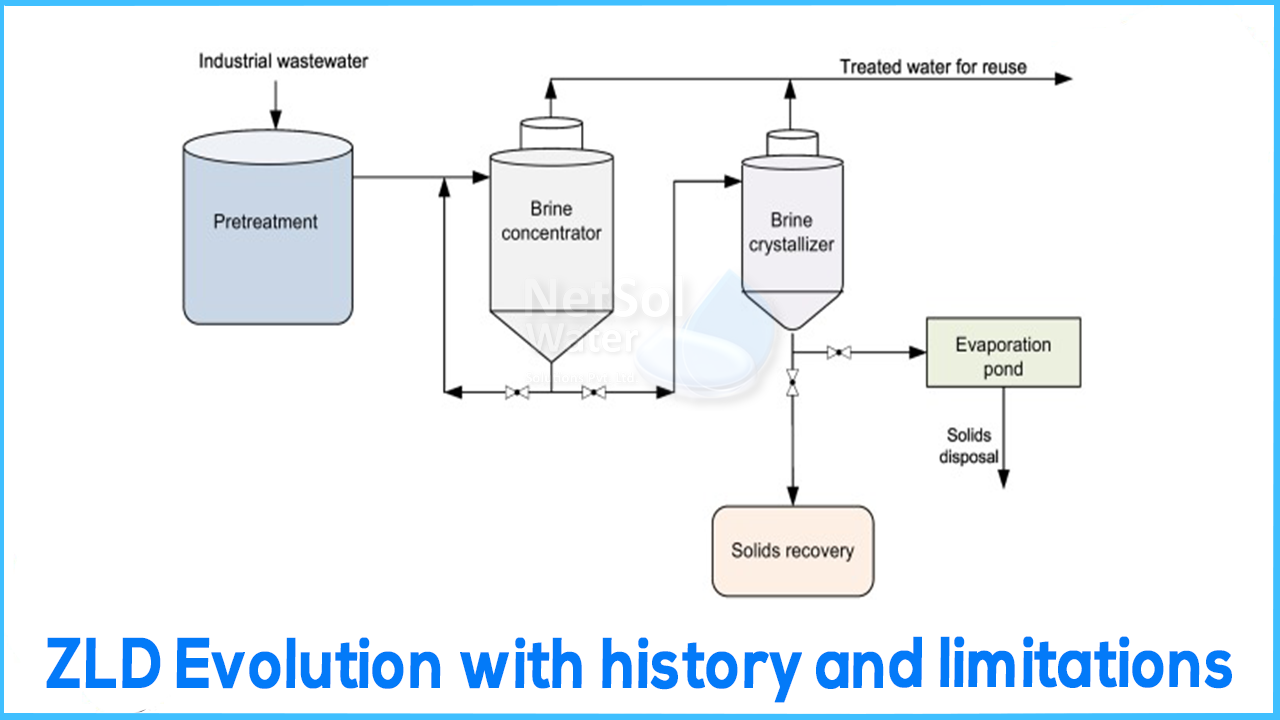
ZLD HISTORY
ZLD is zero liquid discharge from any facility such that all water and its effluent’s is used and reused after treatment using in-house treatment facility. ZLD system is pushed very hard so that the pressure on environment decreases due to untreated discharge and overly polluted discharge into streams.
The ZLD sector was apparently born in the US in the 1970s, prompted by Environment regulatory laws asfederal regulations became strict on salt discharges into surface waters especially due to salt problems in the Colorado River. This river suffered a lot due to unchecked discharge of effluent into its streams.
These regulations mainly referred to Power Plant Discharges, cooling tower purges and scrubbers (after previously introduced regulations on flue gas discharges). All these acts forced the treatment to go for ZLD.
The first ZLDs installed were 500-2000 GPM units based on evaporation / crystallization as the regulations were expected to be more stringent under new Environmental Protection Act.
MAJOR DRIVERS OF ZLD
Currently, the main reason for using ZLD is
- 1. Environmental regulations for the introduction of certain dissolved substances, salt,poisonous elements, nitrate-nitrite-nitrite, etc.
- 2. Water scarcity
- 3. Economy-Recycled water becomes more affordable as water supply from conventional sources becomes more expensive.
- 4. Increased social responsibility and awareness of environmental issues
Although the costs of ZLD are high in most cases, it can be a more economical solution when large amounts of waste need to be transported over long distances
DISADVANTAGES OF ZLD
ZLD still has disadvantages, probably the most significant
- 1. Very high cost
- 2. Custom design on a case-by-case basis
- 3. Difficulties in managing complex flows (for example, petrochemicals)
CURRENT MARKETS AND POTENTIALS FOR ZLD
- Industrial wastewater treatment and recycling
- Energy
- Synthetic fuels
- Primary metals processing
- Petroleum and petrochemicals
- Petroleum refining
- Primary metals processing
- Gravity-assisted drainage steam
- Microelectronics
- Chemicals
- Drainage by Steam Assisted Gravity
- Heavy Oil Recovery
- Combined Heat and Power Generation
- Pulp and Paper
- Coal Mining
- Fertilizers
- Solid Waste
- Battery Production
- PVC production
- Uranium mining
- Coal liquefaction
- Ethanol production
- Uranium extraction
- Internal desalination