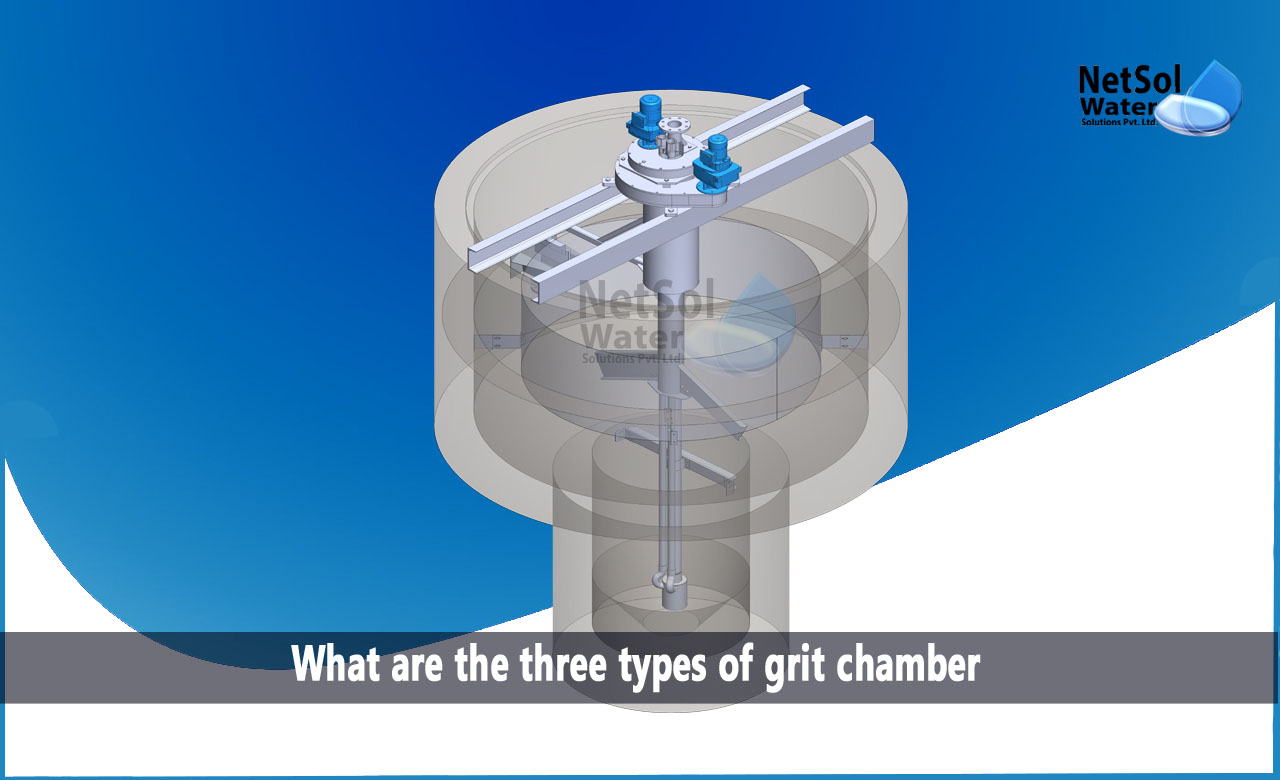
What are the three types of grit chamber?
The separation of gravel, sand, and other materials down to a diameter of between 0.2 and 0.1 mm is the aim of grit removal. Grit chambers are available to:
(a) guard against abrasion on moving mechanical equipment downstream;
(b) lessen the development of heavy deposits in pipe lines;
(c) lessen the amount of grit that builds up in the digester, which causes frequent cleaning.
Let’s look at the three types of grit chambers!
The three main categories for grit chambers are as follows:
1. Velocity-controlled long grit channels with a V shape;
2. Square-shaped rooms with a mild hopper and entry and exit on opposite sides;
3. A vortex-type cone and centrifugal force cause the grit to fall to the bottom.
1: Vortex Type Grit Chamber
The sewage is injected into this sort of grit chamber in the tangential direction, to create a vortex-like flow that will funnel the grit towards the center and cause it to be sucked down, to the bottom chamber. The grit is maintained in suspension using an agitator.
Grit with a heavier specific gravity of 2.4 to 2.65 settles down as a result of the vortex flow, and is then pumped or gravity-drained onto a grit filter bed. When sewage flow rates and durations are highly variable, this unit can be advantageous.
2: Aerated Grit Chamber
A conventional spiral flow aeration tank with air diffusion tubes attached, to one side of the tank makes up an aerated grit chamber.
The rate at which the grit particles tend to settle to the bottom of the tank, relies on the size of the particles and the spiral flow's bottom velocity, which in turn depends on the rate of air diffusion through the diffuser tubes and the tank's shape.
While, the lighter organic particles are carried by the spiralling motion, the heavier particles drop to the ground.
Types of Grit chamber on the basis of cleaning
Grit chambers are of two types: mechanically cleaned and manually cleaned.
· Mechanically cleaned grit chambers
Scraper blades in a mechanically cleaned grit chamber collect the grit that has accumulated on the chamber's floor. By using a variety of devices, including bucket elevators, jet pumps, and air lifts, the grit that has been gathered is raised to the ground level.
The designs of the grit cleaning mechanisms vary as well, but the majority of them are agitation tools that use either water or air, to provide washing action.
· Manually cleaned grit chambers
Grit chambers that must be manually cleaned must be cleaned at least once each week. Using a shovel to clean is the easiest approach.
Except for extremely small STPs of less than 1 MLD, where velocity regulated channels can be cleared by the operator using a shovel, manual clearing of the grit should be avoided.
Disposal of Grit
The majority of the time, grit is washed after being removed from the chamber, unless it contains a sizable amount of organic materials that gives off an unpleasant odour.
They are primarily dumped in a clean landfill. The method of disposal is chosen based on the grit's physical and chemical properties, quality, and accessibility of disposal land, among other factors.
Conclusion
According to a number of additional parameters, including the type and quantity of grit to be handled, head loss requirements, space requirements, topography, and economic considerations with regard to both capital and operational costs, the categories to consider are:
- Mechanically Cleaned
- Manually Cleaned.
Mechanized grit removal units are preferred for flows through sewage treatment plants, which are greater than 10 MLD.
How can we assist?
Netsol Water is passionate about transforming the productivity, efficiency, and profitability of wastewater treatment plants, using decades of experience and knowledge.
Typically, grit is removed automatically, although some smaller factories may employ a manual process. Contact us for a free consultation with a wastewater specialist, to determine the ideal option for your wastewater treatment plant.
Contact us at +91 9650608473 or enquiry@netsolwater.com for expert advice.