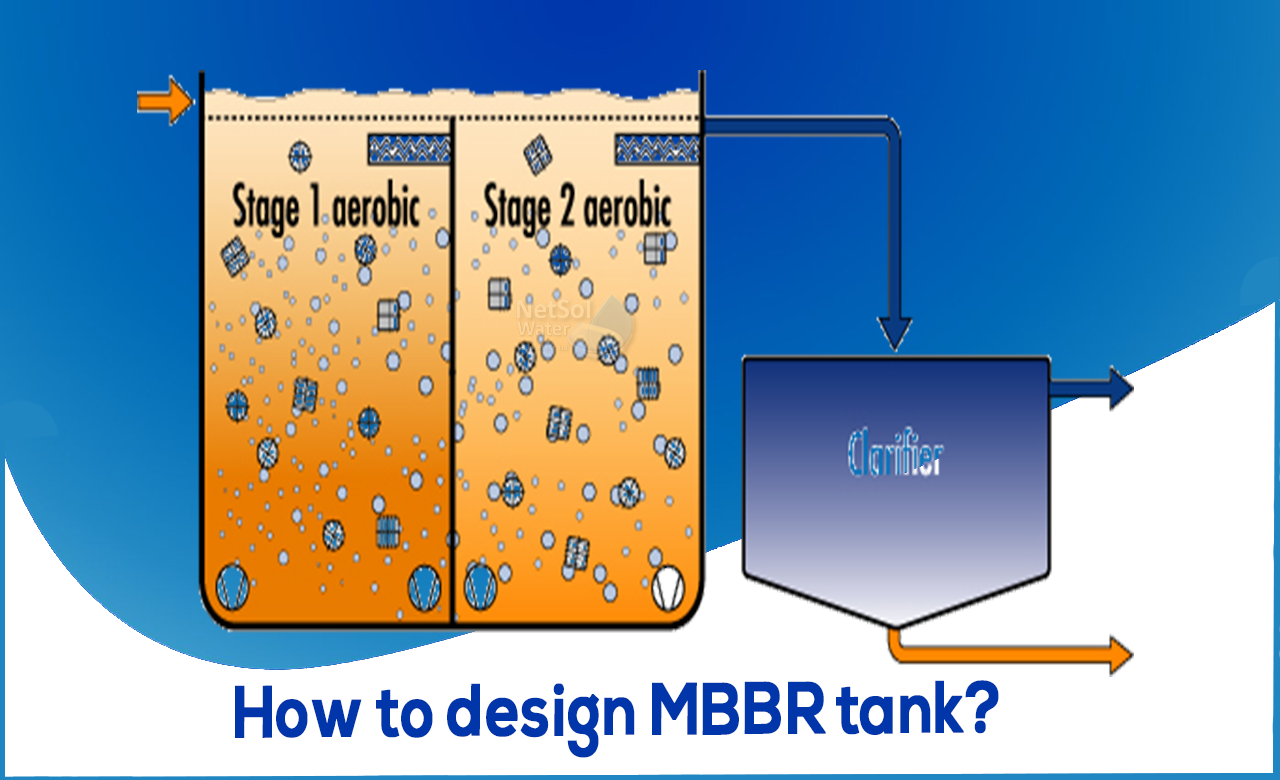
Moving Bed Bio-Film Reactor (MBBR):
In treatment scheme of wastewater, biological processes are also used. One of these biological processes is MBBR or Moving bed bio film reactor.
The MBBR is moving bed bio-film reactor. The carrier is composed of a material with a density close to the density of water (1 g/cm3). One example is high density polyethylene (HDPE), which has a density close to 0.95 g/cm3. Since the carriers are mixed in the tank by the ventilation system, the inflowing wastewater substrate has good contact with the biomass on the carriers.
MBBR is the tertiary treatment process in treatment unit. It is biological treatment plant which uses microorganisms to digest sewage and treating it. From the perspective of water conservation, it is a highly recommended procedure of treatment.
A sieve is required at the outlet of the tank to prevent the plastic support from escaping ventilation. A hybrid MBBR system was also used to achieve higher biomass concentrations in the bioreactor. In this system, floating biomass and sedimentary biomass contribute to the biological process at the same time.
There is also an anaerobic MBBR, which is mainly used for industrial wastewater treatment.
Moving bed bio-film reactors have proven promising effects to put off micro-pollutants from wastewater. Micro-pollutants fall into numerous corporations of chemical compounds along with prescribed drugs, organophosphorus pesticides (OPs), care merchandise and endocrine disruptors.
A 2012 article pronounced defined the usage of MBBR generation to put off prescribed drugs along with beta-blockers, analgesics, anti-depressants, and antibiotics from health centre wastewater. Moreover, software of MBBR as an organic approach mixed with chemical remedy has attracted a notable deal of interest for elimination of organo-phosphorous pesticide from wastewater.
The benefit of MBBRs may be related to its excessive stable retention time, which permits the proliferation of slow-developing microbial groups with more than one feature in biofilms. The dynamics of such microbial groups significantly relies upon on natural loading in MBBR system.
How to design MBBR system?
Let us understand this with the help of an example:
A design wastewater flow of 1.0 MGD containing 170 mg/L BOD (in the primary effluent) is to be treated in an MBBR reactor. Design the MBBR reactor.
Solution:
a) The BOD loading rate will be:
(1.0 MGD)(170 mg/L)(8.34 lb/MG/mg/L)
= 1417.8 lb/day
= (1417.8 lb/day)*(453.59 g/lb)
= 643539.42 g BOD/day
b) Required carrier surface area
= (643539.42g/day)/(7.5 g/m2/day)
= 85805.256 m2.
Assume surface area 600 m2
= 85805.256m2/600 m2/m3.
Volume = 143 m3
Assume 40% carrier fill:
Required tank volume = 220.7 m3/0.40 = 357.52m3
c) The volume of liquid in the reactor can be calculated as:
Volume of tank– [carrier volume (1 – void %)],
Therefore, the volume of liquid is:357.219– [143(1 – 0.60)]
= 300.9 m3
d) The HRT( hydraulic loading rate) at design average flow can be calculated as:
HRT design average = reactor liquid volume*7.48/[Q*106 /(24*60)]
= 984.30*7.48/[1.0*106 /(24*60)]
= 70.8 min HRTpeak hr.
= HRTdesign average/peak hour factor = 70.8/4 = 2.4 min
The author of the blog is associated with Netsol Water Solutions, which is into manufacturing of Effluent Treatment Plant, MBBR Sewage Treatment Plant, and Water Treatment Plants.