Why is RO filter system essential in agriculture?
Agriculture needs RO (reverse osmosis) filter systems for several reasons:
1. Soil health: The use of water with high levels of dissolved solids and impurities can negatively affect soil health, leading to reduced crop yields and decreased quality of produce. RO systems can remove these impurities, leading to healthier soil and increased crop yields.
2. Water conservation: In regions with limited freshwater resources, RO systems can be used to treat and reuse wastewater from agricultural processes, reducing the amount of freshwater needed for irrigation.
3. Crop quality: The quality of the water used for irrigation can affect the quality of crops produced. RO systems can remove impurities and minerals that can negatively affect the quality of produce, leading to higher-quality crops.
4. Plant health: High levels of dissolved solids and impurities in water can lead to damage or death of plants. RO systems can provide water with a balanced composition that is optimal for plant growth and health.
5. Sustainability: The use of RO systems can promote sustainable agriculture practices by reducing the need for freshwater resources, promoting water conservation, and reducing the negative impact of agricultural practices on the environment.
Commercial RO filter for agriculture with flow chart and working:
Commercial RO (reverse osmosis) filter systems for agriculture are designed to remove impurities and minerals from water used for irrigation and hydroponic systems. Here is a general working of a typical commercial RO filter system for agriculture:
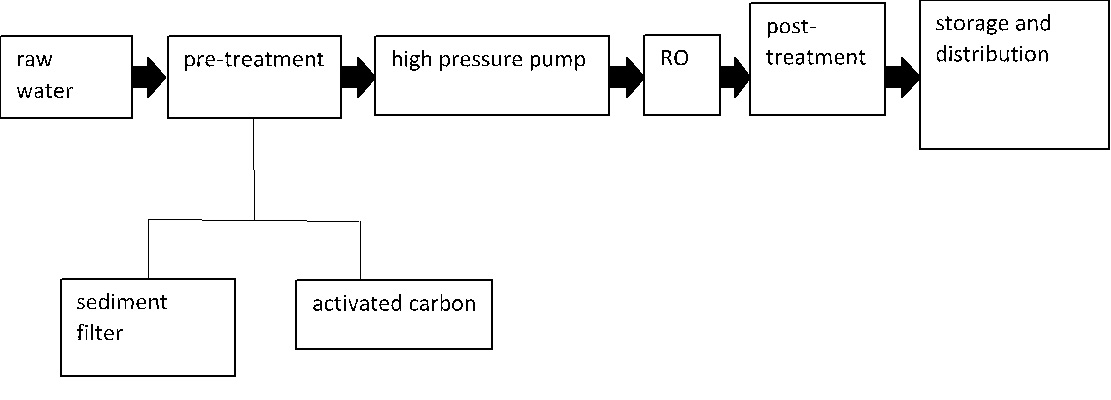
1. Source Water: The first step in the process is to obtain water from a source such as a well, river, or municipal supply.
2. Pre-treatment: The water is pre-treated to remove any large particles, sediment, or debris that may be present. This can involve using a series of filters such as sediment filters, activated carbon filters, and other pre-treatment equipment.
3. High-Pressure Pump: The pre-treated water is then pumped at high pressure using a high-pressure pump. The pressure helps to force the water through the RO membrane.
4. Reverse Osmosis: The water is passed through a semipermeable RO membrane, which removes impurities and dissolved solids from the water. The RO process involves a series of stages, including the feed stage, concentrate stage, and permeate stage.
5. Post-treatment: After the RO process, the water is passed through a series of post-treatment steps, which can include disinfection using UV light, mineralization, pH adjustment, and other treatments to improve the quality and composition of the water for agricultural use.
6. Storage and Distribution: The treated water is then stored in a clean, disinfected tank and distributed to various points of use, including irrigation systems and hydroponic systems.
Conclusion:
The working of a commercial RO filter system for agriculture involves multiple steps to ensure the safety and quality of the treated water for agricultural use. The pre-treatment step removes large particles and sediment, while the RO process removes dissolved solids and impurities. Post-treatment is then used to further purify and adjust the composition of the water for optimal plant growth. Finally, the treated water is stored and distributed for use in irrigation and hydroponic systems, promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com



