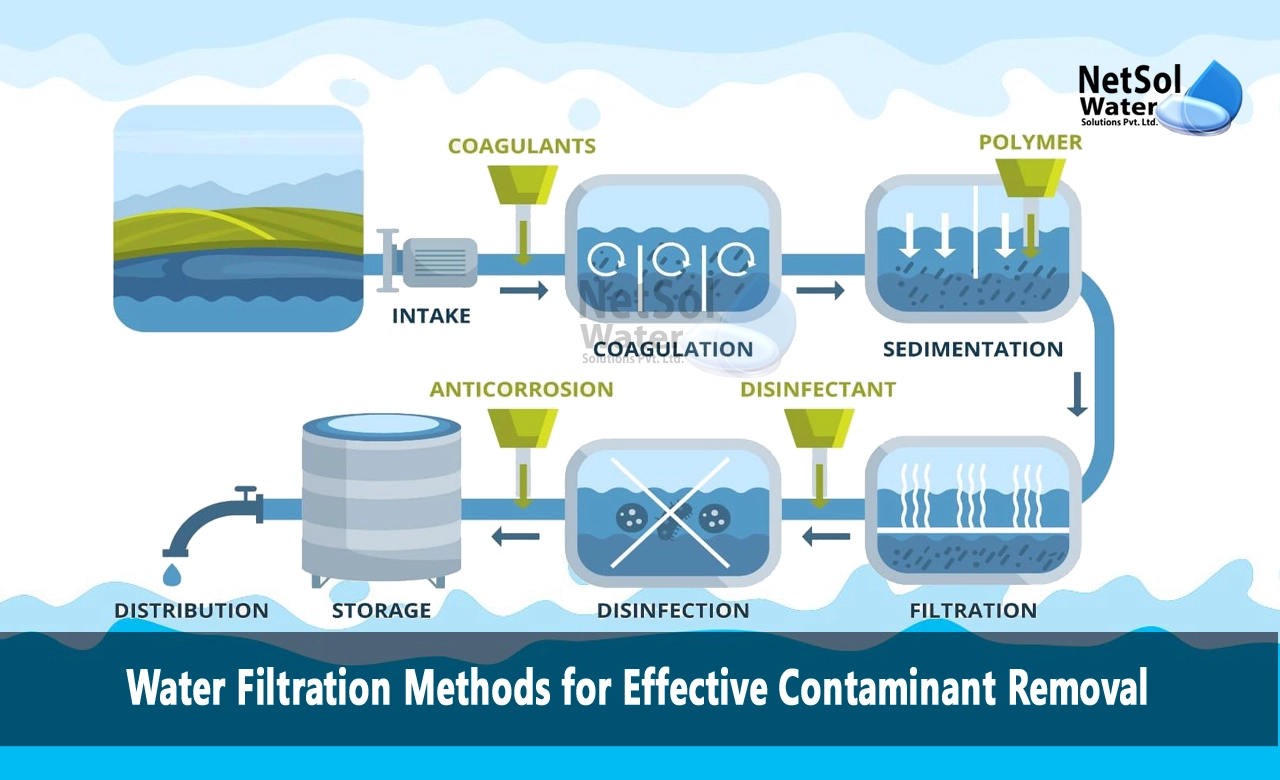
The Common Water Filtration Techniques for Removing Contaminant
Access to clean and safe drinking water is essential for human health and wellbeing. However, water sources can become contaminated with harmful pollutants and pathogens that need to be removed before consumption. Water filtration is the process of removing unwanted contaminants from water using physical, chemical or biological methods. Choosing the right filtration method depends on the types and levels of contaminants present. This blog discusses common water filtration techniques, their effectiveness in removing different contaminants, and recommendations for an integrated filtration system for optimum water treatment.
Water Filtration Methods for Effective Contaminant Removal
1- Sedimentation
Sedimentation is a physical process that removes suspended particles and colloids by gravity settling. The water passes through large tanks at low velocities, allowing particles like clay, silts and sand to sink to the bottom. This pretreatment step is important to filter out dirt and debris that can clog filtration equipment. Sedimentation effectively removes insoluble iron and manganese compounds. But it is less effective for dissolved salts or microscopic pathogens. Typical removal rates are 50-70% for turbidity and up to 95% for bulk particulate matter.
2- Coagulation and Flocculation
Fine particles and colloids often stay suspended in water. Chemical coagulation and flocculation help aggregate the particles for easier removal. Coagulants like aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride are added, which destabilize the particle’s charges and allow them to stick together. Flocculation enhances the process by gentle mixing, causing micro-flocs to collide and form larger floes that settle out faster. This treatment significantly improves sedimentation efficiency, removing up to 90% of fine particles, colloids and microorganisms.
3- Filtration
Filtration methods use physical barriers or media that trap particles and contaminants. Common filtration techniques include sand filters, activated carbon filters, and membrane filters.
Sand filters contain layers of gravel and sand. As water passes through the porous media, particles and microbes get caught in the spaces between sand grains. Typical sand filters can remove up to 99% of parasite cysts and 90% of suspended solids. Activated carbon filters contain highly adsorbent carbon material that can remove certain organic compounds, pesticides, herbicides, chlorine, and bad taste or odor. Granular activated carbon is used in beds similar to sand filters. Membrane filters have very fine nanopores that block particles, bacteria and even viruses. Reverse osmosis forces water through a semipermeable membrane, filtering out salts, metals and organics.
4- Disinfection and Oxidation
Disinfection kills disease-causing microorganisms like viruses, bacteria and protozoa. Common disinfectants include chlorine, chloramine, ozone and ultraviolet systems. Chlorination is widely used for its effectiveness and low cost, but can produce harmful byproducts. Ozone and UV disinfection are chemical-free alternatives. Oxidation removes or deactivates dissolved organic matter and inorganic compounds through chemical reaction. Ozone and hydrogen peroxide are strong oxidants that can reduce levels of iron, manganese, sulfides and persistent organic pollutants.
5- Recommended Integrated Filtration System
A multi-barrier filtration approach is recommended for drinking water to remove diverse contaminants. Pretreatment with sedimentation, coagulation and sand filters will remove particles. Activated carbon filters will adsorb organics and chlorine. Microporous membranes like reverse osmosis should follow to filter out heavy metals, microbes and salts. Finally, a disinfection stage using UV, ozone or chlorination can inactivate pathogens. This integrated system provides redundancy, optimizing the removal of particulate, microbial, inorganic and organic contaminants for safe, contaminant-free drinking water.
Conclusion
Effective water filtration is achieved by combining multiple techniques that target different contaminant types and size scales. Sand, activated carbon, membrane, disinfection and oxidation methods can collectively remove diverse sediments, particulates, pathogens, organics and dissolved inorganics. A well-designed, integrated treatment system is crucial to produce safe and clean drinking water free of harmful pollutants and infectious agents. Appropriate filtration ensures protection of human health against waterborne diseases.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and wastewater treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us know your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473 Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com