What are waste stabilization ponds?
Waste stabilization ponds are ponds that are designed and built for the treatment of wastewater to lower organic content and extract pathogens. They are earthen structures enclosing man-made depressions.
Wastewater, or "influent," enters one side of the waste stabilization pond and exits the other side as "effluent," after spending several days in the pond undergoing treatment.
Waste stabilization ponds are used all over the world to treat wastewater, and they are particularly well suited to countries with hot temperatures. They're most commonly employed to treat sewage and industrial effluents, but they can also be used to treat municipal run-off or stormwater.
A single pond or a series of ponds may make up the system, with each pond serving a particular purpose in the pollution treatment process. If the effluent passes the appropriate effluent criteria, it can be returned to surface water or utilized as irrigation water after treatment.
What is the concept behind stabilization?
Organic matter can be found in sewage and a variety of industrial wastewaters. When wastewater is dumped into surface water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, without being treated, the organic matter in the wastewater serves as food for microorganisms dwelling in the surface waters. Organic matter is used by these organisms to generate energy for their development and reproduction. This is accomplished by respiration, in which organic matter is converted into carbon dioxide and water. These inert components do not pollute the water supply. As a result, this is sometimes referred to as "organic matter stabilization."
However, these creatures utilize oxygen for respiration, therefore, the oxygen concentration in the surface waters is reduced. This is one of the most serious water pollution issues, and it has the potential to harm surface water biota, especially fish.
These biological processes are reproduced in waste stabilization ponds before they occur in incoming surface water, causing pollution problems owing to oxygen consumption. The ponds accept wastewater and, as part of the treatment, stabilize the organic content within them through natural processes similar to those found in surface waters. This is how they came to be recognized as waste stabilization ponds.
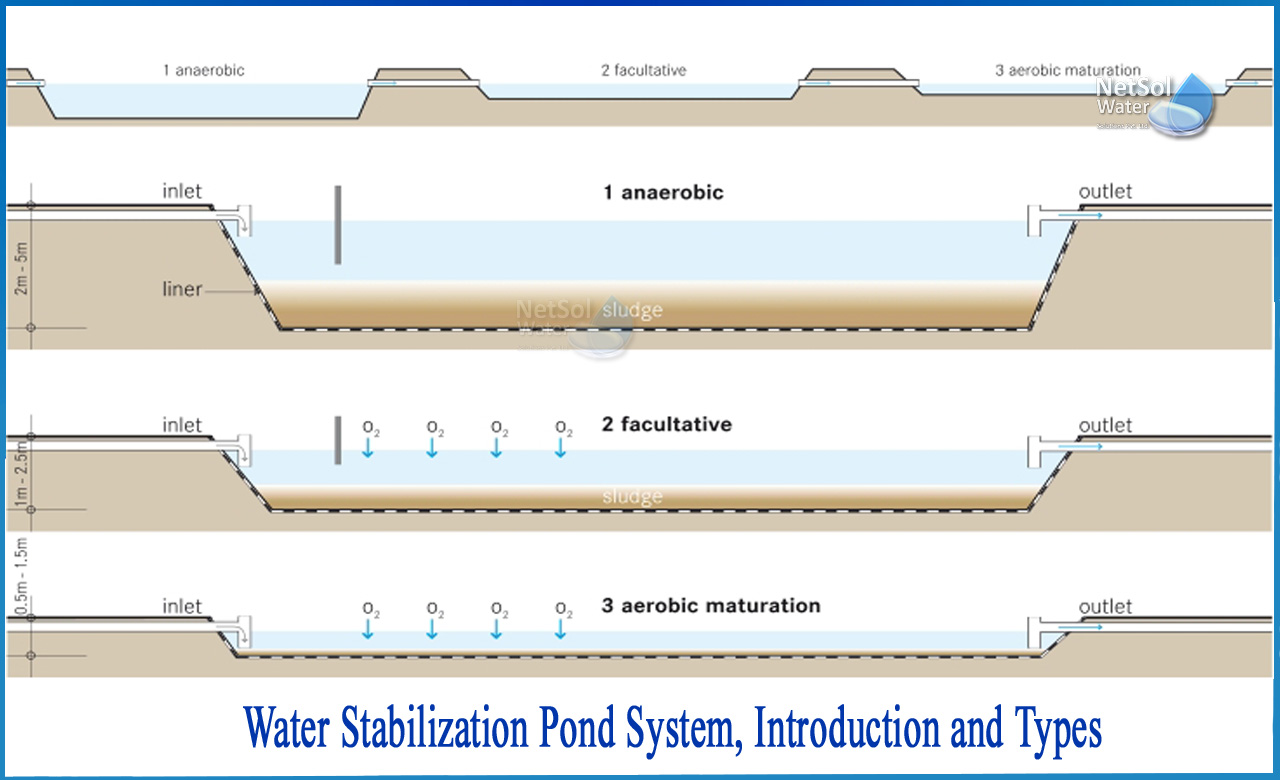
Types of Waste Stabilization Pond
1: Anaerobic ponds: Raw wastewater is pumped into an anaerobic pond. They have a smaller surface area and are also deeper than facultative ponds. The depth lowers the influence of photosynthesis on oxygen production, resulting in anaerobic conditions. These ponds may eliminate half to two-thirds of the influent BOD depending on loading and environmental circumstances. This lowers the amount of organic matter that must be transported to the facultative ponds, reducing their necessary size.
2: Facultative ponds:Primary facultative ponds are facultative stabilization ponds that take raw wastewater. Secondary facultative ponds are those that receive wastewater that has already been treated in anaerobic ponds. Other types of treatment methods, such as up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors, oxidation ditches, or aerated lagoons, may also use facultative stabilization ponds for treatment. Facultative ponds are shallower and have a considerably bigger surface area than anaerobic ponds. Since, the surface area permits air oxygen to dissolve and sunlight to reach the water, it is critical. This promotes photosynthetic activity, which results in the production of more oxygen.
3:Suitability and Applicability: Waste stabilization ponds are particularly effective in eliminating organic materials and, under some circumstances, harmful organisms. Their design requirements haven't changed much over time. Ponds are easy to design, construct, run, and maintain, which is critical in rural places and underdeveloped countries where sophisticated technology and highly qualified workers are few. In tiny communities, construction may be done by local contractors.
Waste stabilization ponds can treat almost any sort of wastewater and work effectively in almost any environment. Although, the intensity of sunshine and temperature are crucial variables in the efficiency of the elimination processes, they are particularly well-suited for tropical and subtropical nations.
Conclusion
Water Stabilization Ponds are the most extensively used treatment method in many countries and locations.As a result, they are one of the WHO-recommended procedures for treating wastewater for reuse in agriculture and aquaculture, owing to their efficacy in eliminating nematodes (worms) and helminth eggs.
In India, Netsol Water can provide water stabilization pond system for treating waste water to reuse it for agriculture and aqua culture purpose to their clients.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.