What is transmembrane pressure and how it is calculated?
The membrane filtration technique is used to create a variety of products. In this procedure, a liquid is sent through a membrane system that separates it into two streams. The material that cannot pass through the synthetic membrane in the filtration system, is referred to as the retentate while the feed is known as the permeate.
The best type of filtration membrane depends on the density of the liquid that needs to be separated. The membrane filtration process depends heavily on pressure. Transmembrane pressure (TMP), its function in the filtering process, and its calculation are all covered in this article.
What is transmembrane pressure?
The pressure across a membrane is referred to as the transmembrane pressure. According to the material composition of each membrane, an ideal TMP exists. Crossflow filtration, however, is vulnerable to both concentration polarisation and membrane fouling, since it requires the recirculation of the feed.
Concentration polarisation happens when, as a result of TMP, the feed component concentration rises close to or on the membrane surface, but vanishes when pressure is released. If concentration polarisation needs to be fixed, the TMP might need to be changed.
Membrane fouling
Feed components that accumulate on the membrane's surface, and persist after pressure is removed, are known as membrane fouling. Cleaning or changing the filter is necessary to address membrane fouling.
The efficacy of the membrane's filtration is impacted by both of these processes!
The TMP of a membrane is kept at or within the usual operating range by membrane filtering systems by design. The membrane maintains its cleanliness and keeps its filtering powers when used, within the ideal TMP range. A dirty filter may be the cause of a high TMP.
An Angstrom, or one hundred millionth of a centimetre, is the unit of measurement for the synthetic minuscule pores used in these filters, which are intended to separate minute particles. Since, even a slight variation in TMP can result in contamination, membrane fouling, or concentration polarisation, these filtration methods are often volumetrically regulated.
How is transmembrane pressure calculated?
TMP is computed by subtracting the permeate pressure from the average feed pressure. The formula for determining transmembrane pressure is as follows:
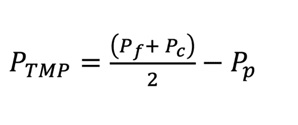
In this equation, PTMP stands for the transmembrane pressure, Pf for the input pressure of the feed stream, Pc for the pressure of the concentrate stream, and Pp for the pressure of the permeate stream. All dimensions are given in kilopascals.
Conclusion
TMP can be manually measured by inserting a pressure transducer into the feed to measure the pre-filter pressure, then inserting the transducer into the retentate on the outside of the membrane, to measure the retentate pressure. The transducer can also be used to gauge the filtered fluid inside the membrane, by averaging the two measurements.
You can optimise pressure and change other variables by using filtration systems, to monitor transmembrane pressure in real-time. Processors can quickly spot polarisation, fouling, and contamination concerns thanks to real-time monitoring, which enables them to take immediate corrective action and prevent unplanned downtime.
Customisation from experts in Membrane Systems like RO Plants
Netsol Water outstanding custom filtering systems can assist you in achieving the high-volume, high-quality output your company requires. For reverse osmosis skid-built systems, we can design, set up, and install them.
Clean-In-Place (CIP) systems can be integrated with your current systems as well. Our technologies give you the ability to remotely manage, and improve your filtration procedures. You can also use pilot testing to make sure your system is operating as it should. We're pleased to offer in-depth instruction and assistance for the machinery we install. For further information or to make a product purchase, contact us at +91-9650608473 or drop a mail at enquiry@netsolwater.com