What is Chlorine Contact Tank (CCT) in STP Plant?
The Chlorine Contact Tank (CCT) serves as the final defence in sewage treatment plants (STPs). This critical component ensures water safety before release into the environment. The CCT disinfects treated wastewater through careful contact with chlorine. Modern water treatment depends on effective disinfection to protect public health.
The CCT stage happens after primary and secondary treatment. It removes harmful bacteria and pathogens from treated water. The process needs precise control of chlorine levels and contact time. These factors determine how well the disinfection works. The CCT design must balance effective treatment with safety considerations.
Water treatment facilities worldwide use CCTs as their main disinfection method. The process remains popular because it works well and costs less than other methods. The CCT process adapts to different water qualities and flow rates. This flexibility makes it suitable for various treatment plants. This blog explains how CCTs work in STPs. You will learn about design features operation methods and maintenance needs. The information helps treatment plant operators and managers optimize their disinfection systems.
CCT Design and Operation Principles
The design of a CCT affects how well it cleans water. Every feature serves a specific purpose. These elements work together to ensure proper disinfection. Let us examine the key design aspects:
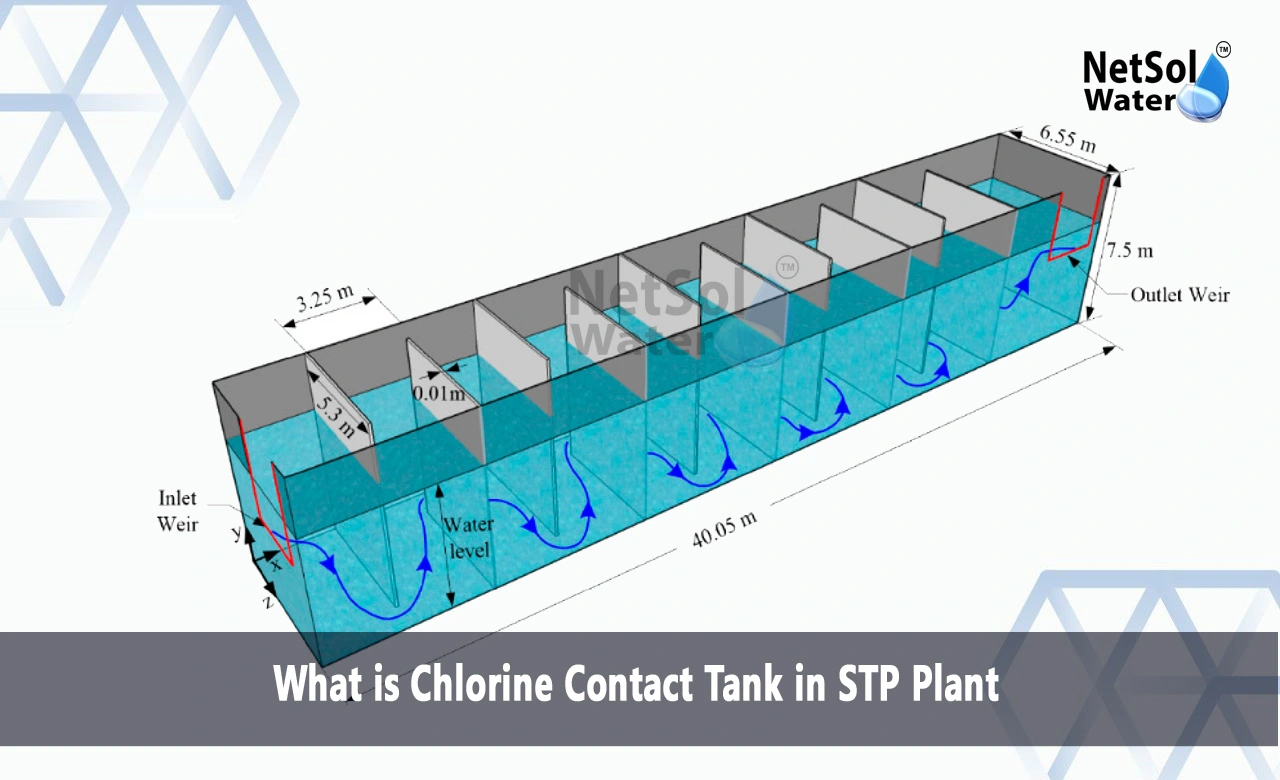
Tank Configuration: The tank shape promotes even water flow. Baffles inside direct water movement. This design ensures enough contact time. The layout prevents short-circuiting of water through the tank.
Contact Time Management: The tank size sets contact duration. Water needs enough time with chlorine. Most systems aim for 30 minutes of contact. This time allows complete disinfection.
Flow Control Systems: Flow meters monitor water movement. Controllers adjust chlorine dosing. These systems maintain proper treatment levels. Accurate control ensures consistent results.
Chlorination Process and Monitoring
The chlorination process needs careful management. Proper monitoring ensures safe water treatment. These activities protect public health and the environment.Let us look at process control elements:
Chlorine Dosing: Automated systems add chlorine to water. Dosing responds to water quality changes. The amount depends on contamination levels. Careful dosing prevents over-chlorination.
Quality Testing: Regular testing checks chlorine levels. Operators measure bacteria counts. These tests confirm proper disinfection. The results guide process adjustments.
Safety Systems: Leak detection protects workers. Ventilation removes chlorine gas. Emergency systems handle problems. These measures ensure safe operation.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
CCT systems need regular upkeep. Good maintenance prevents problems. Quick problem solving keeps systems running well.Let us explore maintenance requirements:
Regular Inspections: Workers check tank conditions daily. They look for equipment wear. These checks catch problems early. Regular inspection prevents failures.
Cleaning Procedures: Teams remove buildup from tanks. They clean sensors and meters. This maintenance ensures accurate operation. Clean systems work better.
Common Problems: Scale buildup affects chlorine mixing. Equipment failures disrupt treatment. Understanding these issues speeds repairs. Quick fixes maintain water quality.
Optimize Your CCT Performance Today
Your knowledge of CCT operations will improve water treatment results. Good disinfection protects public health. CCT systems offer proven treatment solutions.
Need help with your CCT system? Water treatment experts at Netsol Water can evaluate your setup. They will recommend improvements for better performance. Contact us to enhance your STP disinfection process. Your community deserves safe clean water.
Contact Netsol Water at:
Phone: +91-965-060-8473, Email: enquiry@netsolwater.com