How to design ETP plant for Biscuit manufacturing unit?
To meet the growing demand for food goods, such as rolls, bread shops, and dairy products, the food business has shown a promising pattern. In addition to the positive consequences, it may also have a negative impact on the environment, notably because of wastewater produced. Businesses in the food industry, especially bakeries and bread rolls, use a large amount of water during the washing process that is then discharged as wastewater.
Biscuits manufacturing and processing plants produce dry cake from various types of food ingredient mixing. Some biscuits are largely made of flavoring ingredients that are combined with dairy or chocolate ingredients before being sweetened with sugar. The wastewater from the manufacturing of biscuits is distinct; although it is treated in smaller quantities than other industrial effluent, it is ranked as one of the highest contamination parameters in terms of quality. The average daily effluent flow for biscuit manufacturing, which produces 2000 tonnes of biscuits per day, is only 200–300 m3/day.
In this blog, we will discuss in detail the design and working of ETP for biscuit manufacturing industries.
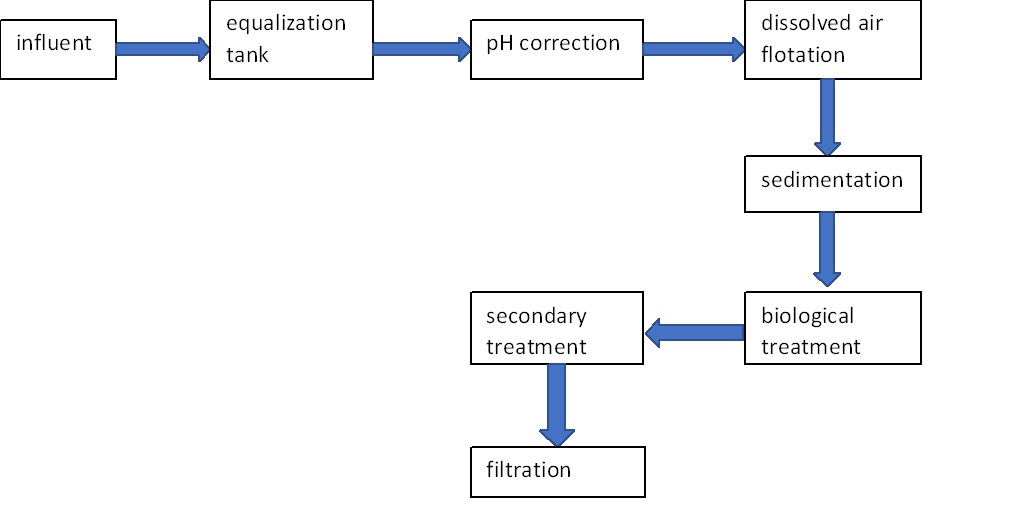
Working procedure of ETP for biscuit manufacturing unit:
Pre-treatment: To screen out any large solids or particles that may be included in the wastewater as part of the pre-treatment procedure. After that, any sand, gravel, or other heavy items are removed by passing the wastewater through a grit chamber.
Equalization tank: As implied by the name, it is a tank used to combine different pollution levels into a single, high-quality mixture (equal flow). Make sure the tank's volume is calculated using the peak hour flow in order to ensure that it is large enough to hold the entire amount and prevent overflow. The best plan is to install an air blower at the bottom of the tank so that the pH, coagulant, and flocculant chemicals can be conveniently dosed in the subsequent chemical processes. The ideal method for dosing pH chemicals is to apply them directly to the pipe that carries wastewater from the EQ tank to the DAF tank.
pH correction: To guarantee effective treatment in following treatment operations, the pH correction procedure involves changing the pH level of the wastewater. To prevent any adverse impacts on the microorganisms used in the biological treatment process, the pH of the wastewater must be kept within a certain range.
Dissolved air flotation (DAF): Wastewater that contains oil and grease always floats on the surface because oil and grease compounds are lighter than water. Additionally, we advise dosing coagulant and flocculant chemicals with the separated tank before the DAF tank in order to attract the appropriate quantity of suspended solid and fat to create blocks that will then readily float on the surface. This will ensure that the FOG is completely separated from the remaining wastewater.
Sedimentation tank: A sedimentation tank is then used to pass through the flocs created during the coagulation and flocculation process. Gravity causes the flocs to fall to the tank's bottom where they create a layer of sludge that is collected and transported for additional processing.
Biological treatment: Microorganisms in the aeration tank break down the organic materials in the wastewater during the biological treatment process. To carry out this process, the microbes need oxygen, which is provided by diffusers positioned at the bottom of the tank. In this process, the organic matter is transformed into carbon dioxide and water.
Secondary sedimentation tank: Following treatment, the wastewater is run into a secondary sedimentation tank, where any microbes and suspended solids that are still present sink to the bottom of the tank.
Filtration: The treated wastewater is sent through a sand filter as the last phase of the treatment process to get rid of any leftover suspended sediments or microbes. After being disinfected, the filtered water is released back into the environment.
Conclusion:
The wastewater treatment facility for the production of biscuits is one of the more difficult facilities to maintain since it produces the highest levels of organic pollutants. The primary method of treatment for this form of wastewater should be biological, using bacterial activity to break down the organic material into smaller pieces before meeting standard discharge on final unit treatment. Consider your options carefully before choosing a unit biological treatment because it will affect the way we administer it on a regular basis to keep making progress. Since bacteria are living creatures just like people, we must handle them with the same consideration we give to excessive levels of organic pollution in order to attain the standard discharge for greater environmental health.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com



