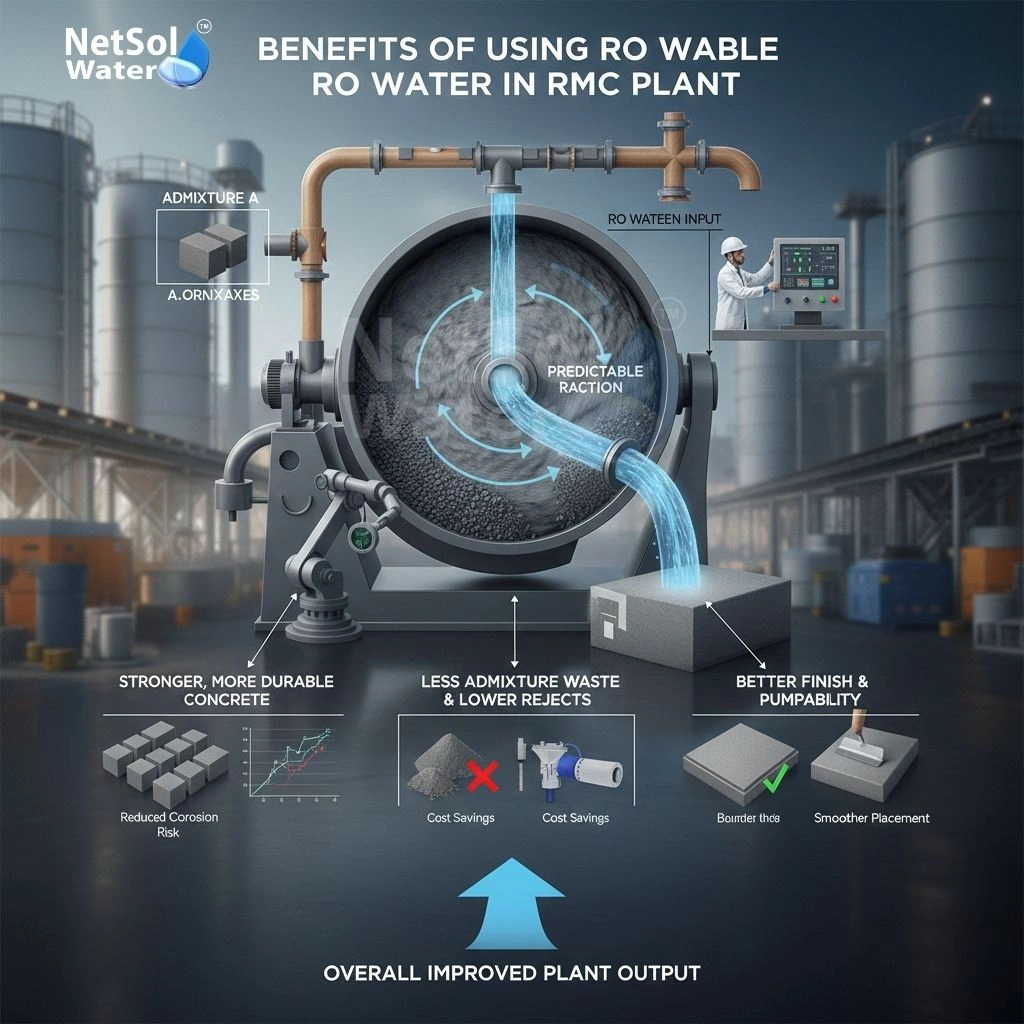
Benefits of using RO water in RMC plant
Better control, lower risk and consistent mixes improve delivery. Let us have a look on some practical benefits and how they translate to plant results.
1: Stronger and more durable concrete
Clean water helps cement hydrate in a predictable way. Predictable hydration means the plant meets the design strength more often. Durability also improves when water does not add harmful salts. This gain reduces risk of premature concrete damage.
2: Less admixture waste and lower rejects
When admixtures work as they should, the plant wastes less product. Fewer batches fail tests and less material goes to waste. This result cuts cost and improves plant output.
3: Better finish and pumpability
RO water helps produce mixes with even consistency. That uniformity improves surface finish and pumpability. Contractors find it easier to place and finish concrete that comes from a plant using clean water.
Cost and economic considerations
Plants weigh capital cost against the long term gains from better quality. Let us have a look on some economic points and how decision makers judge the value.
1: Capital and running costs
RO plants require an initial investment in equipment and in installation. They also require energy and maintenance. Plants calculate these costs and compare them to savings from lower rejects and reduced admixture waste.
2: Return on investment
Plants track metrics such as fewer failed tests, lower warranty claims and improved batch consistency. These metrics help estimate payback time. Many plants find that steady supply of clean water pays off over time.
3: Scale and project fit
Large plants and plants that serve sensitive projects gain more from RO water. Small plants may use blended water or mobile RO plants to reduce cost. Decision makers choose the option that fits their output and their project needs.
Environmental and regulatory factors
Plants must follow codes for water use and for waste disposal. Let us have a look on some compliance steps and how plants manage environmental impact.
1: Waste brine handling
Reverse Osmosis plants produce concentrated brine as a waste stream. Plants must manage this brine responsibly. Options include discharge under permit treatment or sending brine to a disposal facility. Plants plan this step in line with local rules.
2: Water conservation and reuse
Plants can pair RO units with recycling systems for wash water. This approach reduces the total water draw and cuts waste. Reuse limits fresh water intake and helps plants meet sustainability goals.
3: Local rules and permits
Many areas require permits for water treatment and discharge. Plants consult local authorities and follow permit terms. Good record keeping and transparent reporting ease audits and inspections.
Maintenance of RO plants at RMC plant
Poor maintenance reduces water quality and raises cost. Let us have a look on some maintenance routines that plants follow and how they protect system output.
1: Routine inspections and filter changes
RO membranes and prefilters need regular checks. Operators follow a service schedule and they log each task. Timely filter change keeps flow and quality at design values.
2: Monitoring and alarms
Plants fit sensors to monitor pressure flow and conductivity. These sensors trigger alarms when output drops or when salt passage rises. Quick response prevents contaminated water from reaching mixers.
Professional servicing and spare parts
Plants plan for periodic professional service. They also keep critical spare parts on hand. Being ready reduces downtime and keeps the plant running when demand rises.

Integration with plant quality systems
Water must tie to mix design records, batch logs and delivery certificates. Let us have a look on some integration steps and how plants make water part of quality control.
1: Linking water tests to batch records
Each batch should note the water source and test results. This link helps trace any issues back to water quality. It also supports claims management and customer reports.
2: Training and standard operating procedures
Operators need training on RO water handling and on tests. Plants write clear procedures and they update them after audits. Well trained staff reduce mistakes and keep the quality level up.
3: Continuous improvement
Plants review water impact on concrete performance. They use test data to tweak mixes and to tune the RO plant. This feedback loop improves quality over time.
Conclusion
RO water gives plants a steady path to consistent concrete quality and to fewer surprises in the field. Using RO water in RMC plant helps meet strength and finish goals and it helps admixtures perform as intended. Plants that invest in proper storage testing and maintenance gain repeatable results and lower waste. If you want to learn how is RO water used in RMC plant on your site contact us for a consultation. We can review your mix designs, test plans and plant layout and then suggest a clear way forward. Reach out now to discuss practical steps and to get a tailored plan for your plant.
Contact Netsol Water at:
Phone: +91-9650608473, Email: enquiry@netsolwater.com



