A fixed-bed, biological reactor that functions, mainly aerobically is referred to as a trickling filter. It is also known as a trickling bio-filter, bio-filter, biological filter, and biological trickling filter. The filter is continuously "trickled" or sprayed with pre-settled effluent. Organics are aerobically destroyed by the biofilm that covers the filter material, when the water passes through the holes of the filter.
Let’s explore the working of trickling filter technology in sewage treatment and its process flow diagram in this blog.
Working of Trickling Filter Technology in Sewage Treatment
· Adding the sewage that has been settled
From the primary clarifier tank, raw or primary sewage continuously flows into the trickling filter tank. To avoid clogging in the trickling filter system, the sewage must first undergo a number of processes such as screening, grit removal, and primary clarifiers.
The primary influent is free of coarse particles, suspended solids, rags, etc. when it enters the trickling filter unit. A piece of equipment known as a dosing device (tipping bucket) allows the supernatant, to flow upward to the perforated rotary distributor's arms.
· Flushing of sewage
A perforated rotating distributor that distributes the primary sewage, equally over the filter matrix, causes it to flush downward. The filter bed is full of materials that serve as a media for the adhesion of the microorganisms, including rock, gravel, redwood, synthetic material, etc.
Because, biomass is directly connected to the media rather than suspended sewage, the trickling filter is the best illustration of an attached growth system.
· Traversal of the filter media
The filter media is mostly made of porous media, which enhances the available surface area for microorganisms to break down organic materials. There are two types of trickling filters: the normal rate and the high rate, each of which have a varied rate of hydraulic and organic loading. Also, it has air vents and backwashing to reduce odour, fly breeding, and blockage issues.
· Pollution reduction
Organic waste serves as a food source for the microorganisms affixed to the filter bed. Pollutants including organic and inorganic waste suspended in sewage are absorbed, and adsorbed by the microbial slime layer into and over the filter bed.
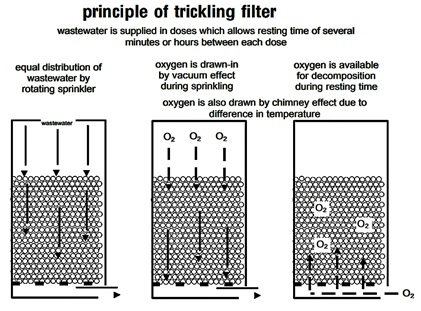
· Utilization of oxygen by microorganisms
The oxygen supply, in the form of dissolved oxygen, is provided by the treated primary sewage that splashes through the arm of a rotary distributor. Through the chimney effect or hoover, oxygen is sucked into the filter medium.
The bio-film layer oxidises the organic components by releasing carbon dioxide gas, water, and other oxidised end products, from the dissolved oxygen contained inside the filter media.
· Coating of slime
It also refers to a slime layer, which has a thickness of 0.1 to 0.2 mm and contains aerobic biomass on the filter bed's surface. The remainder, however, is made up of anaerobic biomass. Since, aerobic microbes use direct sunlight and the greatest quantity of oxygen to break down organic waste, the area above the surface where they are present is said to be in the rapid development phase.
As opposed to this, the lower surface where anaerobic microorganisms are found is thought of as an oxygen-deficient area, where the germs enter the endogenous phase and use their own cells for growth. The biofilm layer gradually thickens by the breakdown of organic matter after a certain point, and then it sloughs off into the liquid flow and is further separated inside the clarifier or sedimentation.
Flow Chart of Trickling Filter
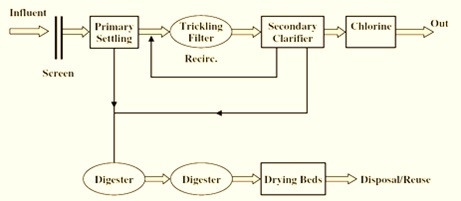
Fig: Flow chart showing Trickling filter as a secondary sewage treatment process
Process flow diagram of trickling filter (TF)

Costs considerations of Trickling Filter
Depending on the type of filter materials and feeder pumps utilised, capital expenses might range from moderate to high. Also, depending on how much electricity the feeder pumps use, operation and maintenance expenses can be low or expensive.
In any case, construction and upkeep require expert design and skilful labour, e.g. to prevent clogging, ensure adequate flushing, monitor hydraulic and organic loads, control filter flies, etc. Energy usage for sprinkler systems and pumps such as those used to raise water to the top of filters is another cost consideration. In contrast to actively aerated systems like activated sludge processes, these needs are minimal.
Leading providers of Sewage Treatment Plants in India
Various businesses and industries can get in touch with the water treatment specialists, at Netsol Water for a number of cutting-edge sewage treatment methods, including aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment. For a range of sectors, we have also produced and designed unique biological wastewater treatment systems like trickling filters.
We have also been offering municipalities wastewater treatment services for a long time. These services include phosphate removal, odour control, sludge dewatering, chlorination and dechlorination, and water clarification, etc. For further information, contact us by phone at +91 9650608473 or by email at enquiry@netsolwater.com.



