What are the operating parameters for MBBR?
As pollution, oxygen consumption, and eutrophication of the aquatic environment have become unavoidable concerns due to high levels of organic matter and nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) present in discharged effluent, the development of cost-effective and efficient biological wastewater treatment processes is highly promising to meet the stringent discharge standard.
What is MBBR technology?
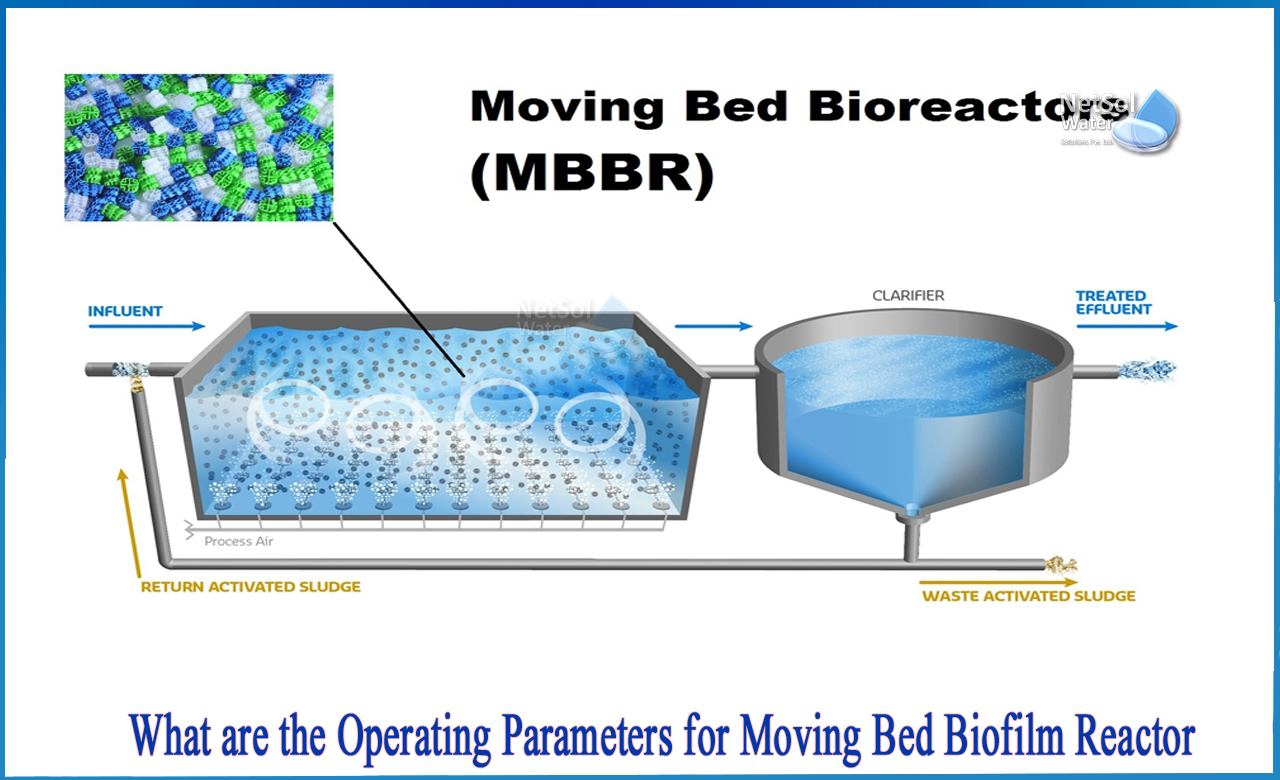
The MBBR process is an attachment growth biological wastewater treatment technology with a general description. As in trickling filters or RBC systems, the microorganisms that perform the treatment are linked to a solid media. The microorganisms that carry out the treatment in a suspended growth biological wastewater treatment process, such as the activated sludge process, are kept suspended in the mixed liquor in the aeration tank.
Microorganisms are attached to a medium that is set in place in traditional attached growth biological treatment procedures like trickling filters or RBC systems, and the wastewater being treated flows over the surfaces of the medium with their attached biological growth. In contrast, the microbes are connected to small plastic carrier media in an MBBR method. MBBR treatment usually takes place in a tank that looks like an activated sludge aeration tank. The carrier media are kept suspended in an aerobic process by a diffused air aeration system, or in an anoxic or anaerobic process by a mechanical mixing system. Typically, a sieve is utilised at the end of the process to maintain the carrier medium in the tank
Moving bed biofilm reactors (MBBRs) have been used as continuous operation biofilm reactors for decades, accumulating significant concentrations of active biomass on the surface of bio-carriers. Due to advancements in design and operation, this technology is dependable and compact, resulting in smaller footprints, much lower suspended solid output, consistent production of high quality and reusable water, and little sludge formation.
The type of biofilm carriers used in MBBR, as well as their shape, surface area, and filling ratio, are all important factors in determining the efficacy and effectiveness of the system or we can say that these are the factors which determine the performance of MBBR.
More carriers can provide more places for microbes to attach and develop. An increase in carrier filling ratio could increase particle–particle collision and promote carrier aeration, thus increasing shear stress on the biofilm. Furthermore, a high aeration rate raises the cost of operating.
To meet the pollutant removal criteria and achieve appropriate costs, the carrier filling ratio and aeration rate of MBBR must be optimised.The selection of a support carrier is critical for the proper running of an MBBR reactor in order to retain a large volume of biomass. The biocarrier utilised in MBBR for wastewater treatment should be low-cost, have a large effective surface area, be mechanically strong, and be microbial aggregation-friendly.
Various design parameters for MBBR are given as:
|
Application |
Substrate |
Removal flux,g/m2·d |
Volumetric removal rate,kg/m3·d |
|
BOD removal, partial |
BOD |
15-20 |
4.5-6.0 |
|
Secondary treatment |
BOD |
5-15 |
1.7-5.0 |
|
Pre-nitrification |
BOD |
4-5 |
1.2-1.5 |
|
Nitrification |
NH4-N |
0.4-1.4 |
0.1-0.4 |
|
Pre-denitrification |
NO3-N |
0.20-1.0 |
0.1-0.3 |
|
Post-denitrification |
NO3-N |
1.0-2.0 |
0.3-0.6 |
The following are the many application situations for the parameters provided in the table:
1. BOD removal, Partial:
When used as a pre-treatment for other biological treatment technologies, MBBR can be configured to work under exceptionally high organic loading, removing a considerable quantity of BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) in a compact space and lowering the load on following systems. Despite this, during high-load operation, the BOD removal rate of MBBR is only about 60-70 percent.
2.Pre-nitrification:
To obtain a greater effect, nitrification must occur at very low BOD concentrations. As a result, if MBBR is used to remove BOD before the nitrification tank, it can run at a lower area loading.
3.Predenitrification:
These are the design values for the A/O process that employ the BOD in the influent wastewater as the carbon source for denitrification.
4.Postdenitrification:
These are the design settings for denitrification in the reaction tank after nitrification using additional organic matter as the carbon source.
For more information, contact Netsol Water.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.