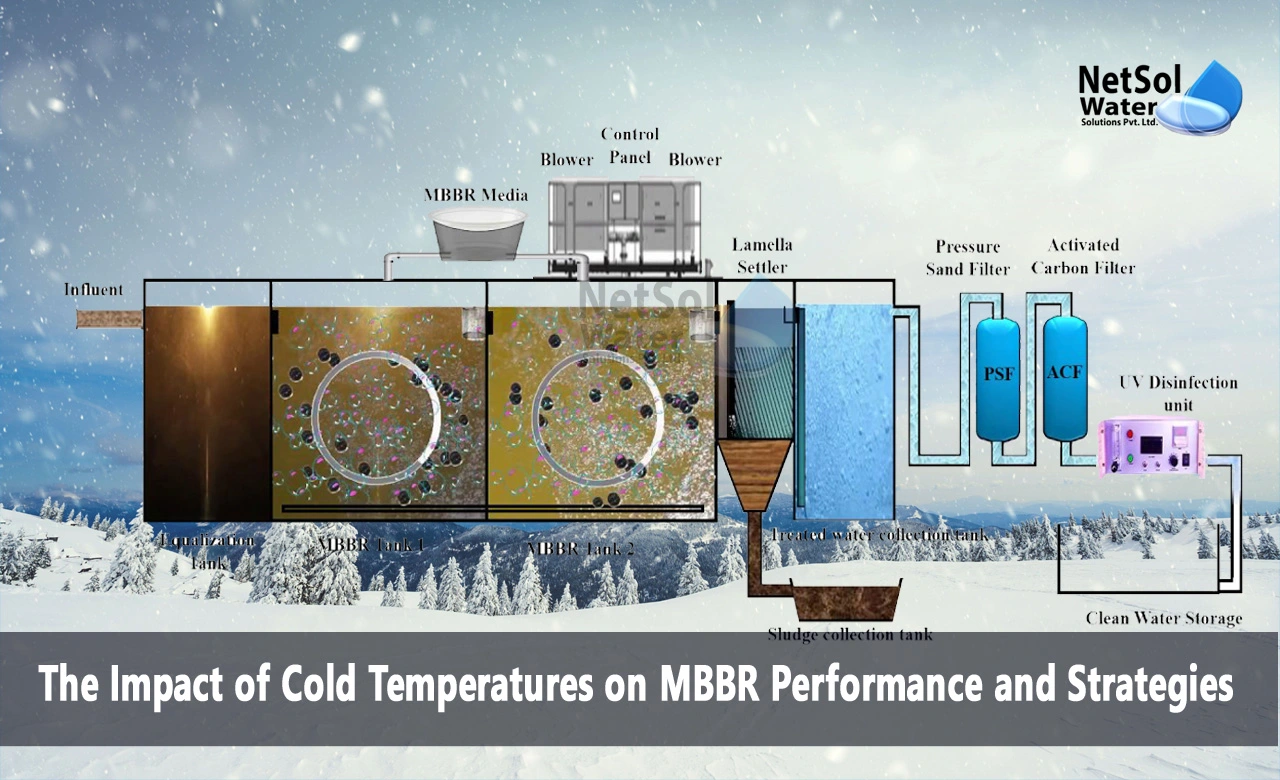
What is the Impact of Cold Temperatures on MBBR Performance?
A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) is a wastewater treatment process that uses small plastic carrier elements to grow biofilm. The biofilm contains microorganisms that remove organic matter and nutrients from wastewater. MBBRs are effective at removing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and ammonia even in cold temperatures. However, precautions need to be taken for smooth operation during winter. Now discusses the impact of cold temperatures on MBBR performance and strategies for successful cold weather operation.
Impact of Cold Temperatures
The activity and growth rate of bacteria in the biofilm reduce significantly below 15°C. The viscosity and density of water increase at low temperatures, resulting in poorer mixing and lower dissolved oxygen levels. Cold influent can rapidly cool the MBBR, reducing biofilm activity. If the reactor freezes, the plastic carriers can be damaged. Cold temperatures also result in lower inorganic nitrogen removal rates. However, BOD removal can continue at cold temperatures if sufficient biofilm is present. Overall, the treatment efficiency of MBBRs can reduce by 50-60% during winter.
Strategies for Cold Weather Operation
Several strategies can help counteract the negative impact of cold temperatures on MBBRs:
1. Insulation: Insulating MBBR tanks using polyurethane foams helps maintain warm temperatures inside. This allows higher treatment efficiency even when influent or ambient temperatures are very low.
2. Supplemental Heating: Heating a section of the influent before it enters the tank can keep the reactor temperature above 10°C. Electric immersion heaters or heat exchangers using steam, hot water, or engine jacket water can be used.
3. Adjusting HRT and Volume: Increasing hydraulic retention time and tank volume provides more treatment time for the biomass to work effectively in the cold.
4. Mixing: Using more mixers per unit volume improves heat distribution and prevents stagnant zones developing.
5. Supplemental Aeration: Adding more air or pure oxygen increases mixing and provides more oxygen to the biofilm.
6. Nutrient Addition: Spiking phosphorus or nitrogen compounds like ammonia and urea provides nutrients to maintain biofilm growth.
7. Protecting Outdoors Piping: Insulating and heating exposed pipes ensures wastewater doesn’t freeze before entering the reactor.
Conclusion
The cold climate negatively impacts the treatment efficiency of MBBR systems. Key strategies like insulation, supplemental heating, adjusting design factors, and improving mixing/aeration should be used to ensure smooth and steady operation during winters. With proper cold weather preparation, MBBRs can effectively treat wastewater even at low temperatures. The plastic carrier elements also provide protection to the biomass against freezing. By implementing suitable measures, MBBRs can be relied on for biological treatment throughout the year.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us know your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473 Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com