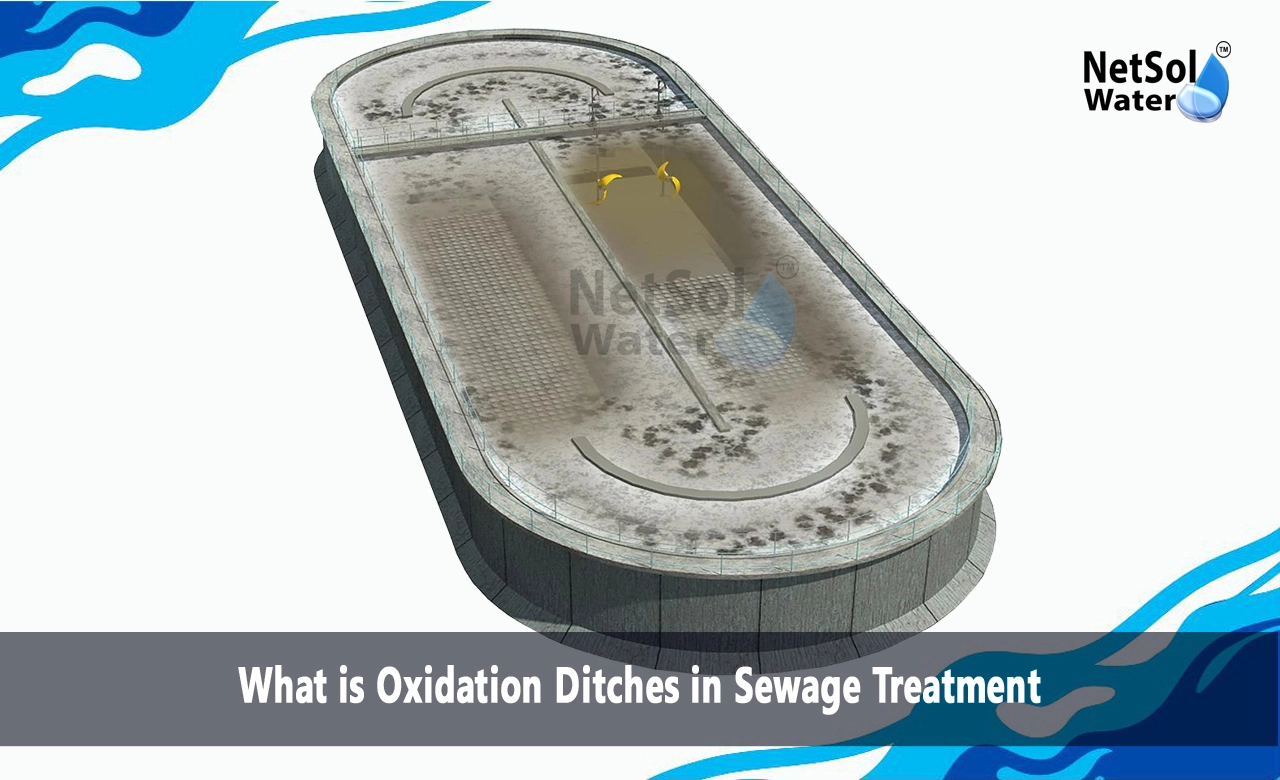
What is Oxidation Ditches in Sewage Treatment?
Sewage treatment is fundamental to protecting public health and preserving our environment. Oxidation ditches, a specific type of activated sludge process, have emerged as a dependable and efficient technology for treating wastewater. We will explores the intricacies of oxidation ditches, delving into their design, function, advantages, and considerations for implementation.
Understanding the Oxidation Ditch
An oxidation ditch is a continuous, oval-shaped tank resembling a racetrack. It houses a biological treatment process that leverages the power of microorganisms to break down organic matter present in sewage. This system falls under the extended aeration activated sludge category, characterized by a longer solids retention time (SRT) compared to conventional activated sludge systems. The extended SRT allows for a more robust microbial population, enhancing the degradation of organic pollutants.
Essential Components of an Oxidation Ditch System
Several key components work in unison to ensure efficient sewage treatment within an oxidation ditch system:
The Oxidation Ditch: This oval-shaped tank, the heart of the system, holds the wastewater undergoing treatment. The tank is typically constructed from concrete or steel and lined with an impermeable material to prevent leakage.
Mechanical Aerators: These rotating devices, often positioned along the sides of the ditch, provide oxygen to the wastewater. They achieve this by churning the mix liquor (a combination of wastewater and activated sludge) and promoting surface aeration.
Secondary Clarifier: Following treatment in the oxidation ditch, the wastewater flows into a secondary clarifier, a large settling tank. Here, the heavier sludge settles at the bottom, allowing the treated, clarified effluent to be separated for further disinfection or disposal.
Sludge Return System: Aportion of the settled sludge from the secondary clarifier is continuously recycled back into the oxidation ditch. This maintains a healthy concentration of microorganisms within the system, crucial for ongoing wastewater treatment.
Waste Sludge Disposal: Excess sludge accumulates over time and needs to be periodically removed from the system. This sludge undergoes further treatment and disposal according to local regulations.
The Biological Powerhouse Within
The magic of sewage treatment in an oxidation ditch lies within the thriving microbial community fostered by the extended SRT. These microorganisms, primarily aerobic bacteria, consume the organic matter present in the wastewater as their food source. The process can be broken down into two key stages:
1. Biodegradation: Aerobic bacteria breakdown complex organic molecules in the wastewater into simpler compounds. This process utilizes the oxygen supplied by the mechanical aerators.
2. Flocculation and Settling: The byproducts of biodegradation, along with bacterial cells, clump together to form sludge. This heavier sludge settles at the bottom of the ditch or within the secondary clarifier for separation.
The extended SRT allows for a diverse microbial population to develop within the oxidation ditch. This includes nitrifying bacteria, which play a vital role in removing nitrogen from the wastewater.
Advantages of Oxidation Ditches
Oxidation ditches offer several advantages over conventional activated sludge systems:
Efficient Treatment: The extended SRT and robust microbial population within the ditch enable efficient removal of organic matter, nutrients, and even pathogens.
Resilient to Fluctuations: Oxidation ditches can handle variations in wastewater flow and organic load with greater stability compared to conventional systems.
Energy Efficiency: The use of mechanical aerators instead of diffused air systems can translate to lower energy consumption.
Compact Footprint: Compared to conventional activated sludge systems with separate aeration tanks and clarifiers, oxidation ditches can occupy a smaller footprint.
Operational Simplicity: Oxidation ditches generally require less operational complexity and can be suitable for smaller treatment plants.
Considerations for Implementing Oxidation Ditches
While oxidation ditches offer numerous benefits, certain considerations need to be taken into account before implementation:
Land Requirement: Compared to some treatment technologies, oxidation ditches typically require a larger land area due to the single, elongated tank design.
Odor Potential: The biological processes within the ditch can generate odors, requiring proper ventilation or odor control measures.
Sludge Management: The extended SRT can lead to higher sludge production compared to conventional systems. Effective sludge management strategies become crucial.
Operational Expertise: While generally considered user-friendly, operating an oxidation ditch still requires a certain level of expertise to maintainoptimal performance.
Conclusion
Oxidation ditches represent a reliable and efficient technology for sewage treatment. Their ability to handle fluctuating loads, efficient pollutant removal, and relative ease of operation make them well-suited for a variety of applications. However, factors like land availability, odor control, and sludge management need careful consideration during the planning and implementation stages. Overall, oxidation ditches offer a compelling solution for communities seeking a robust and sustainable approach to wastewater treatment.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.