Concept of pH
Sorensen, a Danish scientist, described pH as follows:
pH equals the inverse of the logarithm to the base 10 of the hydrogen ion concentration
pH = -10log [H+]
Sorensen later discovered that this definition was erroneous, because higher concentrated solutions appeared to produce differences between calculated and observed results.
As a result, the definition had to be changed to:
As stated by the formula: pH equals the inverse of the logarithm to the base 10 of hydrogen ion concentration.
pH = -10log aH+
The activity of hydrogen ions is not necessarily linear with concentration since it is impacted by factors other than ion concentration, such as:
1: The activity of other ions presents in the solution
2: The solution's temperature
3: The solution's personality.
A variety of "standard liquids" or "buffer solutions" are employed to aid precise pH measurement and scale display.These liquids have known stable values since their ingredients are well determined.
Although a connection to hydrogen ions was suggested in the preceding paragraph, research has demonstrated that the action of hydroxonium ions is more important. In aqueous solutions, free H+ ions do not exist; instead, they are constantly coupled with water molecules.
H+ + H20 ↔ H30+
Apparently, a more suitable definition for pH is:
pH = -10log aH30+
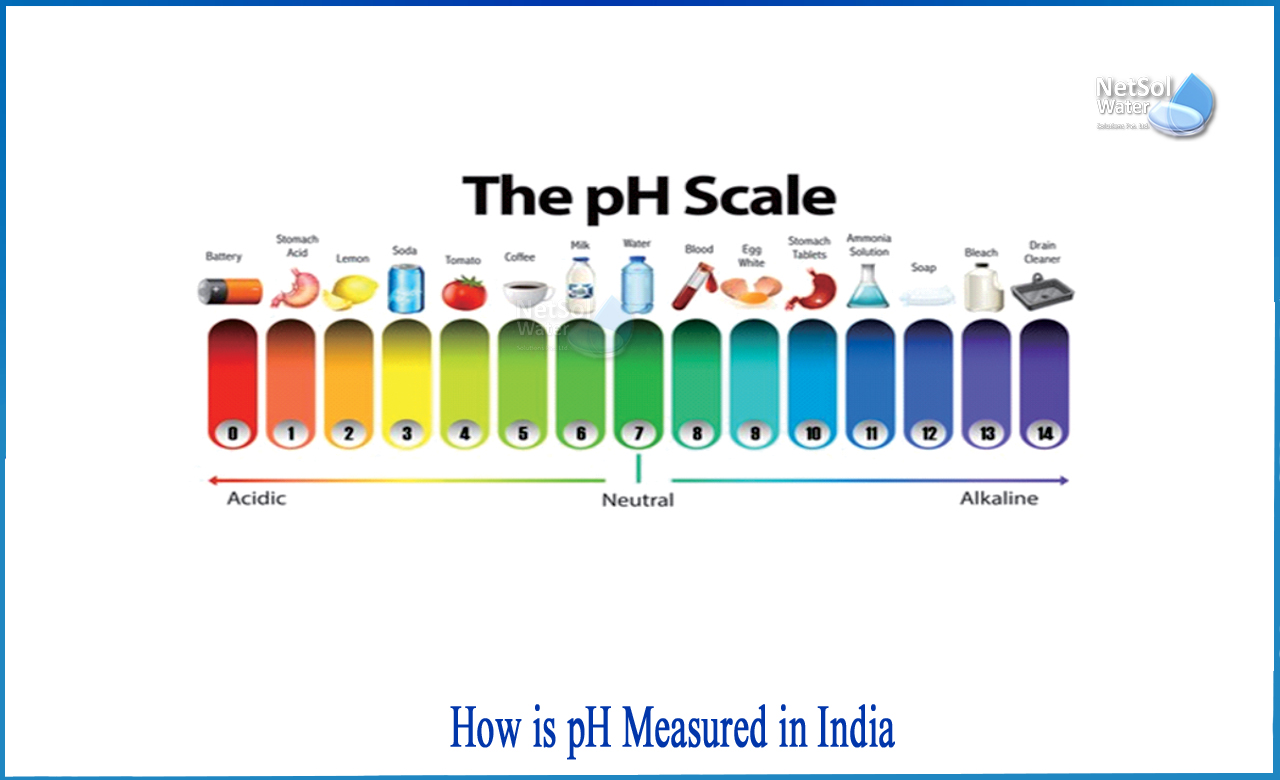
How is pH measured in India?
A neutral solution has a pH of 7, an acid solution has a pH less than 7, and a basic solution has a pH more than 7.
The value of the measured quantity can be shown by:
a) A moving index instrument,
b) A digital instrument, or
c) A combination of the two.
c) A recording device, and
d) A binary coded decimal output.
Different methods, such as pH metering, can be used to determine the pH level:
A: Colorimetric pH measurement: The colorimetric pH measuring principle is based on the pH dependence of colour change.
B: Potentiometric pH measurement: A pH sensitive glass sensor is the most often used pH detecting element. If a glass sensor is not available, other pH sensors are employed (e.g. antimony sensor).
Nernst's law explains the concept of potentiometric pH measurement. When a metal item is submerged in a solution containing ions of the same metal, a potential difference arises, according to Nernst. Nernst characterized the potential difference ‘E’ induced by the exchange of metal ions between metal and liquid as follows:
R = Gas constant (R=8.314J/mol.K)
F = Faraday number (F = 96493 C/ mol.)
n = Valency of the metal
[Mn+] = Metal ion concentration
T = Absolute temperature in Kelvin
Eo = Normal potential
The "normal potential" is the difference in potential between metal and solution when the solution contains 1 mol Mn+/litre. Because hydrogen has some similarities to metals (both exhibit positive ion production), Nernst's law may also be used to a "hydrogen electrode" submerged in a solution containing hydrogen ions.
The formula may be rewritten in the following way:
Indian Standard for measuring pH
pH is measured using Standard ProceduresIS: 3025-Part 11 'Methods of sampling and testing (physical and chemical) forwater and wastewater (pH)’.
What do we have to offer?
The World Health Organization as well as BIS specifies the standard values for pH before disposing the wastewater of in the surface or inland waters. As STP/ETP/WWTP/WTP manufacturers, we can provide you with expert solution and design the best suited treatment plant as per your needs.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.