Introduction to UASB reactor
Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket reactor also known as UASB reactor is a modified version of the contact anaerobic process which is used in wastewater treatment based on an upward movement of the liquid waste through a dense blanket of anaerobic sludge.The biomass grows on the fine sludge particles, which ultimately evolves into high-specific-gravity sludge granules.
Although wastewater containing high suspended solids is successfully treated in UASB reactor, pre-treatment such as sedimentation, neutralization of wastewater is normally desirable in treating wastewater in UASB reactor.
Organic loading in the range of 1-20kg COD/m3.day can be applied with removal efficiency of 75-85% and HRT of 4 to 24hours.
The UASB reactor is an anaerobic methane-producing digester that creates a blanket of granular sludge that is digested by anaerobic bacteria.
Field of application for UASB reactor-
UASB is not suitable for small or rural towns that do not have access to a reliable water supply or electricity. It finds its application in:
• Breweries and beverage manufacturing industries
• Distilleries and fermentation manufacturing industries
• Food manufacturing industries
• Paper and pulp
These four industries are responsible for 87 percent of all applications.
Parts/Components of UASB Reactor
The UASB reactor can be divided in three main parts:
a) Sludge bed,
b) Sludge blanket, and
c) Three phase separator (gas-liquid-solid, GLS separator) provided at the top of the reactor.
Under high turbulence, the three-phase separator allows the reactor to separate gas, water, and sludge mixtures.
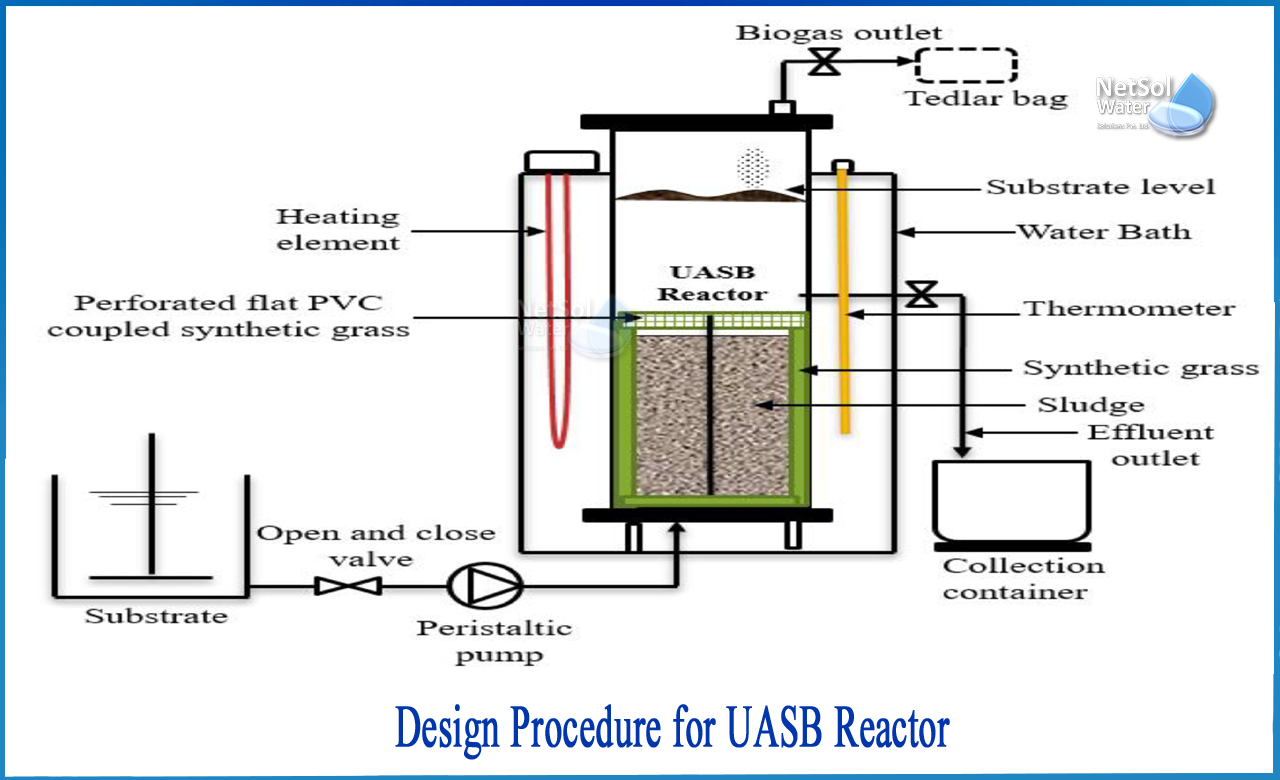
How to Design procedure for UASB reactor?
UASB reactor consists of a tank designed as circular or rectangular, where the wastewater flows upwards through a dense sludge bed with high anaerobic microbial activity. The sludge bed occupies about half the volume of the reactor and consists of microbial granules (1 to 3 mm in diameter) or highly sedimentable flocs.
The sludge is mixed by rising bubbles without the use of any mechanical equipment. The free gas and particles with the attached gas that reaches the top of the tank is deflected downwards by the slanted walls. The cleared effluent is taken from the tank's top, above the sloped walls. The solids profile in the reactor varies from very dense and granular particles close to the bottom to more dispersed and light particles close to the top.
The wastewater enters the UASB reactor from the bottom, and the effluent exits via a settling zone at the top. It is necessary to select proper range of operating parameters for design such as organic concentration, superficial liquid upflow velocity, reactor volume, hydraulic retention time, etc.
1: Reaction volume
The volume of reactor required is calculated based on the greater acceptable value of OLR for a certain COD content as:
Volume = (Flow Rate x COD concentration) / OLR
To prevent overloading, the reactor in terms of SLR, this amount of sludge should be less than 50% of the reactor volume, calculated using OLR. The OLR can be decreased to enhance volume if the volume does not satisfy the standards. As a result, the reactor's capacity has been determined to suit both criteria.
For this amount, the HRT should not be less than 6 hours for any form of wastewater, and it should normally be less than 18 hours to decrease reactor volume and hence expense. It may not be able to achieve this criterion if the wastewater has a very high strength, such as COD higher than 10,000 mg/L. In this case, the HRT may be extended beyond 24 hours and up to 200 hours.
2: Superficial Liquid Upflow Velocity
Higher upflow velocities promote a better sludge selection procedure and improve reactor mixing. The inoculum may be washed out at start-up or during regular operation granules may be fragmented, and the resultant pieces can readily wash out of the reactor at very high upflow velocity, more than 1.0 to 1.5 m/h.
The maximum liquid upflow velocity allowed in the design should be between 1.2 and 1.5 meters per hour. During typical reactor operation, upflow velocities of 0.25 to 0.8 m/h are beneficial for granule formation and accumulation, while maximum upflow velocities of 1.5 m/h at peak flow conditions for brief duration can be employed in design.
3: Reaction-Height and Area
The reactor should be as high as possible to decrease the plan area and the cost of land for three phase separation and influent distribution layout, among other things. The sludge bed's height should be adequate to prevent channeling and keep the liquid upflow velocity within the maximum allowable limits (1.2–1.5 m/h).
As a result, the sludge bed should be at least 1.5 to 2.5 meters tall, and the reactor's height should be limited to 4 meters to provide for easy access to the sludge bed, sludge blanket, and three-phase separator. The maximum height of the reactor, as stated in the specification, is roughly 8 meters, while the commonly used height is between 4.5 and 6.0 meters.
Furthermore, the sludge bed takes up 30 to 60% of the whole reactor volume, the sludge blanket takes up 20 to 30% of the total volume, and the GLS separator takes up the remaining 15 to 30% of the total capacity.
How can we assist?
Netsol Water is a pure-play technology company that offers a variety of wastewater-related solutions around the world, including resource conservation, optimization, recycling, and reuse.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.