Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) for Sugar Mill/Industry
In India, the sugar industry genrates about 1,000 liters of wastewater during crushing 1 Ton of sugar cane. Thats why the effleunt treatment plant for sugar mills are needed, because if the wastewater from sugar industry dischage into nature without treatment, poses wastage of large amount of water & many pollution problems in both aquatic and terresral ecosystems.
Types of waste in sugar mills
Three forms of waste are generated while sugar processing, which include
1: Liquid waste
2: Solid waste
3: Gaseous waste
Sources of effluent in a Sugar industry
Sugar is made by the processes of milling, clarification, evaporation, crystallisation and centrifugation. Here are some sources which lead to the generation of effluent, which include,
1: Mill House- Effluent is generated by cleaning and washing, juice leakages and spillages of mill bearing water.
2: Boiling House- In boiling houses, the wastewater is produces by chemical boiling and tube cleaning of evaporator and pans, excess condensate water, pump leakages, daily and periodical cleanings and washings, laboratory and domestic water usage.
3: Blow-down- Wastewater is produced by the blow down of spray pond water.
4: Excess Condensate
5: Condenser cooling water
6: Soda and Acid Wastes
Sugar mills with Netsol’s Effluent treatment Plants separate solid waste from liquid waste and contribute to the efficient treatment of sugar industry wastewater, which is extremely suitable for the removal of various contaminants.
Characteristics of sugar industry effluent
Brown colour, low pH, high temperature, high BOD, high COD, odour problem, total solids, and high percentage of dissolved organic and inorganic matter are all characteristics of sugar industry effluent. As a result, untreated wastewater can pose a threat to the ecosystem. For every tonne of sugar cane crushed, the industry produces around 1,000 litres of effluent. If the wastewater is discharged without treatment, it pollutes both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Parameters of Raw effluent
The general parameters of raw effluent generated in sugar industry are:
|
Wastewater parameter |
Before treatment |
|
pH |
4-6.5 |
|
Colour |
Brownish |
|
Odour |
Present |
|
TSS |
500-600 mg/l |
|
Oil and grease |
10-50 mg/l |
|
TDS |
5000-6000 mg/l |
|
COD |
2000-3000 mg/l |
|
BOD |
1000-1200 mg/l |
What is ETP in sugar industry?
Effluent Treatment Plant in Sugar Industry/mills (ETP plant for sugar industry) is a mechanism used to treat the wastewater/effluent generated by the sugar mills. Its basic work is to treat and manage industrial liquid waste by following the norms of the pollution control board, for safe discharge into mother nature, or for reusing purposes.
Treatment of effluent in sugar mills
Physico-chemical, biological processes and membrane processes are used in the process design.
A: Treatment using Physico-Chemical/Biological/Membrane processes include:
· Screening
· Oil and grease removal by skimming
· Equalization or Homogenization of effluent
· Dosing of chemical for maintained neutral pH of effluent
· Primary and secondary Clarifier for solid liquid separation
· Chlorination system
· Activated Gravity Separator
· Activated Carbon filter
· Multi-grade or Dual media filter
· Sludge management system ( i.e. Centrifuge or sludge drying beds)
· Anaerobic decomposition with anaerobic digester
· Activated sludge or bio-tower or aerobic decomposition in extended aeration tank or Aerobic lagoon treatment
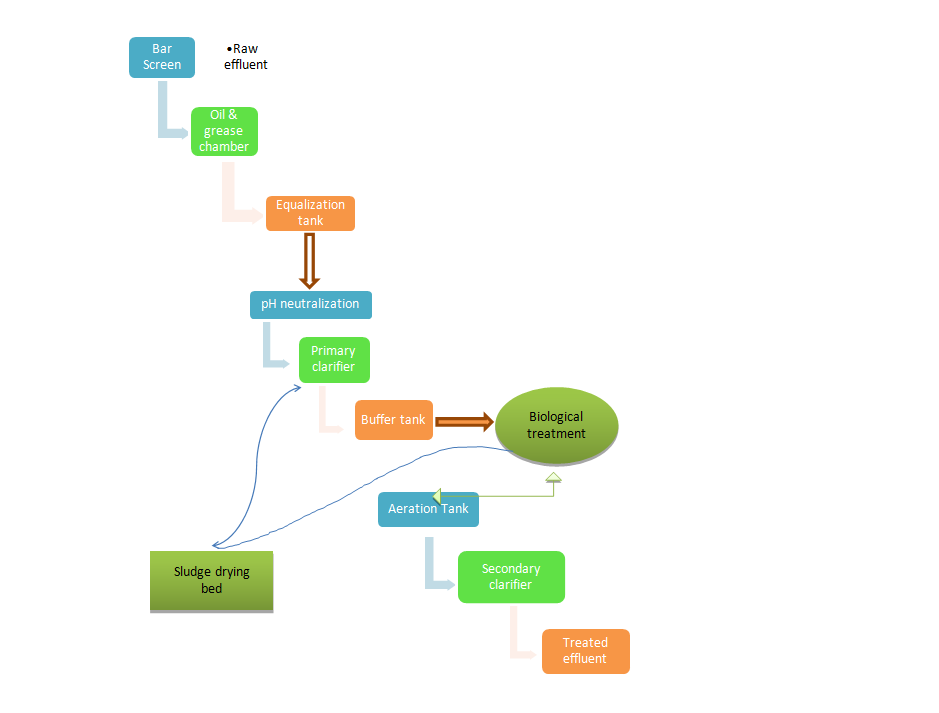
Step-by-step procedure for wastewater treatment in sugar industry
Step-1- Screening: Untreated wastewater has more suspended particles and floatable components, which contributes organic and inert matter to the effluent that must be removed. The untreated effluent is initially passed through fixed bar screens, which separate and remove all of the larger suspended solids and floatable materials. Gravity transports the screened effluent to the oil and grease removal tank.
Step-2- Oil & Grease trap: With the help of gravity, the sugar effluent from the bar screen chamber would enter the O & G treatment chamber. During the detention time (half an hour), oil and grease will float to the surface of the tank and be removed using mechanical equipment such as an oleophilic, belt-type oil skimmer.
Step-3- Equalization tank: The raw effluent is let into the equalization tank, where it is continuously mixed with a floating aerator or an air diffused system to homogenize the combined effluent from various plant sources and preserve homogeneous effluent characteristics.
Step-4- pH neutralization: The pH of the effluent is usually low. So, before letting the raw effluent into the other subsequent units, the equalization tank is fully mixed by dosing lime, caustic soda or soda ash in the equalization tank to neutralize the pH of the raw effluent.
Step-5- Primary clarifier: The primary clarifier receives the neutralized effluent from the Equalization Tank. To remove suspended materials, many types of primary clarifiers (such as conventional or lamella) are used. The clarifier's supernatant is pumped to the next treatment unit. The clarifier sludge is delivered to the sludge drying beds.
Step-6- Anaerobic/Aerobic treatment: In anaerobic treatment, organic matter decomposes in the absence of oxygen while as in aerobic treatment, it decomposes in the presence of oxygen. The sludge is biologically transformed into a range of end products, including methane and CO2. The treatment processes include UASB reactor, Activated sludge process, bio-towers, extended aeration tanks, etc.
Step-7- econdary clarifier: Depending on the operating conditions, each kilogramme of BOD removed produces 0.45–0.80 kg of sludge. The surplus sludge generated must be evacuated to maintain a sufficient mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration in the aeration tank; otherwise, the bacterial population in the aeration tank will be quite high.
The bacteria that are fed in the aeration tank have a life cycle after which they die. Due to the fact that dead bacteria are organic, they contribute to residual BOD and oxygen demand. Thus, the sludge from the secondary clarifier is pumped back to the aeration tank in the appropriate proportion, while the remainder is drained and transported to the sludge management system for further treatment.
Step-8- Chlorination tank: Chlorination will be used to disinfect the waste once it has been processed. Chlorine dosing will be adjusted to keep residual chlorine levels between 0.5 and 1.0 ppm.
Step-9- Multi-grade filter: The suction of the multi-grade filter feed transfer pump will receive treated wastewater. Filter feed pumps transport treated wastewater and treated water collected upstream of the MGF to downstream.
Step-10- Activated carbon filter: Suspended solids, colour and odour are all removed using an activated carbon filter. A cylindrical mild steel vessel with dished ends makes up an activated carbon filter. For advanced treatment, membrane processes like reverse osmosis is used to further treat wastewater for re-use.
Step-11: The treated water overflows into the treated water holding tank as sludge settles at the bottom of the secondary tube settler.Water from the sludge dewatering system is filtered.At the end of the process, the water is released or used for horticulture.
Process flowchart of ETP for sugar mills
Parameters of Treated effluent
The general parameters of treated effluent generated in sugar industry are:
|
Wastewater parameter |
After treatment |
|
pH |
6.5-8.5 |
|
Colour |
Nil |
|
Odour |
Nil |
|
TSS |
<300 mg/l |
|
Oil and grease |
<10 mg/l |
|
Total solids |
<2000 mg/l |
|
COD |
<250 mg/l |
|
BOD |
<100 mg/l |
Conclusion
Netsol Water, a water-inclined manufacturer of effluent treatment plants for the sugar industry, is one of the best in India. Sugar-processing-industry wastewater contains a significant amount of pollutants. Therefore, it becomes important to treat effluent from sugar mills to make safe and secure disposal of effluent into water bodies or reuse it according to Government norms.
For more information regarding our ETPs for sugar mills, contact us on +91 9650608473 or drop a mail at enquiry@netsolwater.com.
You can also find useful information by following us on YouTube and LinkedIn.


 for sugar mills Manufacturer Netsol Water.jpg)
