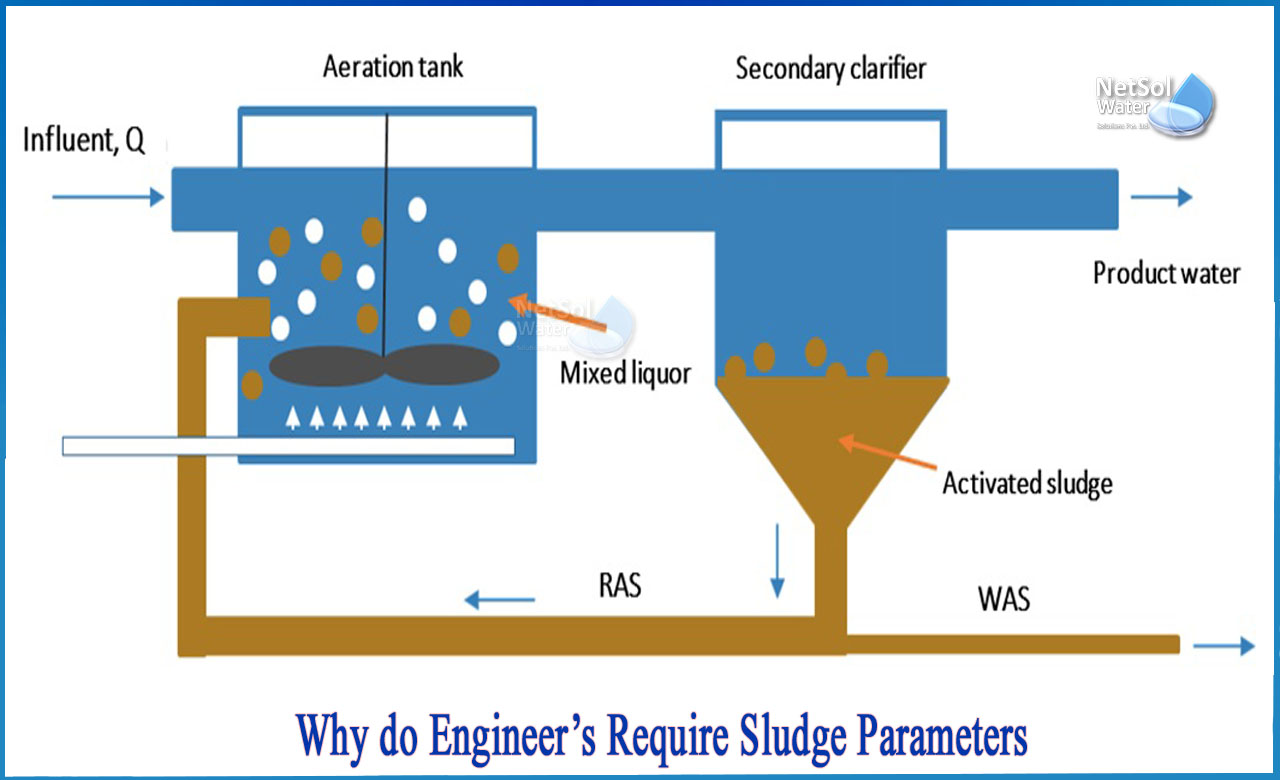
Why do Engineer’s require Sludge parameters?
Sludge treatment refers to any method that makes it easier to transport, store, reuse, or dispose of sewage sludge. To safeguard human and environmental health from the risks associated with sludge, mandatory measures to avoid discharge into the environment must be implemented.
Dewatering, composting, anaerobic digestion, drying–incineration, and sanitary landfill are the most common methods for sludge processing and disposal. The basic goal of sludge dewatering is to minimise the amount of sludge by eliminating as much water as feasible.
What is composting?
Composting is a bio thermal aerobic process that decomposes and reduces the organic portion of sewage sludge by about 25%. Meanwhile, heat can be generated during this process, decreasing the sludge's moisture content. Temperature, dry matter, and volatile solids are all critical to the process's success.
In average, sludge used for compositing should have less than 60% moisture, more than 40% organic matter (dry basis), and an acceptable quantity of heavy metals and POPs, according to regulations. Lower moisture organic matter, such as straw or sawdust, should be added to the 80 percent moisture sludge for composting to bring the water content down to roughly 55–65 percent.
Furthermore, during the composting process, a strong stench will develop, which will be difficult to effectively regulate. Anaerobic digestion entails a series of biological processes (acidogenesis, acetogenesis, hydrolysis, and methanogenesis) in which microorganisms break down biodegradable matter and produce methane-rich biogas (60–70 vol. percent CH4) while also destroying pathogens in the sludge and deleting offensive odours.
When the digested residual meets the environmental limits expressed in local legislation and standards, it is disposed of in agriculture fields as a soil conditioner/fertilizer. As a result, anaerobic digestion is recognised as a critical component of modern WWTP.
Activated Sludge
A plug flow reactor, a complete mixing reactor, or a sequencing batch type reactor based on a population of bacteria that digest organic matter present in the influent stream in the presence of oxygen are all examples of activated sludge systems.
More than 94–98% of the resin acids (like pimaric acid, sandaracopimaric acid, and isopimaric acid) and 41–67% of the sterols (like campesterol, campestanol, -sitosterol, and stigmastanol) are degraded and removed in activated sludge treatment, whereas about 5% of the resin acids and more than 31% of the sterols are removed. In biosludge of the sludge thickener offers excellent operation stability and flexibility to the method.
Categories of Sludge
Free water (65–85% water), interstitial water (15–25%), vicinal water (7%), and water of hydration (7%) are the four types of water found in sludge.
Gravity or flotation thickening are used to remove free water. The addition of flocculants or high mechanical forces is required to eliminate interstitial and vicinal water. Only extreme pre-treatments, such as thermal drying or freezing–thawing techniques, can extract hydration water from sludge flocs.
Sludge Parameters
The supervision and development of sludge treatment plants are based on sludge characteristics. They give the engineer critical information about the sludge's existent (inorganic) components, settling behaviour, dewatering, and heat value.
>Total suspended solids TSS: A 105°C oven filters and heats the mixed liquid from the reactor, the treated water, and the feed. Due to the low temperature, just water evaporates and nothing is burned in this process. The feed, treated water, and reactor are then weighed to determine the amount of solids in each.
>Volatile suspended solid VSS: The filtrate is extracted from the 105°C oven and deposited in a 600°C oven, where the organic materials are burned and the inorganic materials that remain are weighed.
>Index of sludge volume SVI: The mixed liquid is eliminated from the reactor and poured into a slow mixing vessel to settle. The volume of sludge is measured after half an hour. The SVI units are millilitres per gramme.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.