What is microfiltration?
Microfiltration is a filtration method that employs an analytical technique. To separate bacteria and suspended particles from a contaminated fluid, it can be passed over a membrane with microscale pores. This method of analysis is frequently used in conjunction with other separation techniques such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis. This results in a product stream that is free of unwanted impurities.
Microfiltration is typically used as a pre-treatment approach prior to separation techniques such as ultrafiltration. It can also be used as a post-treatment step for granular media filtering. Microfiltration pores typically range from 0.1 to 10 micrometres in size. The membranes employed in this filtration are specifically intended to keep sediments, algae, protozoa, and big bacteria from passing through.Furthermore, ionic components such as water molecules, monovalent species such as sodium and chloride ions, natural organic matter dissolved in the fluid, tiny colloids, and viruses tend to flow through these filters.
One must move the fluid through the membrane at a high velocity (approximately 1-3m/s) in this method of microfiltration. A low to moderate pressure parallel or tangential to the semi-permeable membrane can be used here. The membrane is usually in the form of a sheet or a tabular form. To allow the fluid to travel through the membrane filter, one can utilise a pump. This pump can be either vacuum or pressure driven.
What is ultrafiltration?
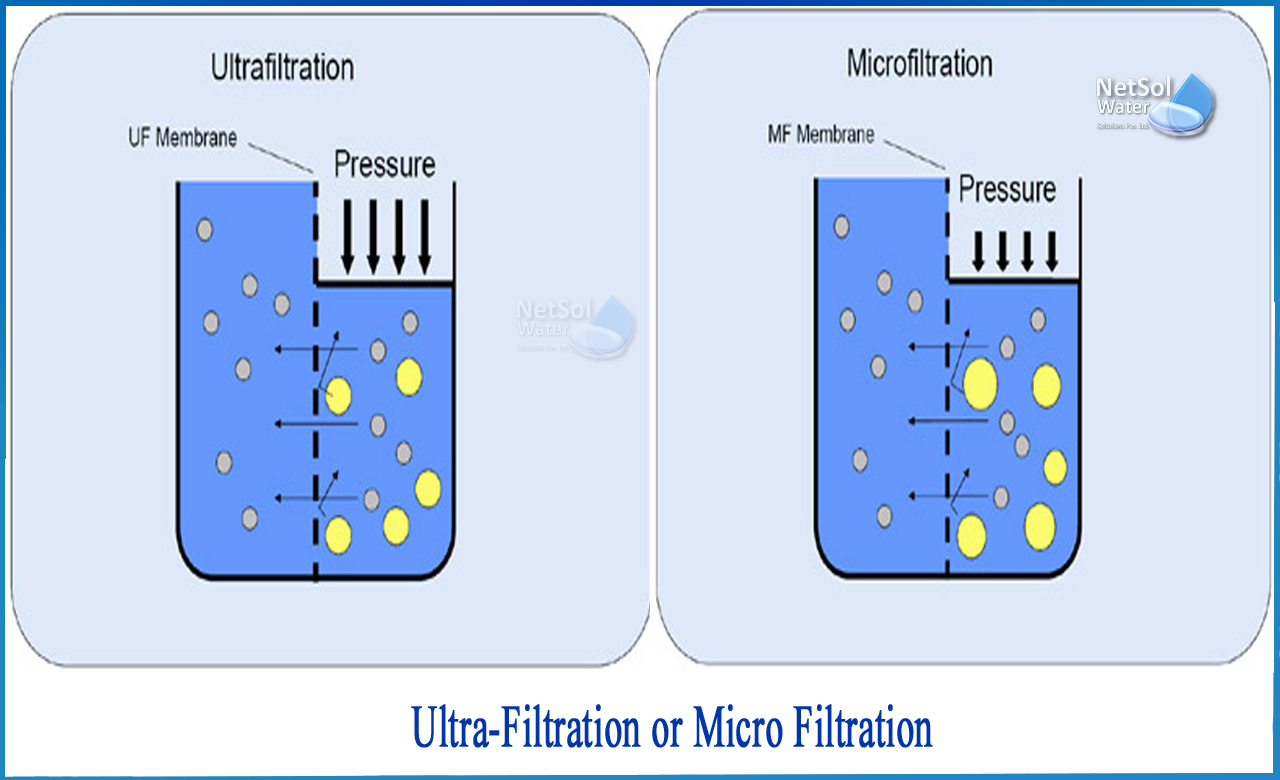
Ultrafiltration is an analytical procedure in which a semi-permeable membrane is separated using a force such as pressure or a concentration gradient. Suspended solids with a high molecular weight cannot flow through the membrane in this approach, but water and low molecular solutes can. The retentate is the residue that cannot pass through the membrane, whereas the permeate or filtrate is the fraction that can pass through the filter. This approach is beneficial in the purifying and concentrating processes.
Ultrafiltration and microfiltration are fundamentally similar in a way that they both perform separation based on the size exclusion or particle capture method. However, it differs from membrane gas separation in a way that the latter uses absorption techniques and diffusion to separate the gases.
In most cases, the pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane must be one-tenth of the particle size to be separated. As a result, it prevents big particles from passing through the membrane. It does, however, inhibit the entry of tiny particles through pores and their adsorption on the pore surface. Because they can block the entrance, we need to make basic cross-flow velocity modifications to disperse the particles.
What are the difference between ultrafiltration and micro filtration?
It all boils down to the pore size. On the basis of membrane separation scale, micro and ultrafiltration are rough as compared to Nano-filtration and reverse osmosis, but still finer than medium filtration.
Microfilter pores range from 0.1 to 10 microns, while ultrafiltration membrane pores range from 0.01 to 0.1 microns. The treatment process employed is determined by the size of the Nano-meter size range to be retained in the product water. The difference in pore size determines whether ultrafiltration or microfiltration is the optimal treatment method for a certain application.
The removal process
Based on the ranges of the pore size of these two separation technologies, here we provide a list of some of the smallest and minute pollutants that each technology is capable of eradicating or decreasing from raw water streams.
Microfiltration (MF) |
Ultrafiltration (UF) |
|
Algae |
Endotoxins |
|
Bacteria |
Plastics |
|
Pathogenic Protozoa |
Silica and Silt |
|
Sediment such as sand, clay & etc. |
Viruses |
Applications of both filtration techniques
In a wide range of industrial and commercial contexts, both microfiltration and UF purification are effective for water/wastewater treatment. This involves the processing of a wide range of finished goods. Only a few of the various uses for each membrane filter technique are listed below-
Microfiltration (MF) |
Ultrafiltration (UF) |
|
Cold sterilization of beverages and pharmaceuticals |
Removing pathogens of milk and medical applications |
|
Clarifying fruit juices, wine or beer |
Separating oil/water emulsions |
|
Separating bacteria from water |
Silt density index reduction for RO |
|
Petroleum refining |
Virus removal from water |
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.