What is trickling filter with diagram?
Trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It is made out of a fixed bed of pebbles, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater runs downward, causing a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to form and cover the medium. Splashing, diffusion, and either forced-air flowing through the bed or spontaneous convection of air if the filter material is porous helps to maintain the aerobic conditions.
Treatment of sewage or other wastewater with trickling filters is one of the most well-known and well-established treatment methods.
Classification of Trickling filters
Trickling filters are determi?ned on the basis of their hydraulic and organic loads. They can be categorized as:
1: Standard Rate Filter
Hydraulic ratings of 1.1 to 4.3 m3/m2/d and organic loadings of 0.08 to 0.41 kg BOD/m3/d are common for standard rate trickling filters. These filters are usually rectangular or round in shape and 1.8 to 2.4 meters deep.
Dosing tanks with automatic siphons or periodic pumps are commonly used to dose them on a regular basis. A thick growth forms in the filter during normal operation until a temperature change or the flow through the filter causes a large portion to slough off. This sloughing is known as "unloading," and it normally happens in the spring or fall. The sloughed material is a humus-like material that is stable and easily settled, and frequently contains a large number of worms and filter fly larvae.
2: Intermediate Rate Filter
Intermediate rate filters, including recirculation, are typically designed to treat hydraulic loadings of 4 to 10 m3/m2/d and organic loadings of 0.24 to 0.48 kg BOD/m3/d.
In the past, there have been instances where the intermediate organic loading encouraged significant biological filter development while the hydraulic loading was insufficient to prevent clogging of the trickling filter medium. Other plants in this range have experienced minimal operational issues. In certain circumstances, high rate filters are actually under-loaded intermediate rate filters.
3: High Rate Filter
High-rate filters are often built to handle far higher loadings than standard-rate filters. A filter that receives BOD loadings ranging from 0.4 to 4.8 kg BOD/m3/d. These filters are normally spherical and range in depth from 0.9 to 2.4 meters.
They are built to receive wastewater on a continuous basis. The high rate of application is achieved by recirculating wastewater that has previously passed through the filter. The continuous rather than periodic sloughing of the filter growths is caused by the strong flow of wastewater over the filter media. Because the solids are not kept as long in the high rate filter as they are in the regular rate unit, they are less stable and continue to exert BOD after leaving the filter.
4: Roughing Filter
Roughing filters are high-rate filters that are used to handle organic loads more than 1.6 kg BOD/m3/d. (It's not uncommon for roughing filters to be loaded at rates exceeding 3.2 kg BOD/m3/d.) These filters are frequently used to pre-treat trash before it is fed to an activated sludge facility. Synthetic media is used in the majority of roughing filters nowadays.
5: Super High Rate Filter
Bigger hydraulic loadings and a substantially greater filter depth are the main distinctions between super and high rate filters. Some ultra-high rate filters can withstand hydraulic loads of up to 162.3 m3/m2/d. The majority of these filters are packed towers with depths of up to 12 meters.
The use of synthetic media allows for higher loading rates and deeper filtering. The most significant aspect of a trickling filter is the microbial layer that forms on the filter medium. The microbial layer organisms feed on the contaminants in the sewage and convert them to solids that drop out of the sewage.
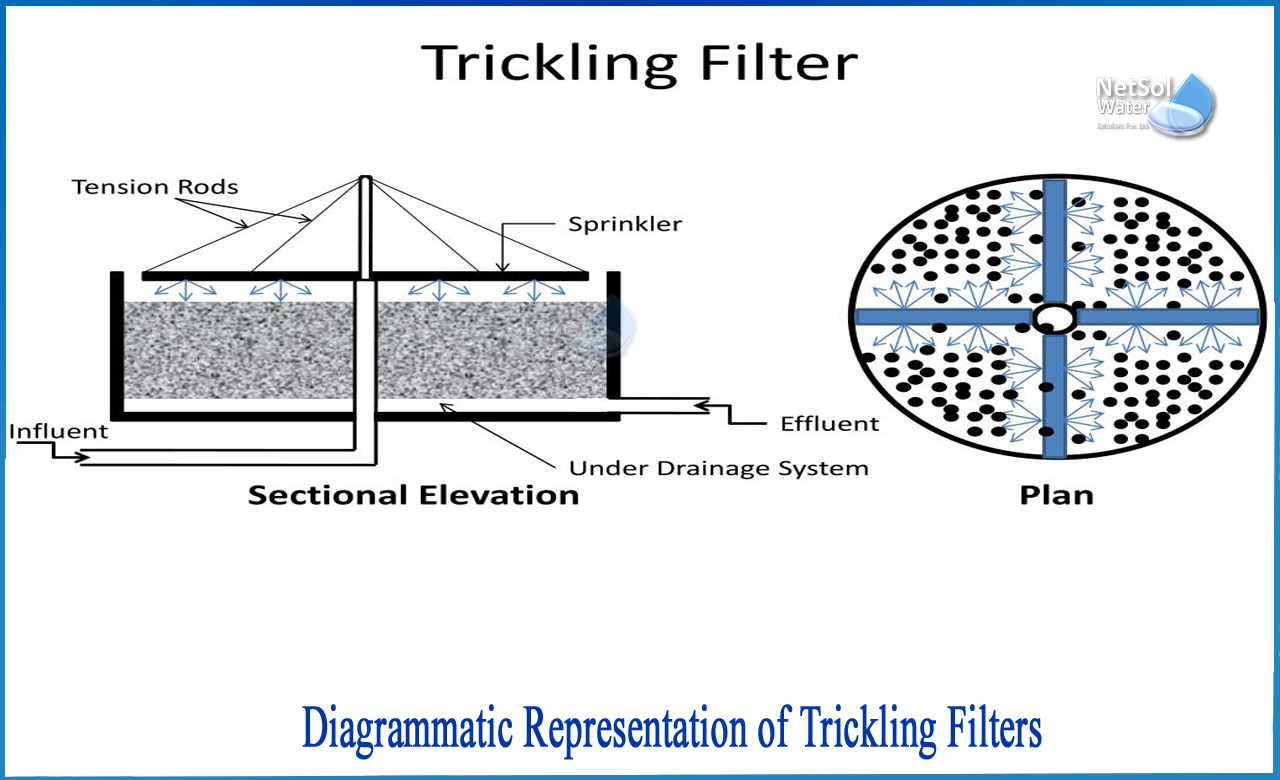
Diagrammatic representation of a Trickling Filter
Construction details of a Trickling Filter:
1-Holding Tank: A tank, rectangular or circular with a fixed nozzle for inlet.
2-Filter Media: Filter media like broken stone, slag or gravel is used.
3-Distribution system: To spread wastewater evenly over the surface of trickling filter.
4-Underdrainage system: To carry away the effluent and solid sludge.
How can Netsol Water assist?
Netsol is a pure-play technology company that offers a variety of wastewater-related solutions around the world, including resource conservation, optimization, recycling, and reuse.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.