How effective is reverse osmosis in Removing Contaminants?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a proven water purification method that effectively removes a wide range of contaminants from water. Its ability to provide clean and safe drinking water has made it a popular choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. In this blog post, we will conduct an in-depth examination of reverse osmosis's efficiency at removing contaminants. We will explore the mechanisms behind RO, the types of contaminants it can remove, and the factors that influence its effectiveness. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of reverse osmosis, you can make informed decisions about water treatment and ensure the highest quality of water for you and your family.
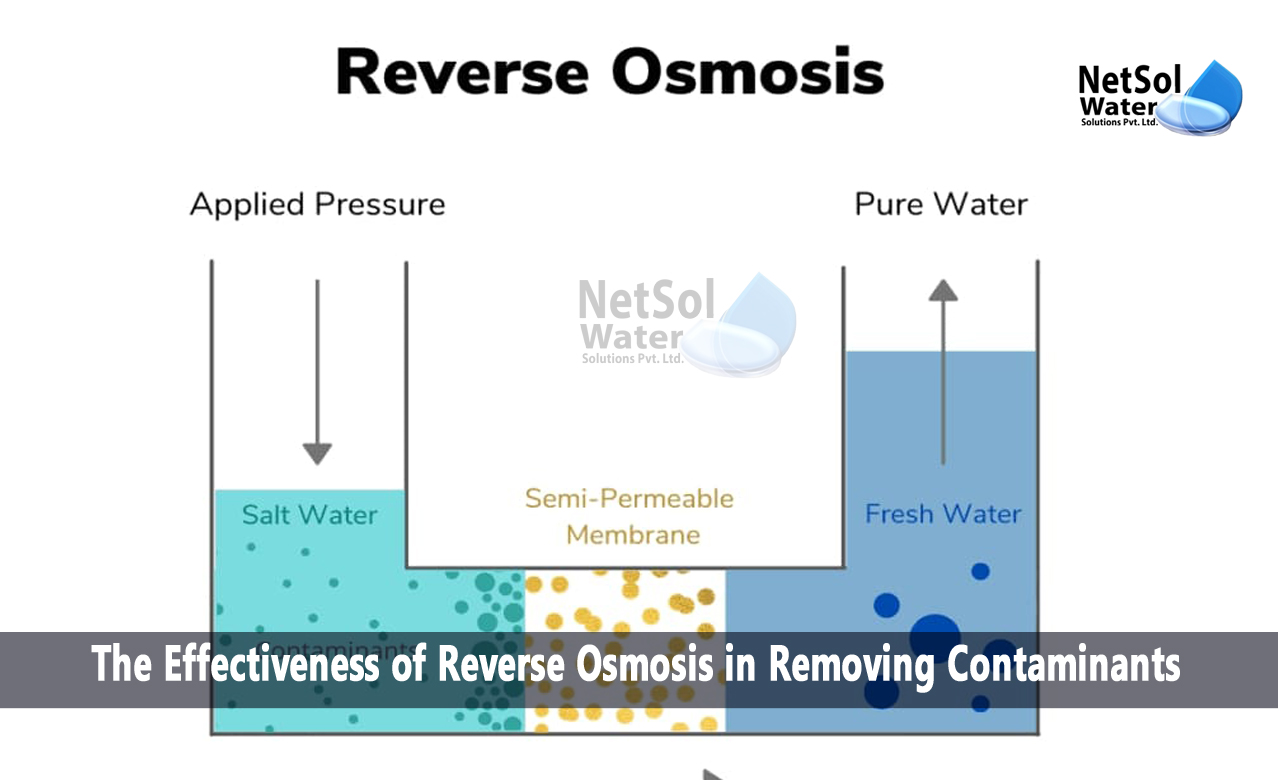
1. Mechanisms of Reverse Osmosis:
To understand the efficiency of reverse osmosis in removing contaminants, it's crucial to grasp the underlying mechanisms involved:
· Semi-Permeable Membrane: RO utilizes a semi-permeable membrane with microscopic pores that allow water molecules to pass through while blocking larger particles and contaminants.
· Pressure Application: Water is pressurized and forced through the membrane, creating a concentration gradient that drives the separation of water from dissolved contaminants.
· Size Exclusion: The membrane's pores are designed to exclude contaminants based on their size, preventing their passage and allowing only pure water to permeate.
2. Contaminants Removed by Reverse Osmosis:
Reverse osmosis is highly effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, including:
· Inorganic Compounds: RO can remove heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and fluoride. It also eliminates nitrates, sulfates, and other dissolved inorganic salts.
· Organic Compounds: RO is efficient in removing organic contaminants, such as pesticides, herbicides, pharmaceuticals, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It can also reduce the presence of chemicals like chlorine and chloramines.
· Microorganisms: Reverse osmosis membranes effectively block bacteria, viruses, and parasites, providing an additional layer of protection against waterborne pathogens. However, it's important to note that RO should be combined with other disinfection methods for complete microbial removal.
· Dissolved Solids: RO removes dissolved solids, including minerals and salts, that contribute to water hardness. This results in improved taste, reduced scaling, and enhanced overall water quality.
· Sediments and Particles: The semi-permeable membrane effectively filters out suspended particles, sediment, rust, and other visible impurities, resulting in clearer and visually appealing water.
3. Factors Affecting Reverse Osmosis Efficiency:
The efficiency of reverse osmosis in removing contaminants can be influenced by several factors:
· Membrane Quality: The quality and performance of the RO membrane play a crucial role in contaminant removal. High-quality membranes with smaller pore sizes and enhanced rejection capabilities yield superior results.
· Water Pressure: Adequate water pressure is essential for optimal reverse osmosis performance. Higher pressure facilitates better permeation through the membrane, improving contaminant rejection rates.
· Feed Water Quality: The initial quality of the feed water impacts RO efficiency. Higher concentrations of contaminants may require more extensive pre-treatment or additional stages of filtration.
· Membrane Fouling: Fouling occurs when contaminants or deposits accumulate on the membrane surface, reducing its efficiency. Regular maintenance, including membrane cleaning or replacement, is necessary to minimize fouling and maintainoptimal performance.
· pH and Temperature: Extreme pH levels or temperature variations can affect membrane performance and lifespan. Optimal operating conditions, typically within a specific pH and temperature range, help ensure consistent and efficient contaminant removal.
4. Limitations of Reverse Osmosis:
While reverse osmosis is highly effective, it has certain limitations to consider:
· Wastewater Generation: Reverse osmosis systems produce wastewater as a byproduct due to the separation process. Proper disposal or recycling methods should be implemented to minimize environmental impact.
· Efficiency for Certain Contaminants: Some contaminants, such as certain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and gases, may have lower rejection rates through reverse osmosis. In such cases, additional treatment methods may be necessary.
· Need for Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring of system performance, including membrane integrity and water quality testing, is important to ensure consistent contaminant removal. Membrane replacement and maintenance are necessary to sustain efficient operation.
Conclusion:
Reverse osmosis is an efficient and reliable water treatment method for removing a wide range of contaminants. Its ability to eliminate inorganic compounds, organic contaminants, microorganisms, sediments, and dissolved solids makes it a popular choice for ensuring clean and safe drinking water. However, factors such as membrane quality, water pressure, feed water quality, and maintenance must be considered to maximize the efficiency of reverse osmosis systems. By understanding its capabilities and limitations, you can make informed decisions about water treatment options and ensure the highest quality of water for your specific needs.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.