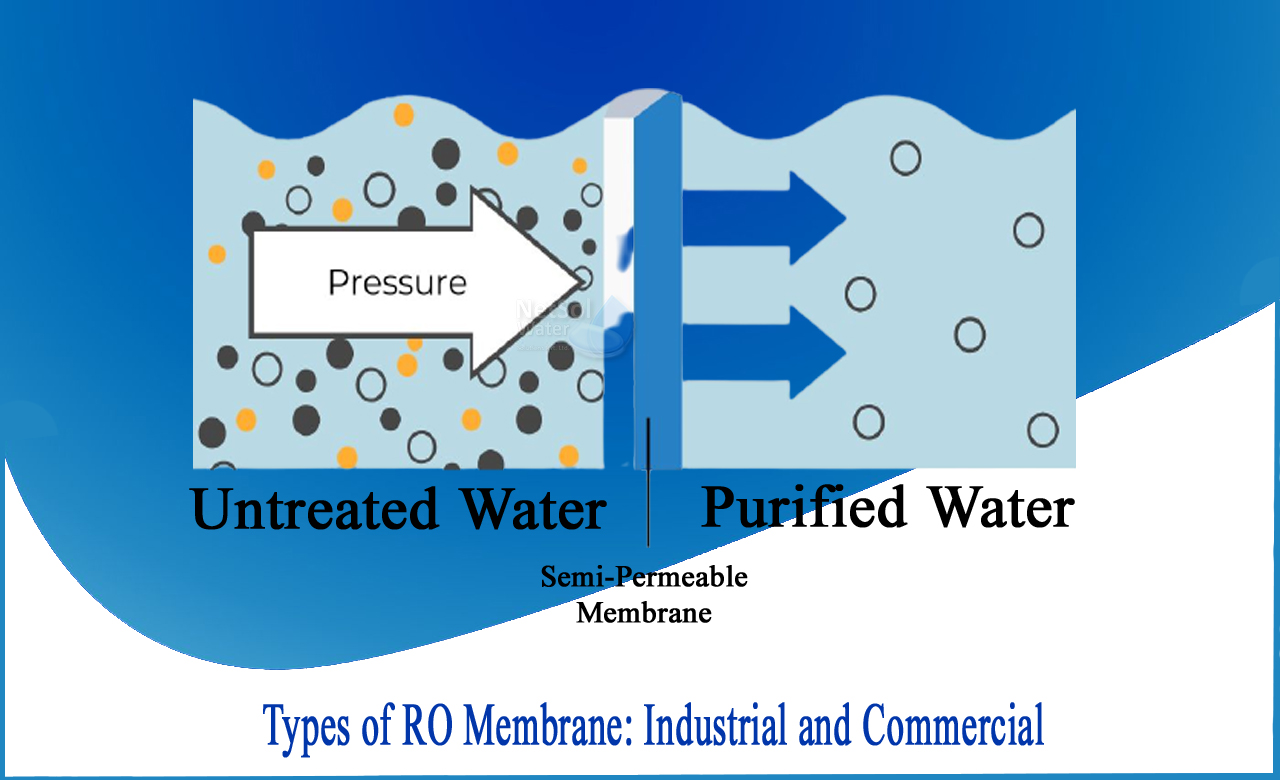
"Reverse osmosis or RO is a form of filtration that employs a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows only pure water to pass through while filtering bigger molecules or contaminants."Pressure is supplied to overcome a colligative property and osmotic pressure that is directed by a thermodynamic parameter and a chemical difference of a solvent in reverse osmosis.
It occurs when a pure solvent is allowed to follow one end of a membrane, permitting a solute to remain on the membrane's permissible side.The pressure-driven membrane method of reverse osmosis (RO) is used to purify water. Water travels through the membranes more easily than the impurities being removed in all pressure-driven membrane processes.By lowering the conductivity of water (TDS) and eliminating chloride ions and/or sulphate, reverse osmosis can be used to control corrosion. However, it is frequently required to mix some filtered tap water with RO permeate to guarantee that the water delivered to equipment is not overly pure. Blending, for example, is frequently employed to achieve a water TDS criterion set by an equipment maker (coffee, espresso, steamer, etc.).
WHAT IS TDS?
TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) is a metric that measures the total amount of inorganic and organic compounds dissolved in water. These components could be suspended in molecular, ionized, or micro-granular form. Calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, bicarbonate, chloride, and sulphate are examples of inorganic compounds that typically contribute to TDS measurements. Organic chemicals that may contribute to TDS can come from a variety of sources, including chemical application on land, industrial chemical releases into the environment, vegetable matter, and/or animal matter. TDS is measured in a laboratory by weighing the mass of solids left after water has been entirely evaporated.
WORKING OF REVERSE OSMOSIS
Diffusion is a process through which molecules move from a location of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. There is a net movement, which means that more molecules are moving in one direction than in the other. Water molecules and a concentration gradient flow through a semipermeable membrane in osmosis, allowing water to pass through but blocking the passage of ions and other bigger molecules such as sodium, chlorine, bacteria, glucose, and so on.
The technique or technology used to remove ions, mineral compounds, and other pollutants from drinking water is known as reverse osmosis. Greater pressure is exerted in this procedure, pushing the water to pass through the semipermeable membrane in the opposite direction of natural osmosis.
Consider a semipermeable barrier that separates freshwater from concentrated aqueous solution. Freshwater crosses the semipermeable membrane via natural osmosis and dilutes the concentrated solution.Pressure is exerted to the concentrated aqueous solution in reverse osmosis, forcing the water molecules to cross the membrane and into freshwater.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OSMOSIS AND REVERSE OSMOSIS
-The main distinction between osmosis and reverse osmosis is that osmosis is a natural process in which water molecules pass along a concentration gradient, whereas reverse osmosis is a water purification procedure in which water molecules pass across a semi-permeable membrane against the concentration gradient.
-The idea of osmosis is important because it aids in the maintenance of osmotic pressure within animal and plant cells. As a result of the difference in solute concentration between the two sides, osmosis is defined as the net transfer of water from one side of a semi-permeable membrane to the other.Water diffuses over a selectively semi-permeable membrane, which enables water to pass but prevents the passage of other molecules that are either big or ions. Furthermore, there is a related notion of osmosis known as reverse osmosis, which is used in the water purification process to make water pure.