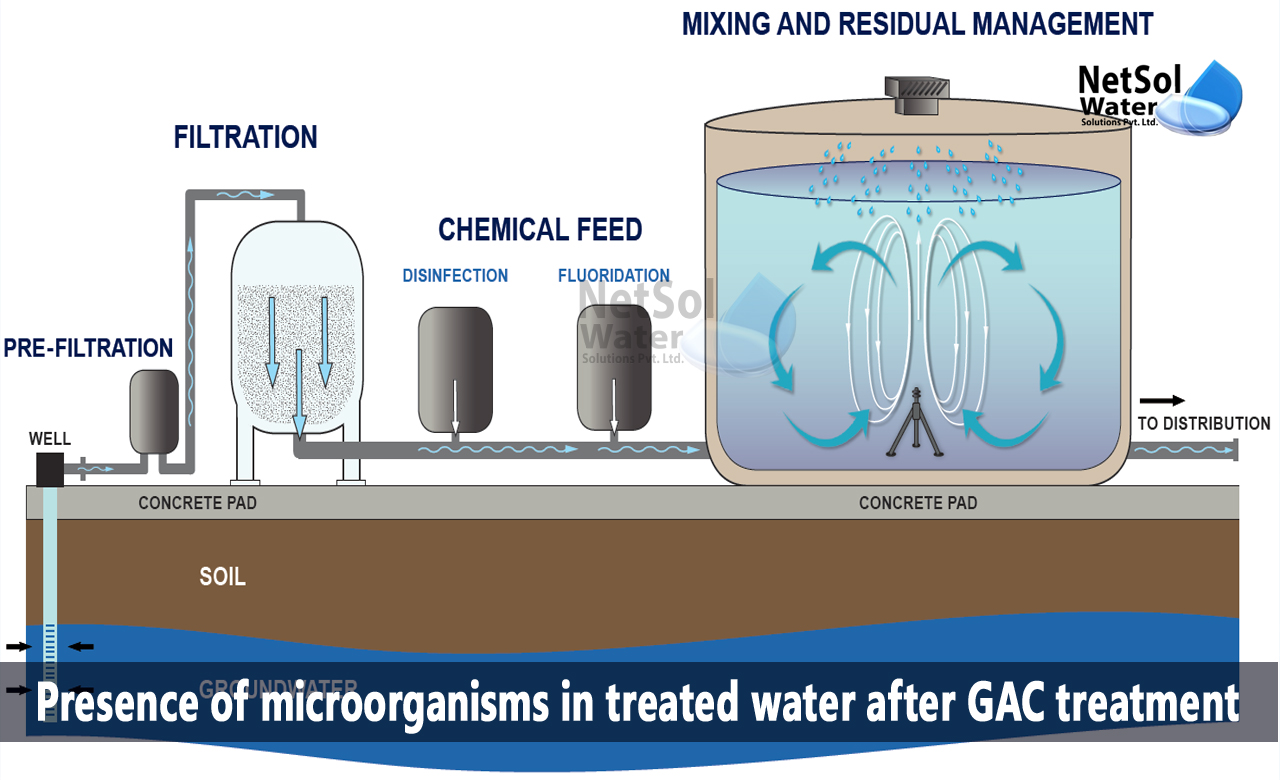
The line that supplies water to the GAC tank frequently creates a vacuum, when the water treatment train is stopped and these vacuum results in a back flow. Therefore, we need to understand that why do active microorganisms start to appear in the treated water, after a certain amount of time if the water fed to the GAC tank does not contain them.
Presence of microorganisms in treated water after GAC treatment
Water flow in the anticlockwise direction of operation is referred to as a counter flow. This happens when the water that feeds the GAC tank is supplied, from a lower level and when the two additional conditions are met:
· The GAC tank's water supply pump has been turned off.
· The check valve connected to the AGC tank's water supply line does not shut off completely.
Due to the vacuum created as a result, the water treatment train's backflow is created. In fact, it's crucial to install vacuum breaker valves in water treatment trains, when this potential exists to avoid the tanks from collapsing in the event of a vacuum.
What happens when there is a backflow of water?
1: In the event of a backflow, water without any lingering oxidizing agent concentration is pumped into the GAC tank.
2: Microorganisms can enter the GAC bed if there is a leak in the effluent line, leading from the GAC tank or if the water becomes contaminated by microbes somewhere in the discharge process.
3: They have a rough surface to cling to in the charcoal, which is ideal.
4: They also discover the organic material that the GAC has absorbed. It begins to play at that point.
5: Disinfected water once more enters the GAC bed from the top when the water treatment process is restarted. In the first few centimetres of bedding, the remaining chlorine is eliminated. This is true because free chlorine and GAC quickly neutralize each other.
As a result, the water in the centre and bottom of the bed is devoid of free chlorine, which allows the bacteria to grow.
Why can chlorine dioxide efficiently disinfect GAC beds while other oxidants cannot?
1: Because, it doesn't have enough oxidation potential to react with reducer activated carbon, chlorine dioxide can be used to clean GAC beds. In other words, DC junctions are not broken by chlorine dioxide.
2: It penetrates the deepest crevices of its fissures by not responding with the GAC.
3: Chlorine dioxide performs its oxidative action at these acidic sites. By doing this, it effectively deactivates microorganisms and sanitizes the bed.
4: It's also important to note that chlorine dioxide has a higher capacity to oxidise, than the other oxidants employed in disinfection, although having a lower oxidation potential than the others.
5: The chlorine atom, Cl, in chlorine dioxide has a valence of +4, which is the cause. When it oxidises, it takes on a -1 valence and dissolves as the chloride ion, Cl-, in water. In other words, it steals 5 electrons (which is what an oxidant does). Because of this, chlorine dioxide has a larger oxidation capacity despite having a lower oxidation potential, than other oxidants.
Are there any substances than inorganic oxidants that can clean CAG beds?
Organic substances exist that can clean GAC beds. Due to their organic nature, carbon adsorbs them and shortens their useful lives. On the other hand, they are typically unsuitable for use in food production or drinking water procedures.
Is it possible to clean GAC beds using techniques that don't rely on oxidising substances?
Steam or a pH adjustment can both be used to sterilise a GAC bed.
· When done correctly, steam disinfection is quite effective. The entire litter should be heated to a temperature of at least 70 °C, and kept there for an hour. This technique can only be used if the tank, the interior nozzles, and the pipes are made of steel. Plastics are not resistant.
· Changing the pH of the water that floods the GAC bed to extreme levels, such as very low (near 2) or very high (close to 13), can be used to disinfect surfaces. A strong acid, such as sulphuric or hydrochloric, must be added in order to lower the pH of the water. This is only feasible if every substance that will come into contact with the acid, is chemically resistant enough to halt oxidation and corrosion.
By raising the pH, you can disinfect by adding a powerful alkali like soda or potash. The drawback is that when they have done their job of disinfecting, a lot of water is needed to rinse them out of the GAC bed and remove them.
On the other side, the resultant water must be neutralised whether an acid or an alkali is employed, which creates a high salinity wastewater.
How may we be of help?
A wide range of industrial water filters are available from Netsol Water, and they may be customised to meet the demands and requirements of any particular project. In addition, we provide top-notch RO plants and activated carbon filters that can be used for any tertiary water treatment or water purification application.
Because, of our exclusive contract and global supply, we are able to provide solutions for water and wastewater treatment that are of unmatched quality, and priced incredibly affordable.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.