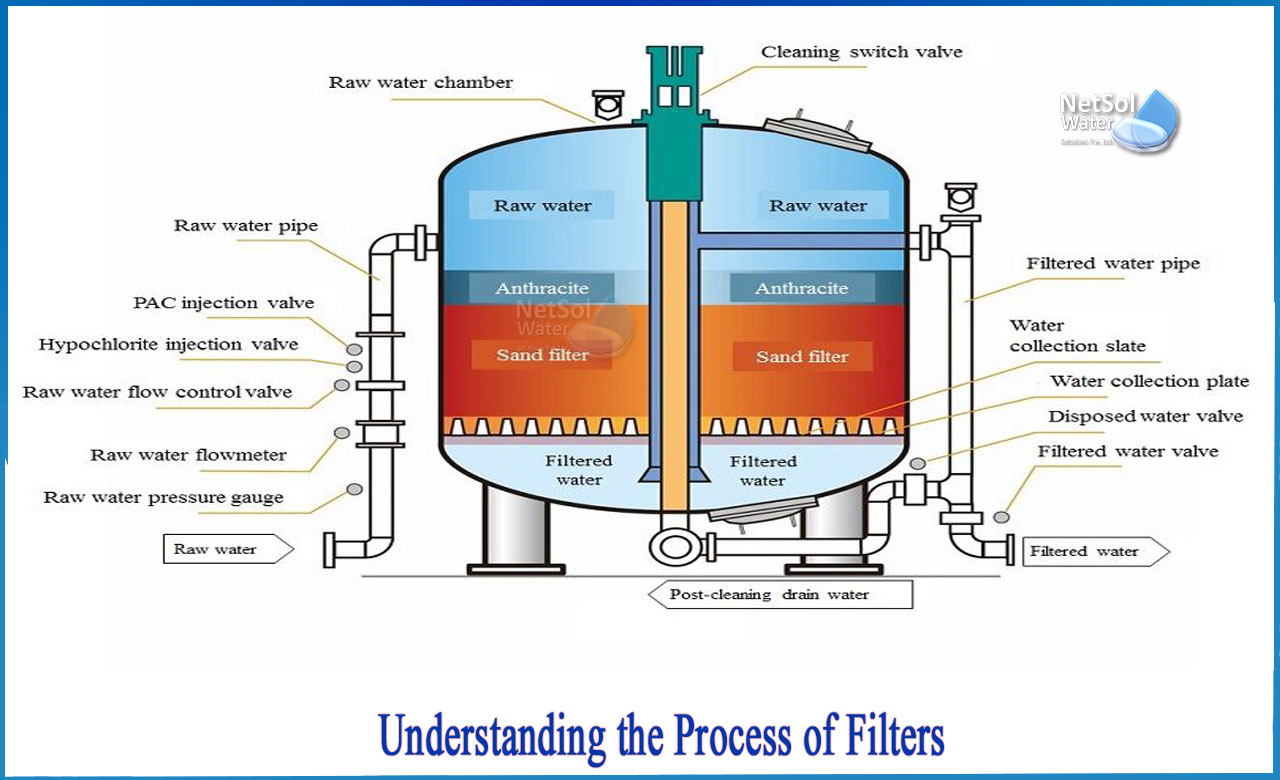
What is the process of filtration step by step?
Filtration is the process of removing particles suspended in water. Straining, flocculation, sedimentation, and surface capture are some of the mechanisms used to remove waste. Filters are classified according to their primary method of capture, which is either exclusion of particles at the surface of the filter media (straining) or deposition within the media (in-depth filtration).
What are strainers?
Strainers are typically made up of a thin physical barrier made of metal or plastic. They are commonly used at the inlet to the treatment system in water treatment to exclude large objects. These could be scraped manually or mechanically. The distance between the bars varies between 1 and 10 cm. Intake screens with closely spaced plates or even fine metal fabric can have much smaller spacing. Micro strainers are typically used to remove fine silt and, in particular, algae.
Filters, as they are commonly understood in water treatment, generally consist of a medium within which most of the particles in the water are intended to be captured. Such filters could be produced as disposable cartridge filters that are suitable for both domestic (i.e. point-of-use treatment) and small-scale industrial applications.
There are larger cartridge filters that can be cleaned. Pre-coat filtration is one method in which a porous support surface is given a sacrificial coating of diatomaceous earth or another suitable material after each cleaning of the filter. A small amount of diatomaceous earth is also applied continuously during filtration. However, sand or another appropriate granular material (e.g., anthracite, crushed glass or other ceramic material, or another relatively inert mineral) is typically used as the filter medium in municipal water treatment filters. Filtration with such filters is known as in-depth granular media filtration.
Step by step process:
Step 1-Raw water enters the filter through the inlet, passing first through the coarse screen to remove large debris and sediment, and then through the inner fine screen to remove the remaining smaller particles.
A differential pressure switch (DPS) monitors the pressure caused by debris accumulation on the inner screen and begins the self-cleaning process when the pressure changes. The screen's buildup is then discharged.
STEP 2-When the flush valve is opened to the atmosphere, a strong suction force is created at the scanner nozzles, effectively removing dirt particles from the screen and discharging them from the filter.
Because of the small nozzles with high velocity and suction forces, the forced backwash ensures powerful, efficient, and complete cleaning of every point in the screen. Efficient cleaning allows the filter to run continuously without interruption. The screens are cleaned efficiently, restoring the DP to its original value.
STEP 3-A thorough cleaning procedure cleans the media, restoring the DP to its original value.As inefficient cleaning leaves some solids on the filter's screen, the DP does not return to its original value. Filter clogging isunavoidable with ineffective cleaning.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.