What is the Conventional Aeration and Tapered Aeration?
Air is cycled through, combined with, or dissolved in a liquid or materials during aeration.
Aeration is the process of bringing water and air together to remove dissolved gases and oxidize dissolved metals such as iron, hydrogen sulphide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This process happens in the secondary treatment procedures of activated sludge treatment in wastewater treatment facilities, and is often the first significant step at a drinking water treatment facility. An aeration system with an appropriately distributed oxygen supply is critical for optimal wastewater treatment and microbiological development.
The quantity of surface contact between air and water determines the efficacy of aeration. The size of the water drop or air bubble is mostly responsible for this. By exposing droplets or thin sheets of water to the air, or by introducing tiny bubbles of air and allowing them to rise through the water, aeration puts water and air into close contact. The dissolved gases are subsequently extracted from the solution and released into the atmosphere.
Processes for Activated Sludge: Partial list
1. Conventional aeration
In a traditional ASP, the aeration tank's flow model is plug flow. Both the influent wastewater and recycled sludge enters the tank at the top and are aerated for sewage treatment for around 5 to 6 hours. The operation of diffusers or mechanical aerators mixes the influent and recycled sludge.The rate of aeration remains consistent throughout the tank's length.
Adsorption, flocculation, and oxidation of organic materials occur during the aeration phase. This kind of ASP is designed using an F/M ratio of 0.2 to 0.4 kg BOD/kg VSS. d and a volumetric loading rate of 0.3 to 0.6 kg BOD/m3.d. In the aeration tank, lower mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS) concentrations of 1500 to 3000 mg/L are maintained, with a typical cell residence duration of 5 to 15 days. Sewage treatment necessitates a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 4 to 8 hours. For the treatment of industrial wastewater with greater BOD concentrations, a higher HRT may be necessary.
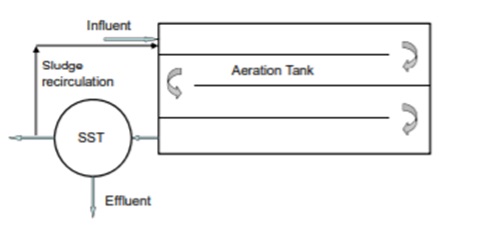
Conventional activated sludge process
2. Tapered Aeration
The BOD load in a plug flow aeration tank is highest at the input and decreases as wastewater travels towards the effluent end. As a result, in tapered aeration, the highest amount of air is delivered at the beginning and gradually decreases as the process progresses; hence, tapered aeration is named. The efficiency of the aeration unit will be boosted as a consequence of tapering aeration, as well as overall economy.
In the design, an F/M ratio of 0.2 to 0.4 kg BOD/kg VSS.d and a volumetric loading rate of 0.3 to 0.6 kg BOD/m3.d are used. The mean cell residence time should be 5 to 15 days, and the MLSS should be 1500 to 3000 mg/L.Sludge recirculation ratio of 0.25 to 0.5 and HRT of 4 to 8 hours is maintained. Despite the fact that the design loading rates are comparable to traditional ASP, tapered aeration provides higher performance.
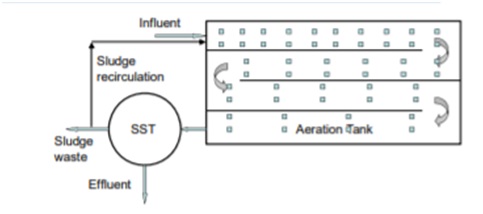
Tapered aeration activated sludge process
Netsol helps!
If you are curious to know more about the types of aeration process or if you encounter any problem in your processing units related to aeration, you can directly contact Netsol Water Solutions for best expert advice, as we are renowned manufacturers of WWTP and WTPs.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.



