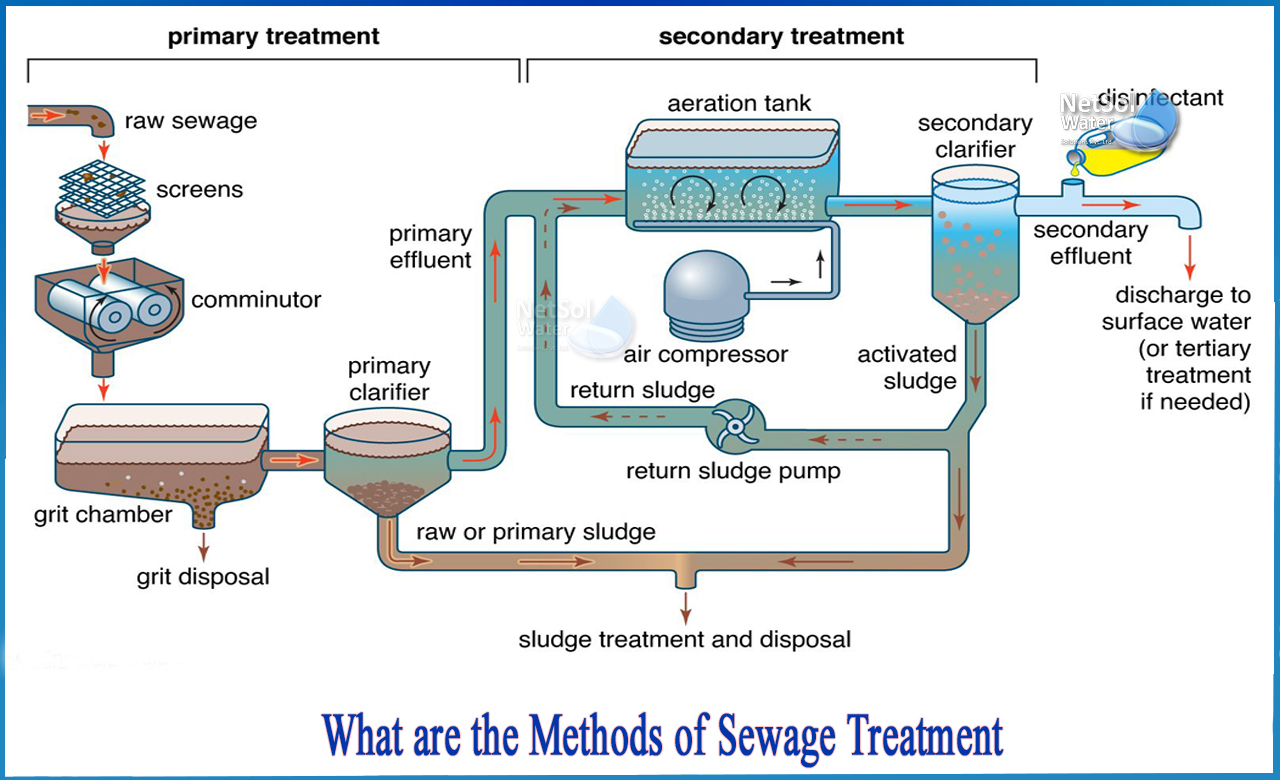
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
Our modern lifestyle allows us to use a variety of things to make our lives more pleasant and convenient, but this comes with a cost. Wastewater, which might be in the form of water trickling down the shower or runoff from wet roadways, is a common result of our present lifestyle. This effluent should not be consumed or used by humans.Fortunately, wastewater treatment technologies that filter and treat wastewater by removing impurities such as sewage and chemicals can make the wastewater potable and useable.
What is sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment refers to a procedure for removing pollutants from domestic and industrial wastewater. Physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment are the most common sewage water treatment procedures. These technologies disinfect the wastewater, removing all sewage elements and converting it to treated water that is acceptable for human use and the environment.Before this unclean used water reaches natural water bodies like lakes, rivers, oceans, and estuaries, the full confinement removal procedure takes place.
Because pure water is in short supply, the distinction between clean and contaminated water is entirely based on impurity concentration and intended use.To put it another way, water is considered polluted when it is unfit for any specific purpose, such as drinking, fishing, or swimming. Contamination of water occurs mostly as a result of the discharge of dirty wastewater into groundwater or surface water. Different sewage management technologies can also considerably reduce water contamination.
Methods of Sewage Treatment:
Contaminants such as chemicals and sewage can be removed from wastewater and recycled for future uses using a variety of wastewater treatment processes.
Generally, there are four types of sewage treatment, which are described below with key points:
Physical Treatment:
Physical procedures are utilised to purify the effluent at this stage. Solids are removed using methods such as screening, sedimentation, and skimming. There are no chemicals used in this method.Sedimentation, which is the process of suspending insoluble/heavy particles from wastewater, is one of the most used physical wastewater treatment processes.
You can separate the pure water once the insoluble stuff has settled to the bottom.Aeration is another excellent physical water treatment method. To deliver oxygen to the water, this procedure involves moving air through it. The third approach is filtration, which is used to remove all pollutants. To pass the wastewater and separate the pollutants and insoluble particles present in it, specific filters can be used. The most common filter is the sand filter. This procedure can also be used to easily remove oil off the surface of some wastes.
Biological Treatment:
The organic components found in sewage, such as human waste, food, and oil, are decomposed by a variety of biological processes.This breaks down organic substances in wastewater, such as soap, human waste, oils, and food, using a variety of biological processes. In biological treatment, microorganisms decompose organic materials in wastewater. It's broken down into three categories:
Aerobic processes: Bacteria digest organic materials and convert it to carbon dioxide, which plants can use. This procedure makes use of oxygen.
Fermentation: It is used in anaerobic procedures to ferment waste at a specified temperature. The anaerobic process does not need oxygen.
Composting: It is an aerobic treatment method that involves mixing wastewater with sawdust or other carbon sources.
Chemical Treatment:
This therapy employs the use of chemicals in water, as the name implies. Chlorine is a typical oxidising agent used to destroy microorganisms that degrade water by adding pollutants to it. Ozone is another oxidising agent that is used to treat wastewater. Neutralization is a process that involves adding an acid or base to the water to bring it back to its natural pH of 7. Chemicals stop bacteria from growing in water, resulting in pure water.
Sludge Treatment:
This is a solid-liquid separation process in which the solid phase must have the least amount of residual moisture and the separated liquid phase must have the least amount of solid particle residues.Dewatering of sludge from industrial wastewater or sewage plants is an example of this, in which the residual moisture in dewatered solids dictates disposal costs and the quality defines the pollution load returned to the treatment facility. Both must be kept to a minimum.
Wastewater has a large impact on the environment, so it's crucial to treat it properly. You not only safeguard the organisms that live on it, but you also protect the earth as a whole by cleaning wastewater.
For more details, contact Netsol Water.