Designing an ETP for Honey Processing and working functions
Effluent treatment plants (ETPs) are an essential requirement for industries to manage and treat their wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. The honey manufacturing and exporting industry produces a significant amount of wastewater that requires treatment before it can be discharged into water bodies.
The purpose of this is to design an effluent treatment plant for a honey manufacturer or exporter and explain the process flow diagram and working functions.
Design Basis
To design an effluent treatment plant for a honey manufacturer or exporter, the following parameters need to be considered:
· Flow rate of wastewater
· Chemical oxygen demand (COD) of wastewater
· Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of wastewater
· pH of wastewater
· Total dissolved solids (TDS) of wastewater
· Total suspended solids (TSS) of wastewater
· Oil and grease content in wastewater
Based on the above parameters, the design basis for the effluent treatment plant would be as follows:
Process Flow Diagram
The process flow diagram for the effluent treatment plant is shown in Figure 1.
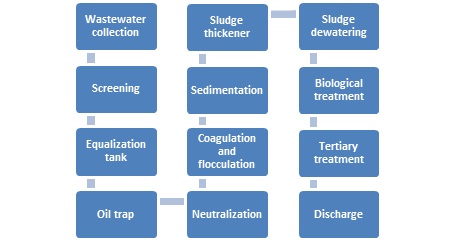
Figure 1 - Process Flow Diagram showing ETP for honey processing
Working Functions
The working functions of each unit operation in the effluent treatment plant are explained below:
1. Wastewater collection: The wastewater generated by the honey industry is collected in a tank or a sump.
2. Screening: The wastewater from the honey manufacturing process is first screened to remove large particles and debris that could cause blockages in the downstream process. The screened wastewater is then sent to the equalization tank.
3. Equalization tank: The equalization tank is used to balance the flow rate and composition of the wastewater. It also helps to reduce the shock loads on the downstream process. The wastewater is stored in the equalization tank for a certain period before it is sent to the next unit operation.
4. Oil trap: This step separates oil and grease from the effluent using gravity or skimmers.
5. Neutralization: The pH of the wastewater is adjusted to the required range using an acidic or alkaline solution. The neutralized wastewater is then sent to the next unit operation.
6. Coagulation and flocculation: Coagulants and flocculants are added to the wastewater to form flocs that settle down in the sedimentation tank. The coagulants and flocculants used in the process depend on the type of wastewater and the level of impurities present in it.
7. Sedimentation: The flocs that are formed in the coagulation and flocculation process settle down in the sedimentation tank, and the clarified water is removed from the top. The settled sludge is sent to the sludge thickener.
8. Sludge thickener: The sludge from the sedimentation tank is sent to the sludge thickener, where it is concentrated by gravity. The thickened sludge is then sent to the sludge dewatering unit.
9. Sludge dewatering: The thickened sludge from the sludge thickener is dewatered using a filter press or centrifuge. The dewatered sludge is then sent for disposal or further treatment.
10. Biological treatment: The wastewater from the sedimentation tank is sent to the biological treatment unit, where it is treated using an aerobic biological process. The aerobic bacteria in the reactor consume the organic matter in the wastewater and convert it into carbon dioxide and water.
11. Tertiary treatment: The treated wastewater from the biological treatment unit is sent to the tertiary treatment unit, where it undergoes further treatment to meet the desired effluent quality. The tertiary treatment can include processes like activated carbon filtration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis.
12. Discharge: The treated wastewater is finally discharged into the environment after meeting the required effluent quality standards.
Summary:
So the design of an effluent treatment plant for a honey manufacturer or exporter requires consideration of various parameters such as flow rate, COD, BOD, pH, TDS, TSS, and oil and grease content. The process flow diagram and working functions of each unit operation in the effluent treatment plant have been explained in detail. The use of formulas to calculate parameters such as COD, BOD, TDS, and TSS has also been discussed. A well-designed effluent treatment plant is essential to ensure that the wastewater from the honey manufacturing and exporting process is treated and discharged into the environment without causing harm to the ecosystem.
Leading manufacturer of sewage treatment plants in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.