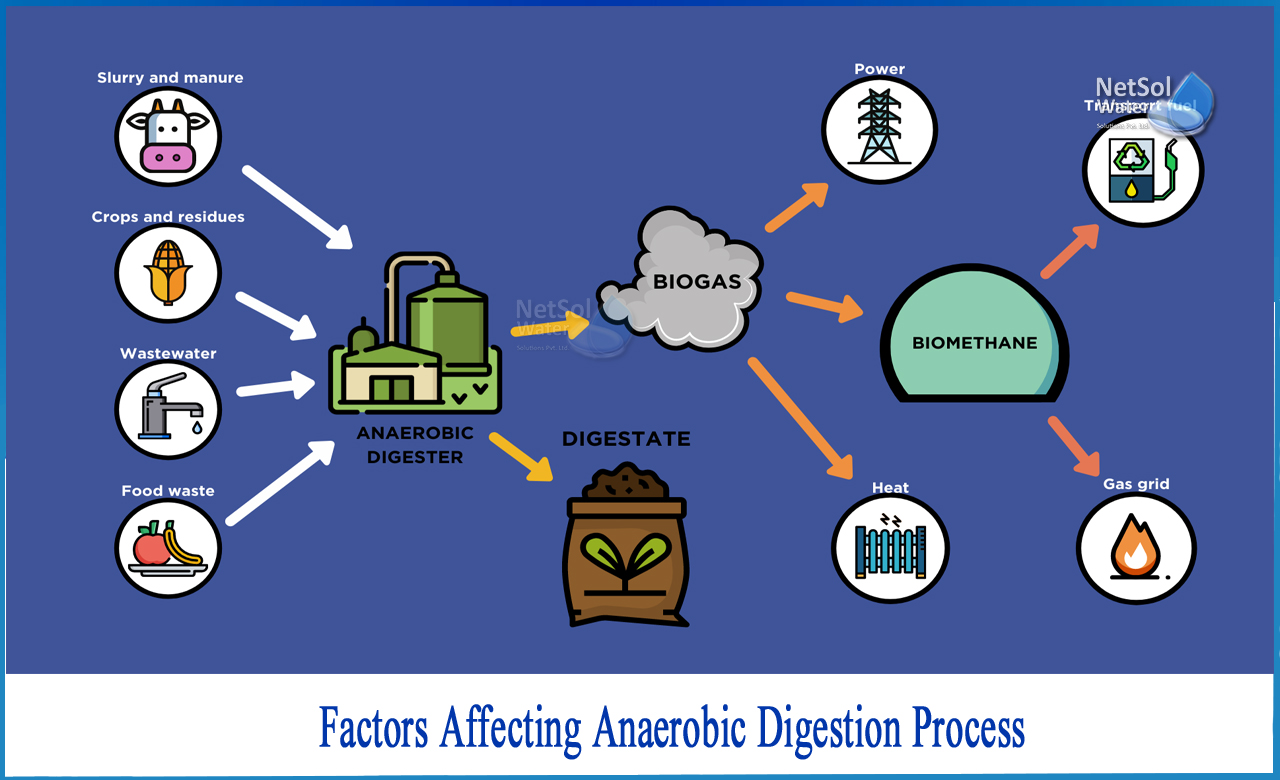
What is anaerobic digestion process?
Anaerobic digestion is the process by which bacteria breaks down organic matter such as animal manure, bio-solids from wastewater, and food waste in the absence of oxygen.
Anaerobic digestion for biogas production takes place in a closed container called a reactor. Reactors are designed and built in a variety of shapes and sizes to suit the site and raw material conditions. These reactors contain a complex microbial community that decomposes (or digests) waste and produces the resulting biogas.
The reactors depend on a lot of factors, which are discussed below:
1: pH
pH value of the composition of food waste (taken into consideration) is of huge importance. It is a pivotal factor in the digestion. The modern world, post its urbanization has resulted in an excessive release of food waste which contains a large amount of organic matter (nature is unable to treat this amount of waste) which can be decomposed, hence leading to the harnessing of biogas from it.
The biogas generation is highly affected by the parameters like its pH value range, optimum temperature, retention time, loading capacity and the composition of the food waste used. It is known that the biogas production yield and the degradation efficiency is said to be higher for the substrates having an optimum range value of pH7 comparing with other pH range values.
The pH value plays an important role because microorganisms or methanogens are very sensitive to acidic environmental conditions. Acidic environments inhibit their growth and methanogenesis. On the other hand, raising the pH above 7.5 to 8 can allow methanogens to multiply and interfere with the acetic acid production process. A certain amount of buffer, such as CaCO3 or lime, is added to the system to balance the pH. However, to achieve higher biogas yields, the optimum pH values should be kept between 7.5 and 8.
2: Operating temperature
Operating temperature is an important factor in determining the performance of AD reactors as it is an important requirement for the survival and optimal prosperity of microbial communities.
Bacteria have two optimal temperature ranges, called mesophilic and thermophilic optimal temperatures. Mesophilic fermenters show very good power efficiency when operating in the temperature range of 25-40 degrees Celsius, and thermophilic fermenters has a range of 50-65 degrees Celsius.
Thermophilic fermenters allow for higher load factors and produce higher methanogenesis, substrate degradation, and pathogen destruction. Higher temperatures reduce the required retention time by accelerating the decomposition reaction of organic materials.
Thermophilic anaerobes are susceptible to toxins and small changes in the environment and take longer to cross the redox population. This system is not well suited for commercial use as it requires an additional energy supply due to self-heating.
The mesophilic AD reactor uses a powerful microbial consortium that is highly resistant to environmental changes, highly stable and easy to maintain. These systems do not require an additional energy supply for heating. However, it has the disadvantages of long residence time and slow biogas production rate. However, they are easy to operate and maintain and have a low cost of capital, making them suitable for commercial scale plants.
3: Loading speed
Loading speed is another important parameter in the anaerobic digestion process.
This is determined by measuring the amount of volatile solids in the biological AD system that can serve as an input to the system. Never increase the load factor of your system. This can result in lower or average biogas production. System overloads are usually caused by the presence of degradants or inhibitors in the system and insoluble fatty acids that can interfere with biogas production pathways.
High loading causes increase in the amount of acidogenic bacteria which stimulates pH fall and hence results in the elimination of methanogenic bacteria or methane producing microorganisms hence causing the system to crash.
4: Retention time
Retention time or “residence time” in the AD systems is the amount of time a feedstock staysin an anaerobic digester.
It is calculated in terms of no. of days (n) as in the case of the following equation.
n (No. Of days) = Operating volume (V / Flow rate)
It is the average time required for the organic material residing in a digester to decompose considering the COD of the influent or the particles residing in and also the BOD or biological oxygen demand of the liquid waste materials. The longer is the retention time period, the higher is the degradation of the organic matter.
Retention time also depends on the operating temperature and content of the solid waste material of an AD system.
Conclusion
One of the best available processes of digestion is anaerobic digestion and its functioning is dependent upon all of the above mentioned parameters. We can get desired results by tweaking one or two parameters. If we have problem, it is easier to detect by analysing the effluent characteristics.
How can Netsol Water help?
Netsol is India’s leading waste water and water treatment solution company which covers all the needs of any water treatment scheme on all levels. We have the expertise to provide waste water solutions at domestic, industrial and municipal level.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.