What is an environmental management system?
An Environmental Management System (EMS) is a framework that assists an organisation in achieving its environmental goals by regularly reviewing, evaluating, and improving its environmental performance. The assumption is that this consistent review and evaluation will identify opportunities for improving and implementing the organization's environmental performance.
The EMS does not impose a minimum level of environmental performance; instead, each organization's EMS is tailored to its own unique objectives and targets. An EMS assists a company in meeting its regulatory requirements in a systematic and cost-effective manner. This proactive approach can help to reduce the risk of noncompliance while also improving health and safety practises for employees and the general public. An EMS can also aid in the resolution of non-regulated issues such as energy conservation, as well as the promotion of stronger operational control and employee stewardship.
Elements of environmental management system:
· Creating programmes to achieve these goals and objectives;
· Monitoring and measuring progress toward achieving the goals;
· Examining the organization's environmental objectives;
· Analysing its environmental impacts and compliance obligations (or other legal and regulatory requirements);
· Setting environmental goals and targets in order to reduce environmental impacts and meet compliance obligations;
· Ensuring environmental awareness and competence among employees; and
· Reviewing the EMS's progress and making improvements
Benefits of EMS:
· Environmental performance can improve
· Improved compliance
· Pollution avoidance
· Conservation of natural resources
· New clients/markets
· Enhanced efficiency/cost savings
· Employee morale can improve
· Improved image among the general public, regulators, lenders, and investors
· Employee environmental awareness and responsibilities
Repeating cycle of EMS:
An EMS motivates a company to constantly improve its environmental performance. The system operates in a loop. The organisation first commits to an environmental policy, which serves as the foundation for developing a plan that establishes objectives and targets for improving environmental performance. The following step is implementation.
Following that, the organisation assesses its environmental performance to determine whether the objectives and targets have been met. If goals are not met, corrective action is taken. The results of this evaluation are then reviewed by top management to determine whether or not the EMS is effective. In a revised plan, management revisits the environmental policy and sets new targets. The revised plan is then implemented by the company. The cycle is repeated, and continuous improvement takes place.
Stages of environmental management system:
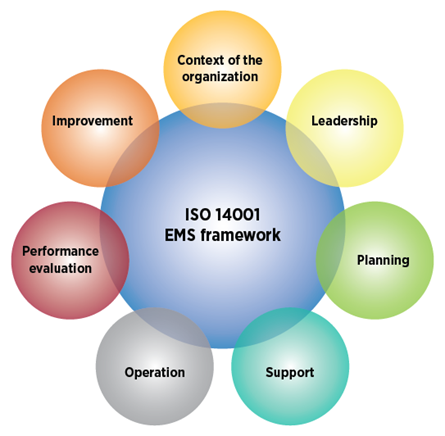
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) framework for the ISO 14001 standard is the most commonly used framework for an EMS. This framework, which was established in 1996, is the official international standard for an EMS that is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act methodology.
The ISO 14001 standard defines five major stages of an EMS, which are described below:
1. Commitment and policy: Top management pledges to improve the environment and establishes the organization's environmental policy. The policy is the EMS's foundation.
2. Planning: Planning entails identifying the environmental aspects of an organization's operations. Environmental aspects are items that can have a negative impact on people and/or the environment, such as air pollutants or hazardous waste. An organisation then decides which aspects are significant by selecting criteria that are important to the organisation. For example, an organization's criteria could include worker health and safety, environmental compliance, and cost. After determining the most important environmental aspects, an organisation establishes objectives and targets. The final stage of planning entails developing an action plan to achieve the goals. This includes delegating responsibilities, developing a timetable, and outlining clearly defined steps to achieve the goals.
3. Implementation:A company implements the action plan by allocating the necessary resources (human, financial, etc.). Employee training and awareness for all employees is an important component (including interns, contractors, etc.). Documentation, adherence to operating procedures, and the establishment of internal and external communication lines are also steps in the implementation stage.
4. Evaluation: A company monitors its operations to see if its goals and objectives are being met. If this is not the case, the company takes corrective action.
Review:The results of the evaluation are reviewed by top management to determine whether or not the EMS is effective. Management determines whether the original environmental policy is consistent with the values of the organisation. The plan is then revised to improve the EMS's effectiveness. The review stage creates a loop of continuous improvement for a company.



