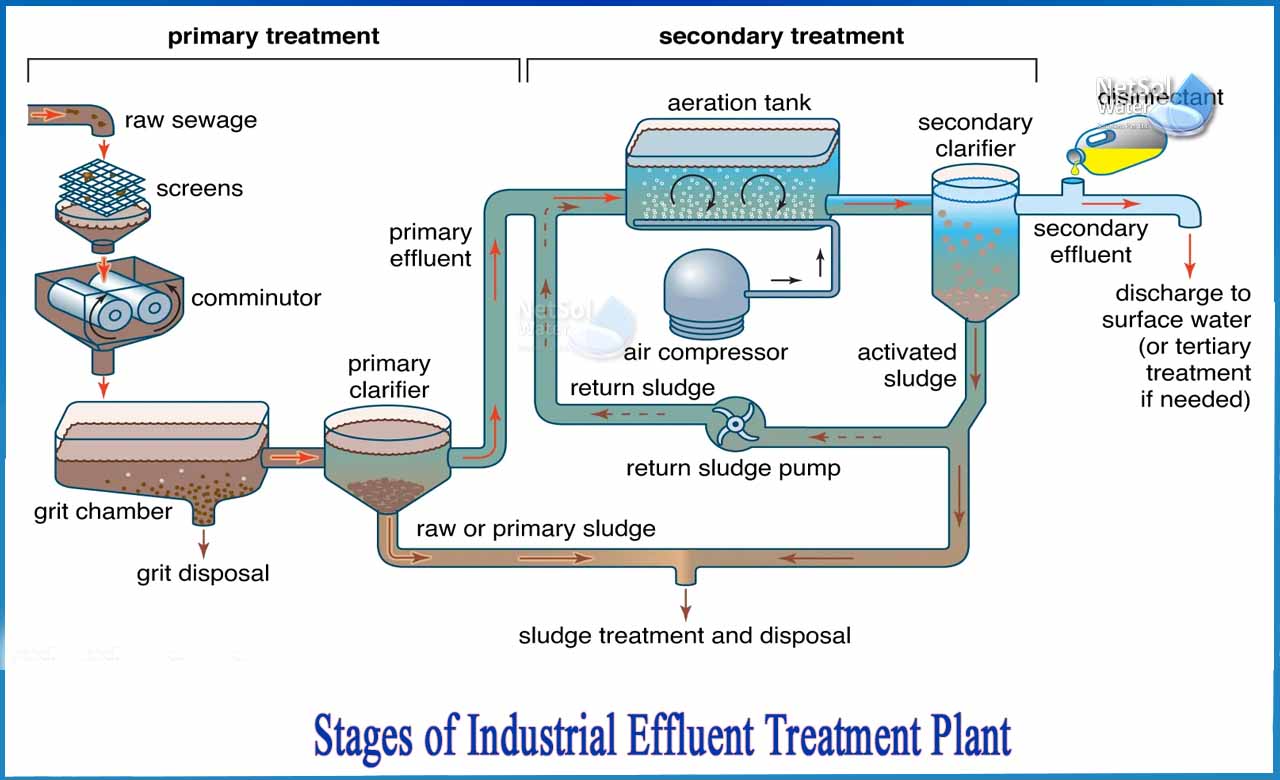
How many Stages in Industrial ETP Plants?
The following stages are involved in the industrial effluent treatment plant process:
1: Preliminary treatment
The goal of this step is to physically separate large contaminants. Cloth, paper, plastics, wood logs, and so on. This level/process includes the following:
· Screening is the first unit operation in a waste water treatment plant. A screen is a device with uniform openings that serves the purpose of removing large floating solids.
· Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process that removes suspended solids from water using gravity.
· Grit Chamber: The wastewater that flows into the grit chamber removes the dense inorganic solids that have made their way into the sewers, such as gravel, metal fragments, and sand. Grit removal can help to prevent pump damage and operational difficulties.
· Clari?fiers are tanks designed with mechanical means to continuously remove solids deposited by sedimentation prior to biological treatment.
2: Primary treatment
The primary goal of this treatment is to remove floating and settleable materials such as suspended solids and organic matter. Both physical and chemical methods are used in this treatment. It includes the following:
· Flocculation: This is a physical process that does not involve charge neutralization. It entails aggregating destabilized particles into large aggregates so that they can be easily separated from the water.
· gulation is a process in which coagulants are added to a liquid in order to rapidly settle minute solid particles into a larger mass. It allows for particle removal via sedimentation and filtration.
· Neutralization: The main goal of this process is to keep the pH in the range of 6-9 to meet the needs of the various processing units in the ETP system.
3: Secondary or biological treatment
The goal of this treatment is to treat the effluent from primary treatment further to remove suspended solids and residual organics. Biological and chemical processes are involved in this step.
· The activated sludge process uses air and a biological floc made up of bacteria to treat industrial waste water.
· Aerated Lagoons: A treatment pond with artificial aeration to promote waste water biological oxidation.
· Trickling filters, also known as sprinkling filters, are commonly used in the biological treatment of domestic sewage and industrial waste water.
· Rotating Biological Contactor: This method involves exposing wastewater to a biological medium in order to remove pollutants before discharging the treated wastewater into the environment.
4: Tertiary/advanced/disinfection treatment
The goal of tertiary treatment is to provide a final treatment stage to improve effluent quality before it is reused, recycled, or discharged into the environment.
· Chemical coagulation and sedimentation are used to improve solids removal from effluent after primary and secondary treatment.
· Filtration: To ensure high quality water, the clarified wastewater is first passed through the adjacent filtration plant, which contains large filter blocks.
· Pressure is used to force effluent through a membrane that retains contaminants on one side while allowing clean water to pass through on the other.
· UV Disinfection: It is thought to be an excellent disinfectant for industrial waste water. By ensuring water quality, it leaves no residual disinfectant in the water. It generates no disinfection byproducts.
For design, manufacture and installation of ETP’s, STP’s and other water and waste water related products, contact Netsol Water.