What is sewage sludge?
Sewage sludge is a byproduct of wastewater treatment. It is made up of both organic and inorganic materials, as well as a high concentration of plant nutrients, organic chemicals, and pathogens. As a result, it is critical to properly treat such sludge in order to minimize its environmental impact.
To help you understand the treatment techniques and process requirements, here is a brief overview of the sludge treatment process:
Thickening typically results in sludge solids concentrations ranging from 3% to 5%, whereas the point at which sludge begins to have solid properties is between 15% and 20% solids. Thickening also implies that the process is gravitational, with solids being compacted by the difference in particle and fluid densities.
Sludge thickening and dewatering operations (depending on the process used) rely heavily on sludge conditioning to function properly. Sludge conditioning influences the solids concentration and solids capture efficiency of thickened or dewatered sludge.
Sludges have several characteristics, including industrial-derived constituents, that may jeopardize attempts at solid-liquid separation. The presence of colloidal particles increases sludge specific resistance and has a negative impact on sedimentation processes. Most sewage sludges have a net negative charge, which causes the particles to repel each other and thus resist agglomeration into larger particles. Sludge particles contain bound water, which results in low cake solids after solid-liquid separation if retained. Sludge conditioning operations aim to improve the efficiency of solid-liquid separation processes by modifying one or more of the aforementioned sludge characteristics.
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment Process
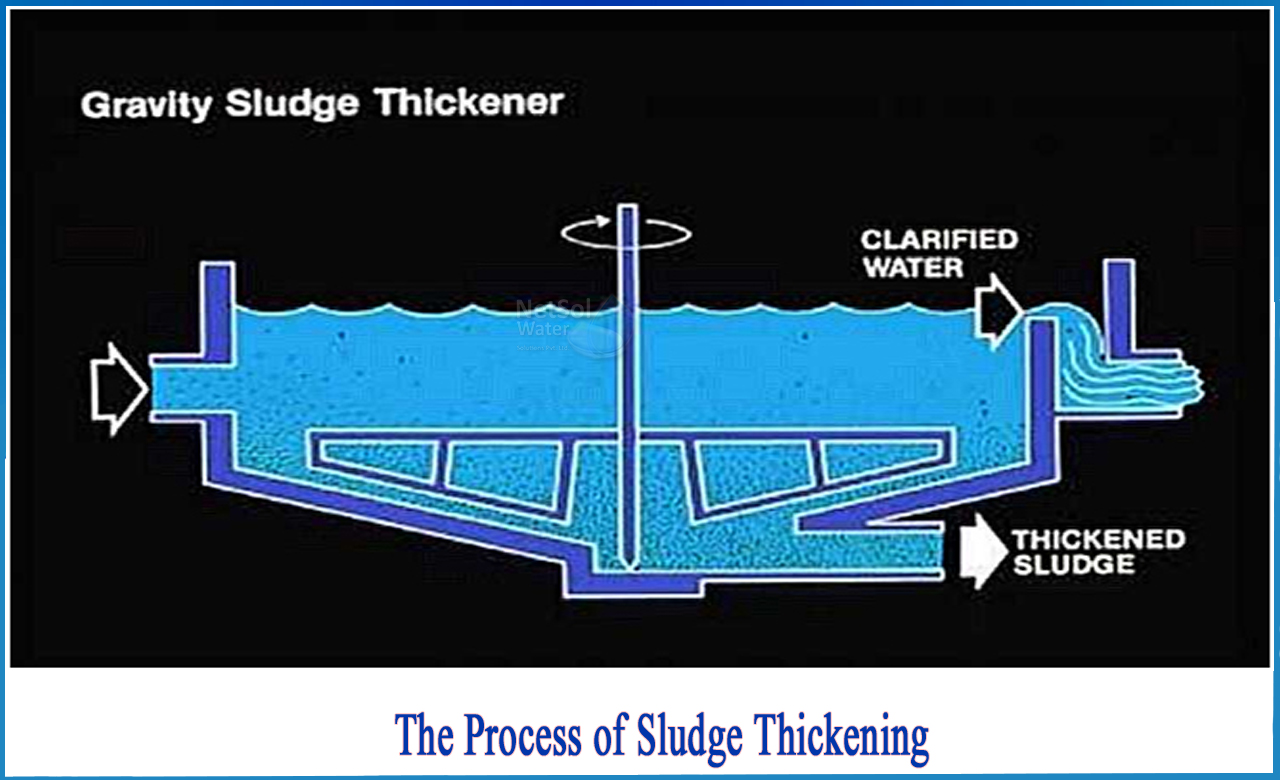
Step 1 – Sludge Thickening
Thickening is the first step in the sewage sludge treatment process. The sewage sludge is thickened in a gravity thickener in this step to reduce its overall volume, allowing for easier handling of the sludge. Dissolved air flotation is another option for effectively thickening sludge by using air bubbles to allow the solid mass to float to the top.
Step 2 - Sludge Digestion
After collecting all of the solids from the sewage sludge, the sludge digestion process begins. This is a biological process that decomposes the organic solids in the sludge into stable substances. This process also helps to reduce the total mass of solids while destroying any pathogens present, allowing for easy dewatering. The sludge digestion process is divided into two stages.
The dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank in the first stage to allow anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria. These bacteria hydrolyze the large proteins and lipid molecules in the sludge, breaking them down into smaller water-soluble molecules that they then ferment into various fatty acids.
The sludge then flows into the second tank, where it is converted by other bacteria into a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane, which is collected and reused to power the digestion tank and generate electricity (depending on the quantity retrieved).
Step 3 - Dewatering
Following the recovery of useful gases and other byproducts, the remaining sludge is dewatered before final disposal. In most cases, despite its solidified state, dewatered sludge contains a significant amount of water, up to 70%. As a result, it is critical to dry and dewater the sludge beforehand. While sludge-drying beds are the most common method for carrying out this process, they are extremely time-consuming and may take weeks to complete. Waste management plans are also utilizing solid-liquid separation devices to carry out this process in order to speed up these processes.
In fact, centrifugation is quickly becoming one of the most popular methods of sludge dewatering. By passing the sludge through a centrifuge, it is possible to recover all of the water and handle the solid waste in less time and at a lower cost. The rotary drum vacuum filter and the belt filter press are two other options.
4th Step – Disposal
Depending on its chemical composition, once the sludge has been effectively dewatered, it can be buried underground in a sanitary landfill or used as a fertilizer. If the sludge is too toxic to be reused or buried, it can simply be incinerated and converted into ash.While sewage sludge is typically treated using a standard plan of action, it is critical to consider factors such as the origin of the sewage, the treatment process used to reduce the sewage to sludge, and the possible byproducts that can be retrieved from it for further use before deciding on a sludge treatment plan. This will not only help you optimize your overall output, but it will also help you save money by salvaging useful materials for secondary use prior to final disposal.
For more information, contact Netsol Water!
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.