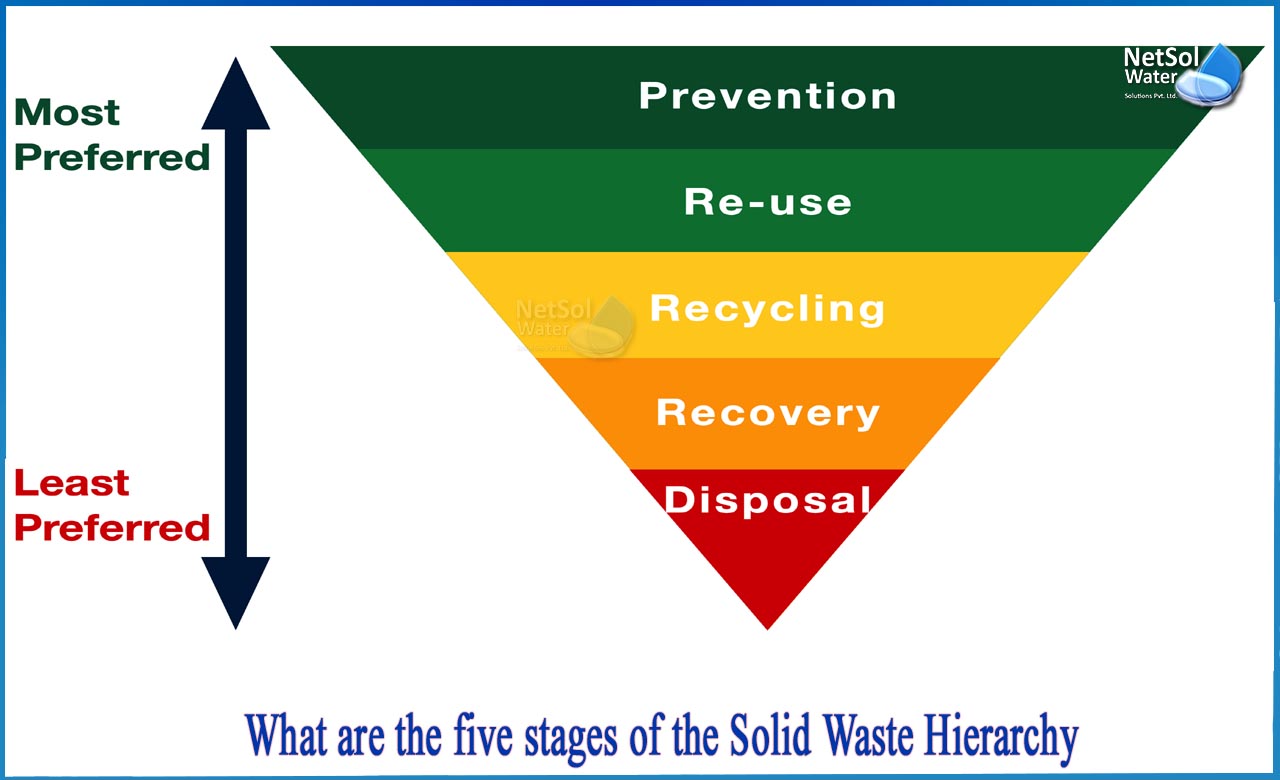
What are the five stages of the solid waste hierarchy?
Sustainable materials management of solid waste is a holistic approach to utilizing and recycling materials efficiently throughout their life cycles. This strategy is based on the waste hierarchy, which consists of five steps: waste reduction at the source, material reuse, recycling, and energy recovery and landfilling.
1: Reduce waste at the source
Any activity linked to the design, manufacturing, procurement, or use of materials or goods that can lead to a decrease in the amount of waste created in the first place, is referred to as waste reduction.
Reducing waste at the source is at the top of the waste treatment hierarchy because, from an environmental standpoint, the greatest waste treatment is prevention.
How can we cut down on waste production?
· Do not utilize throwaway items.
· Consume in moderation and with caution.
· Purchase things with as little unneeded packaging as possible.
· Instead of discarding out and buying new things, repair and reuse them.
· Purchase used goods and apparels.
· Manufacturers can produce more items that are longer lasting and less hazardous.
Waste Reduction Obstacles
Cost: The primary expenses associated with source reduction are incurred through research, data gathering, waste system management, product design, and enactment of necessary laws, education/awareness raising and campaigning. These are, however, significantly cheaper than the expenses of handling garbage after it has been created.
Change in attitudes and behaviour: A reduction-at-source system is based on a shift in attitude and conduct. This shift is required both from citizens – who would have to buy and consume fewer things – and from decision makers, who may, for example, adopt legislation incentivizing people to consume less, or businesses to produce less packaging.
2: Reuse
Reusing products means using them more than once for the same purpose. It helps to minimize the quantity of waste created and eventually landfilled.
Product reuse examples include:
- Beverage bottle refilling.
- Purchasing, selling, or giving items from and to thrift stores.
- Taking books and other items from libraries.
3: Recycling
The act of sorting items from the trash and utilizing them as raw materials to generate new goods is known as recycling. It offers numerous environmental advantages since it both reduces landfilling and increases resource efficiency.
4: Energy recuperation
Energy recovery, often known as waste-to-energy, is the process of producing electricity, heat, or fuel from non-recyclable waste.
Energy recovery types include:
a. Mass burn: Waste is burnt at extremely high temperatures in enormous facilities. The energy produced is utilized to power the mass burn process as well as to generate electricity or heat.
b. Refuse-derived fuel (RDF): In industrial facilities, high-quality, high-calorie, pre-sorted waste is burnt and utilized to produce fuel (mostly cement factories and power stations).
c. Gasification: The non-combustion conversion of organic molecules into a synthetic gas.
d. Pyrolysis: The high-temperature breakdown of organic substances.
5: Landfilling
Due to the enormous environmental costs of burying our waste in the ground, landfilling is the least desired form of waste treatment in the waste hierarchy. It is the primary method forwaste disposal in India.
What do we offer?
Netsol Water are pleased to introduce ourselves as a leading water and wastewater treatment company in India, specializing in the design and manufacture of WTPs, WWTPs, ETPs, STPs, as well as Energy Management, and Solid Waste Management services. Netsol Water Solutions is a one-stop utility partner for both industrial and commercial clients, helping them improve resource productivity and bottom lines while safeguarding the environment.
For further information or product purchase related query, contact Netsol Water at +91-9650608473 or drop a mail at enquiry@netsolwater.com.