Electrochemical Oxidation for Cyanide Removal in Metal Finishing Effluents
In metal finishing, cyanide compounds are commonly employed in processes like electroplating and metal cleaning, presenting environmental and health hazards in effluents. Electrochemical oxidation has surfaced as a promising solution for cyanide removal from these effluents, providing a sustainable and effective approach to tackle this pressing issue. In addition to its effectiveness in removing cyanide from metal finishing effluents, electrochemical oxidation also offers advantages such as scalability and adaptability to different treatment scenarios. This technology can be tailored to meet specific industry needs while minimizing operational costs and environmental impact. Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance the efficiency and reliability of electrochemical oxidation systems, ensuring continuous improvements in cyanide treatment processes for the metal finishing industry.
Understanding Cyanide and Its Implications
Cyanide is a dangerous substance that can harm both people and nature. Even small amounts of cyanide can hurt animals living in water. It sticks around in the environment and builds up in the food chain, causing problems for a long time.
The metal finishing industry uses cyanide in its processes, like cleaning and coating metals. Getting rid of cyanide from the waste they produce is really important to follow the rules and keep the environment and people safe.
Electrochemical Oxidation: Principles and Advantages
Electrochemical oxidation is an advanced oxidation process (AOP) that utilizes electrochemical reactions to degrade and remove pollutants from wastewater. In the context of cyanide removal, this technology involves the application of an electrical current to generate highly reactive oxidizing species, such as hydroxyl radicals (•OH), which effectively oxidize and break down cyanide compounds.
The key advantages of electrochemical oxidation for cyanide removal include:
1. Efficient Cyanide Degradation: The powerful oxidizing species generated during the electrochemical process can effectively break down cyanide compounds into less toxic or harmless byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas.
2. Versatility: Electrochemical oxidation can effectively treat a wide range of cyanide concentrations and can be applied to various types of metal finishing effluents, including those containing complex mixtures of pollutants.
3. Environmental Compatibility: Unlike conventional chemical treatment methods, electrochemical oxidation does not require the addition of hazardous chemicals, minimizing the generation of secondary pollutants and reducing environmental impact.
4. Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial capital investment for electrochemical oxidation systems may be higher, the long-term operational costs can be lower compared to other treatment methods, owing to reduced chemical consumption and efficient energy utilization.
5. Compact Footprint: Electrochemical oxidation systems have a relatively small footprint, making them suitable for installation in space-constrained facilities or as part of integrated treatment systems.
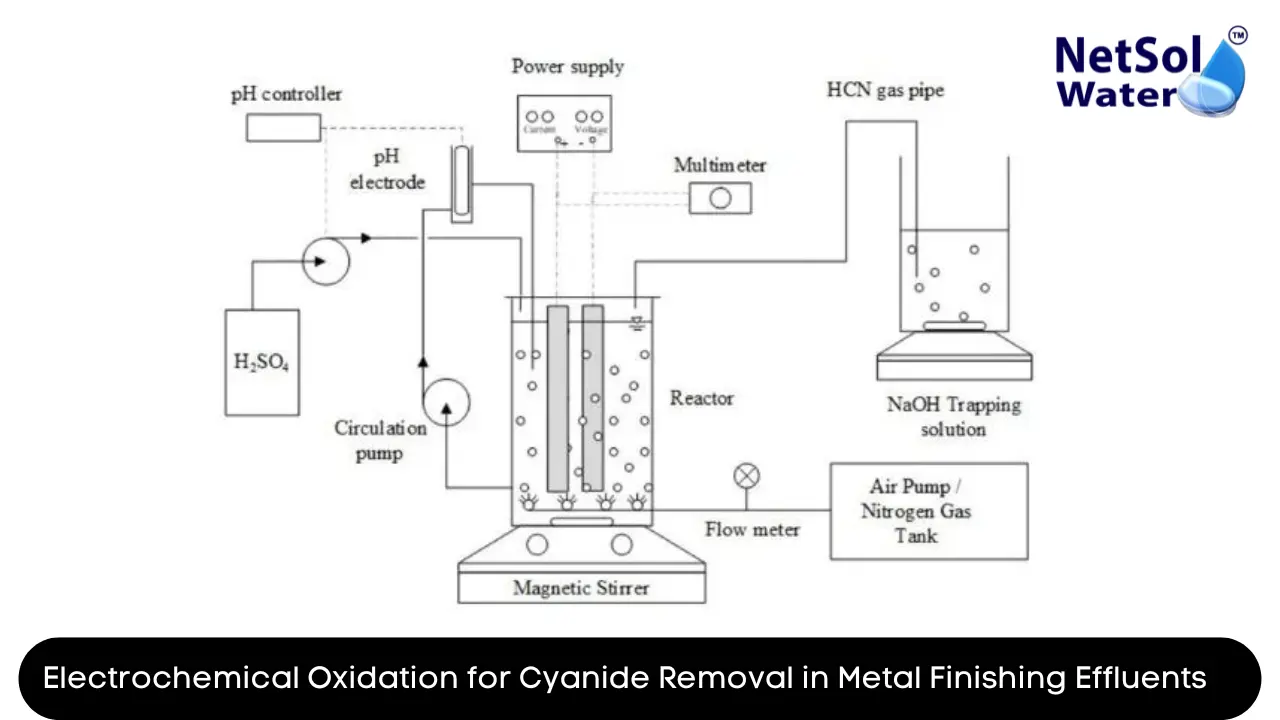
Process Overview and Key Components
The electrochemical oxidation process for cyanide removal typically involves the following key components:
1. Electrolytic Cell: The heart of the electrochemical oxidation system is the electrolytic cell, which consists of electrodes (anode and cathode) immersed in the effluent solution. The cell design, electrode material, and configuration play a crucial role in the efficiency of the oxidation process.
2. Power Supply: An external power supply provides the electrical current necessary to drive the electrochemical reactions within the cell, generating the desired oxidizing species.
3. Reaction Conditions: Various parameters, such as pH, temperature, and current density, can significantly influence the effectiveness of the electrochemical oxidation process. Optimizing these conditions is essential for maximizing cyanide removal efficiency.
4. Pre-treatment and Post-treatment: Depending on the characteristics of the metal finishing effluent, pre-treatment steps (e.g., pH adjustment, solids removal) may be required to ensure optimal performance of the electrochemical oxidation system. Additionally, post-treatment processes, such as filtration or adsorption, may be employed to remove any remaining pollutants or byproducts.
Implementation and Integration
Using electrochemical oxidation to remove cyanide in metal finishing wastewater treatment plants needs careful planning and considering these factors:
Understand the Wastewater: Check what's in the wastewater from metal finishing, like how much cyanide there is, the pH level, and if there are other bad stuff in it. This helps design the electrochemical system right.
Plan the System: Make sure the electrochemical system is designed and sized correctly based on what's in the wastewater, how much of it there is, and what we want to do with it. Things like what the electrodes are made of, how the cells are set up, and how big the reactor is all matter for how well the system works.
Fit it into the Plant: Electrochemical oxidation can be added to existing wastewater treatment plants by itself or with other methods like using chemicals, filters, or bacteria. This helps treat the wastewater completely.
Follow the Rules: When using electrochemical oxidation, it has to meet the environmental rules and standards before releasing the treated water back into the environment.
Operating and Keeping it Going
To keep electrochemical oxidation systems working well for removing cyanide, we need to:
Take Care of the Electrodes: Check, clean, and change the electrodes often to keep the system working right and to stop it from getting clogged or not working.
Watch and Control the Process: Keep an eye on important things like pH, temperature, and how much electricity is used to make sure the electrochemical process is working as best as it can.
Train the People: Make sure the people running the system know how to do it right, fix problems, and keep it running smoothly.
Be Safe: Wear the right gear, know what to do in an emergency, and handle any dangerous stuff carefully to keep everyone and the environment safe.
Conclusion
Electrochemical oxidation is a good way to get rid of cyanide from wastewater in metal finishing. It works by using chemical reactions and strong substances to break down cyanide, making it less harmful to the environment and meeting the rules. It's flexible, doesn't cost a lot, and doesn't take up much space, so it's a good choice instead of the old methods. Using electrochemical oxidation can help metal finishing companies manage their wastewater better, keeping people safe and protecting the environment as things change.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com