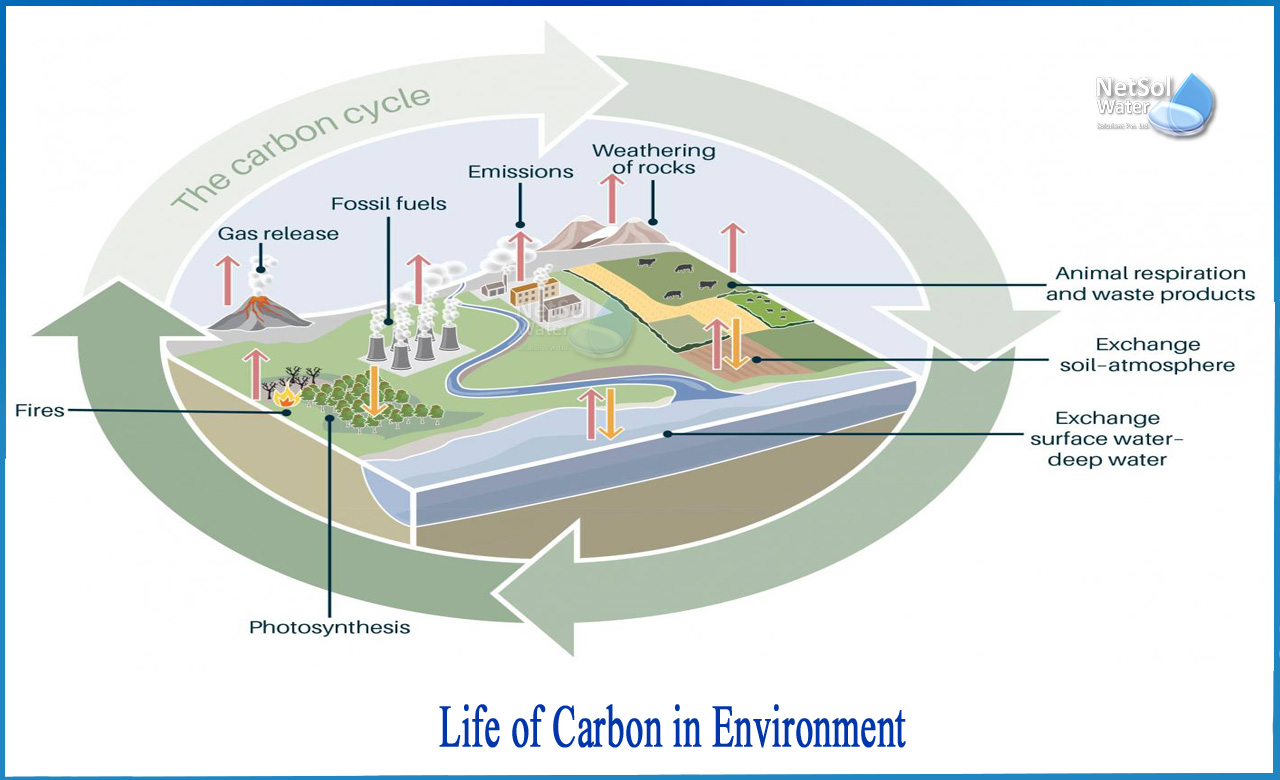
What is the life cycle of carbon?
Carbon can be found in the oceans, rocks and soils, all forms of life, and our atmosphere. Carbon and how it cycles through the Earth's systems are critical to our planet's well-being and functioning.
Carbon is constantly making headlines.
Have you heard of the greenhouse effect and carbon dioxide?
By controlling the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the carbon cycle plays an important role in regulating Earth's global temperature and climate. The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that keeps the Earth warm enough for life to exist. Earth would be much colder if the greenhouse effect did not exist.
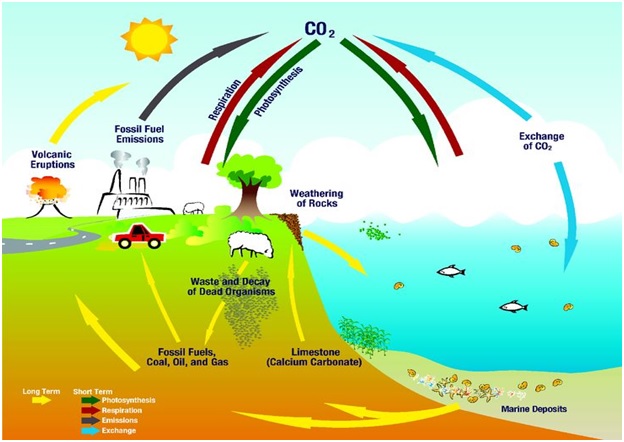
The carbon cycle
Carbon dioxide(CO2)
Carbon dioxide is a significant greenhouse gas because it aids the Earth's atmosphere in retaining heat generated by the Sun. Too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can cause the planet to become abnormally hot.
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased by 30 percent since the 19th century industrial revolution. Only then will we be able to make sound "carbon decisions" that will affect our future.
All of this extra carbon must be disposed of in some way. So far, land plants and the oceans have absorbed about 55 percent of the extra carbon that humans have released into the atmosphere, while the remaining 45 percent has remained in the atmosphere. The land and oceans will eventually absorb the majority of the extra carbon dioxide, but up to 20% may remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years.
Atmosphere
The fact that so much carbon dioxide remains in the atmosphere is significant because CO2 is the most important gas in controlling Earth's temperature.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and halocarbons are all greenhouse gases that can absorb and re-emit a range of energy, including infrared energy emitted by the Earth. The re-emitted energy spreads in all directions, but some of it returns to Earth and heats the surface. Earth would be frozen at -18 degrees Celsius if greenhouse gases were not present (0 degrees Fahrenheit).
Based on current carbon dioxide concentrations, this temperature rise is not the end of the warming. Because the ocean absorbs heat, greenhouse warming does not occur immediately. Because of CO2 already in atmosphere, the Earth's temperature will rise by 0.6 degrees Celsius. The extent to which temperatures rise above that threshold is determined in part by how much more carbon humans emit into the atmosphere in the future.
Ocean
Through direct chemical exchange, approximately 30% of the carbon dioxide that humans have emitted into the atmosphere has diffused into the ocean. Carbonic acid is formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean, increasing the acidity of the water. Or, to put it another way, a slightly alkaline ocean becomes slightly less alkaline. Since 1750, the pH of the ocean's surface has dropped by 0.1, representing a 30% decrease in acidity.
Ocean acidification has two effects on marine organisms.
Carbonic acid first reacts with carbonate ions in water to form bicarbonate. However, those same carbonate ions are required by shell-building animals such as coral to form calcium carbonate shells. Because there is less carbonate available, the animals must expend more energy to construct their shells. As a result, the shells become thinner and more delicate.
Land
Land plants have absorbed approximately 25% of the carbon dioxide that humans have emitted into the atmosphere.
Plants were able to grow more as there was more atmospheric carbon dioxide available to convert to plant matter in photosynthesis. Carbon fertilization refers to this increased growth. Plants could grow anywhere from 12 to 76 percent faster if atmospheric carbon dioxide is doubled, as long as nothing else, such as water scarcity, limits their growth.Scientists do not know how much carbon dioxide increases plant growth in the real world because plants require more than carbon dioxide to grow.
Conclusion
Climate change is expected to cause the most significant changes in the land carbon cycle. Carbon dioxide raises temperatures, which extends the growing season and raises humidity. Both of these factors have resulted in some additional plant growth. Warmer temperatures, on the other hand, stress plants. Plants require more water to survive as the growing season lengthens and warms. Plants in the Northern Hemisphere are already slowing their growth in the summer due to high temperatures and water scarcity, according to scientists.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.