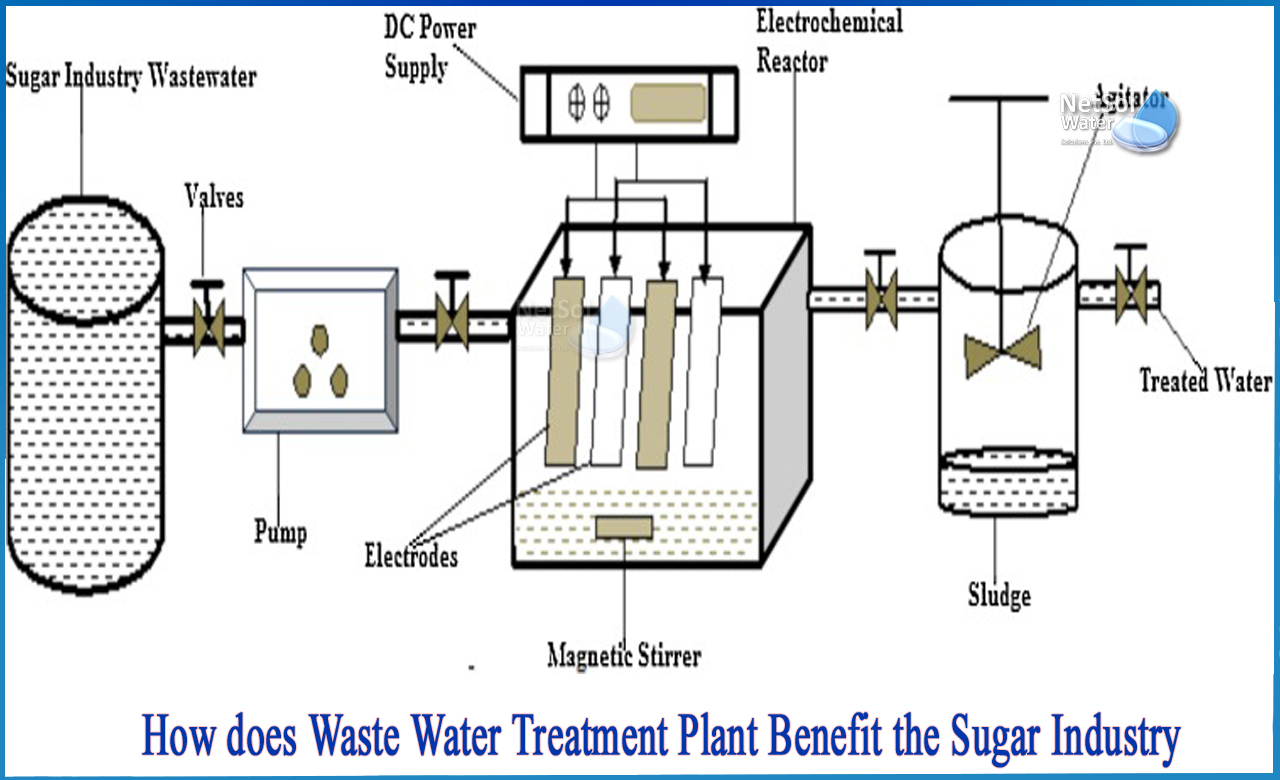
How does Waste Water Treatment Plant benefit the sugar industry?
Sugar is one of the giant agricultural product and industries processing sugar are critical for Indian financial system. Sugar enterprise is one of the crucial agro- industry. The enterprise has created giant socio-monetary effect on rural agro- based financial system, and Indian financial systems in general.
The residues from Sugar Mills are a part of the organic masses. These being incredibly putrescible create environmental risks if accredited to be thrown away without right remedy and next cautious disposal. The cane sugar production is vital for many other food processing units.
Sugar is utilized in cakes, ice cream, candy, and smooth beverages in addition to - different meals and beverages. In India, maximum of the Sugar mills is located around Maharashtra Konkan region and function for approximately four to eight months simply after the harvesting of the Sugarcanes.
Sugarcane is usually harvested manually in India, which gets rid of the wearing of soil and trash to the manufacturing unit in conjunction with the Sugarcanes.
Conditions become worse because the flow waft reaches a totally low stage and while sufficient dilution water isn't to be had throughout the length of operation of the Sugar generators (early November to stop of May or June).
Putrefaction of the polluted flow water due to the heavy discharge of waste, resulting in odour nuisance close to Sugar mills has not been anunusual phenomenon. When the untreated effluents are discharged into the environment, they disrupt the ecological vicinity of organisms.
Effluent discharges from Sugar mills represent some of chemical pollution, which includes oil and grease, carbonate, bicarbonate, nitrite, phosphate, further to overall suspended solids, dissolved solids, risky solids, and scopes of different toxicants.
This pollution should result in adjustments in temperature, humidity, oxygen supply, pesticideetc. amounting to a partial or entire alteration of the physical, chemical, and physiological spheres of the biota.
Basically, Sugar is sucrose, a disaccharide extracted from Sugarcane.
Sugar production may be categorised as follows:
1. Gur and Raw Sugar manufacture.
2. Khand sari-manufacture of unrefined low-grade Sugar.
As in line with COINDS/8/1980-eighty-one of Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Sugar factories are labelled on the idea of crushing capability as under:
-Small unit –as much as 1500 TCD
-Medium -1501 to 3000 TCD
-Large – Above 3000 TCD
The main units that use water in sugar factories are:
(i) Boiler water supply.
(ii) Cooling water for condenser.
(iii) Process water for immersion, lime preparation, dilution to control, dilution of evaporators and fillers, filtration sludge, fly ash treatment and pipe wastewater. Sugarcane from fields contains an average of about 70% water. Most of this water should be drained as factory wastewater.
Wastewater sources of the sugar industry:
Various wastewater sources occur in the sugar industry but, the amount of wastewater depends on the size of the factory. Centrifugation produces another type of wastewater called "molasses". Molasses is an important ingredient in distilleries.
Wastewater treatment in the sugar industry:
As in other industries, sugar factory pollution can be reduced by improving water and material consumption within the factory. Sugar industry produces a lot of wastewaters which can be reused, discharged as effluent in the water bodies by carefulwater treatment. Careful handling of water in various facilities and recycling as much as possible will significantly reduce the amount of waste. By recycling water, you can reduce the amount of factory waste. Dry cleaning of floors and floor cleaning with a controlled amount of water also reduce the amount of waste to some extent. Organic pollution of waste can only be reduced by proper operational management. When the evaporator and vacuum pan are overloaded and a large amount of syrup boils, sugar is lost from the water in the condenser, increasing both the amount and strength of the wastewater.
Conventional treatment:
Traditional wastewater treatment systems are carried out by activated sludge processes (ASPs) from various units of sugar mills.
Various units include bar screens, skimmers, levelling tanks, aeration units, purifiers and sludge drying floors etc.
Other treatment options are:
1. Anaerobic lagoon technology.
2. Anaerobic digestion.
3. Upstream anaerobic sludge cover (UASB).
4. Upward flow (UBF) sealing filter.
5. Aerobic biotransformation.
6. Fixed bed reactor with solid membrane.
Anaerobic treatment of wastewater using the lagoon and digestion tank has proven to be more effective and economical. An anaerobic lagoon with a residence time of 15 days and a load of 0.38 kg BOD / m3d can achieve 89.6% BOD removal. If the BOD load is 0.65 kg / m3 / day and the residence time at a controlled temperature of 37 ° C is 2.4 days, a BOD reduction of about 70 % can be expected from the anaerobic fermenter. Wastewater from anaerobic treatment equipment contains sufficient nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus). In aerobic waste stabilization basins, BOD can be further reduced.
Wastewater treatment plant in the sugar industry:
If sufficient land is available, Indian conditions recommend a two-step biological treatment with an anaerobic lagoon followed by an aerobic waste stabilization basin. Today, the use of fixed film technology is becoming more important.
UASB's fast anaerobic treatment technology is reported to be the best because it treats high organic loads with low hydraulic retention time (HRT). Over 90% COD removal can be achieved in less than 12 hours over a thermophilic temperature range of 45 ° C. As claimed by researchers, UASB technology is the best of the other treatment options available.
For more information and installation of ETP plants contact Netsol Water! As we are the top brand for manufacturing Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) for Sugar Mill/Industry.