What are the types of ASP?
Aeration is an element of the secondary treatment process in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. In secondary treatment, activated sludge is the most prevalent method.
Aeration is a sludge-activated technique in which microbial growth in wastewater is encouraged. The microorganisms then feed on organic matter, generating flocs which are easy to separate. The bacteria that create the "active sludge" flocs are constantly recirculated back to the aeration basin after settling in a separate settling tank, boosting decomposition rates.
Water-fall aeration using spray nozzles is the most frequent type of aeration in industrial settings. Air is diffused into a receiving vessel holding counter-current running water in the air diffusion technique of aeration. Aeration is used to enhance the quality and minimize contamination in liquids, soils, and foods. In this process, soluble iron and manganese are oxidized to insoluble precipitates. Aeration can also help with bacteria management by reducing ammonia and hydrogen sulphide levels.
Partial list on Types of APSs: Step aeration and completely mixed aeration
What is Stepped aeration?
The procedure is known as step aeration when sewage is introduced at many points along the aeration channel. This will lighten the burden on the sludge that is returned. The aeration in the tank is consistent.
In the design, F/M ratio of 0.2 to 0.4 kg BOD/kg VSS. d and a volumetric loading rate of 0.6 to 1.0 kg BOD/m3.d are used. The mean cell residence time should be 5 to 15 days, the MLSS should be 2000 to 3500 mg/L, the HRT should be 3 to 5 hours, and the sludge recirculation ratio should be 0.25 to 0.75.
The load on the returned sludge changes if sewage is added to the returned sludge at more than two sites along the aeration channel. The B.O.D. of mixed liquor is varied at different times. Tapered aeration (managing dispersed air) or reducing the load on oxidizing returning sludge can also help with this. The design loading rates in step aeration are somewhat greater than in traditional ASP. It performs better because the organic load on the return sludge is reduced.
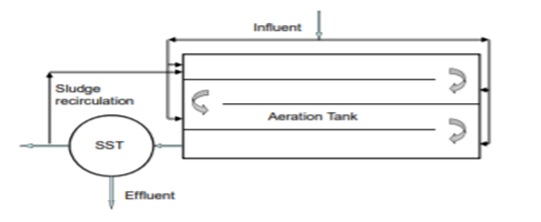
Step aeration activated sludge process
What is completely mixed aeration?
A totally mixed flow regime is employed in this type of aeration tank. The wastewater is equally spread, together with the return sludge, from one side of the tank to the other, and the effluent is collected at the other.
This type of ASP is designed with F/M ratio of 0.2 to 0.6 kg BOD/kg VSS.d and a volumetric loading of 0.8 to 2.0 kg BOD/m3.d. In the aeration tank, higher mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS) on the order of 3000 to 6000 mg/L are maintained, with a typical cell residence time of 5 to 15 days. Sewage treatment necessitates a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 3 to 5 hours.For the treatment of industrial wastewater with greater BOD concentrations, a higher HRT may be necessary. The sludge recirculation ratio usually falls between 0.25 and 1.0.
This type of ASP is better able to manage changes in organic matter concentrations, and its performance will not be adversely impacted if a harmful substance arrives in the influent in a minor concentration for a short period of time. Completely mixed ASP is used in businesses where variation in wastewater properties is typical because to this feature.
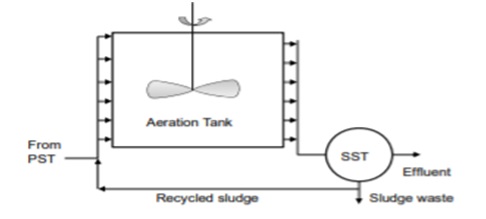
Complete mixed activated sludge process
Netsol can help!
Netsol Water is the proud manufacturer of the wastewater treatment plants in addition to the raw water treatment plants. We provide all the processing units according to the requirements of customers. In addition to this, if you are curious to know more about the processes involved in the units, you can feel free to call Netsol.



