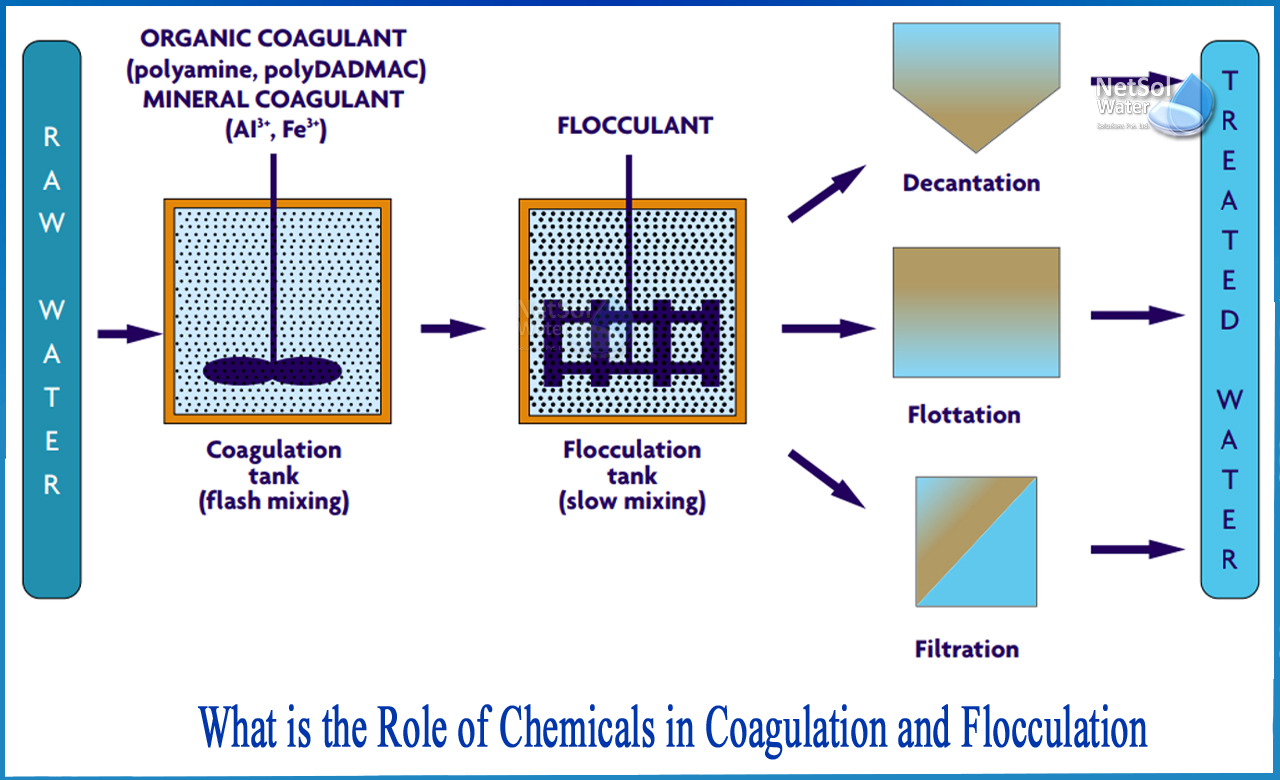
What is the role of chemicals in coagulation and flocculation?
Coagulation and flocculation are essential processes in various fields. In drinking water treatment, we have been purifying water with coagulants for a long time.
Already in 2000 BC, the Egyptians used almonds painted around the ship to purify the water of the river. The use of alum as a coagulant by the Romans was recorded around 77 AD. By 1757, alum was used for coagulation in the water treatment of British municipalities.
In modern water treatment, coagulation and flocculation continues to be an integral part of the overall treatment process. Since 1989, the US regulatory limit on treated water turbidity has been gradually increased from 1.0 NTU in 1989 to 0 today. Many water utilities are committed to consistently producing treated water with a turbidity of less than 0.1 NTU to prevent contamination by pathogens.
This article outlines the process and provides the latest considerations-
Role of chemicals in coagulation
Commonly used metal coagulants fall into two general categories: aluminium-based and iron-based.
Aluminiu?m coagulants include aluminium sulphate, aluminium chloride, and sodium aluminate. Ferrous coagulants include ferrous sulphate, ferrous sulphite, ferric chloride and ferric chloride sulphate. Other chemicals used as coagulants are slaked lime and magnesium carbonate.
The effectiveness of aluminium and iron coagulants is primarily due to their ability to form multivalent polynuclear complexes with enhanced adsorption properties. The nature of the complex forms can be controlled by the pH of the system.
When metal coagulants are added to water, metal ions (Al and Fe) are rapidly hydrolyzed, but somewhat uncontrolled, forming a variety of metal hydrolyzed species. The efficiency of rapid mixing, pH and dose of coagulant determine which hydrolyzed species are effective for treatment.
Prehydrolyzed inorganic coagulants, based on both aluminium and iron to produce the correct hydrolysis species regardless of the process conditions during treatment are developed.These include aluminium chlorohydrate, polyaluminum chloride, polyaluminum sulphate chloride, polyaluminum silicate chloride and forms of polyaluminum chloride with organic polymers. Iron forms include polyferric sulphate and ferric salts with polymers. There are also polymerized aluminumiron blends.
Other types of coagulants
Polymer based- The principal advantage of pre-polymerized coagulants arethat they are able to function efficiently over wide ranges of pH and raw water temperatures. They are not very sensitive to low water temperatures. Lower doses are required to reach the water treatment goal. There is less chemical residue. It produces less residual chloride or sulphate and lowers the final TDS of the water. They also produce less metal residue.
Prepolymerized Inorganic Coagulants are manufactured at a variety of basicity ratios, base concentrations, base addition rates, initial metal concentrations, aging times, and aging temperatures. Because these products are so specific, the optimal formulation for a particular water is case specific and must be determined by glass testing. For example, in some applications, alum outperforms some polyaluminum chloride formulations.
Conclusion
Thus we can see, there are lots of chemicals traditionally used in industries for coagulation and flocculation which is also called as agglutination. The dosage of these chemicals is decided by the requirement of the treatment plant.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.