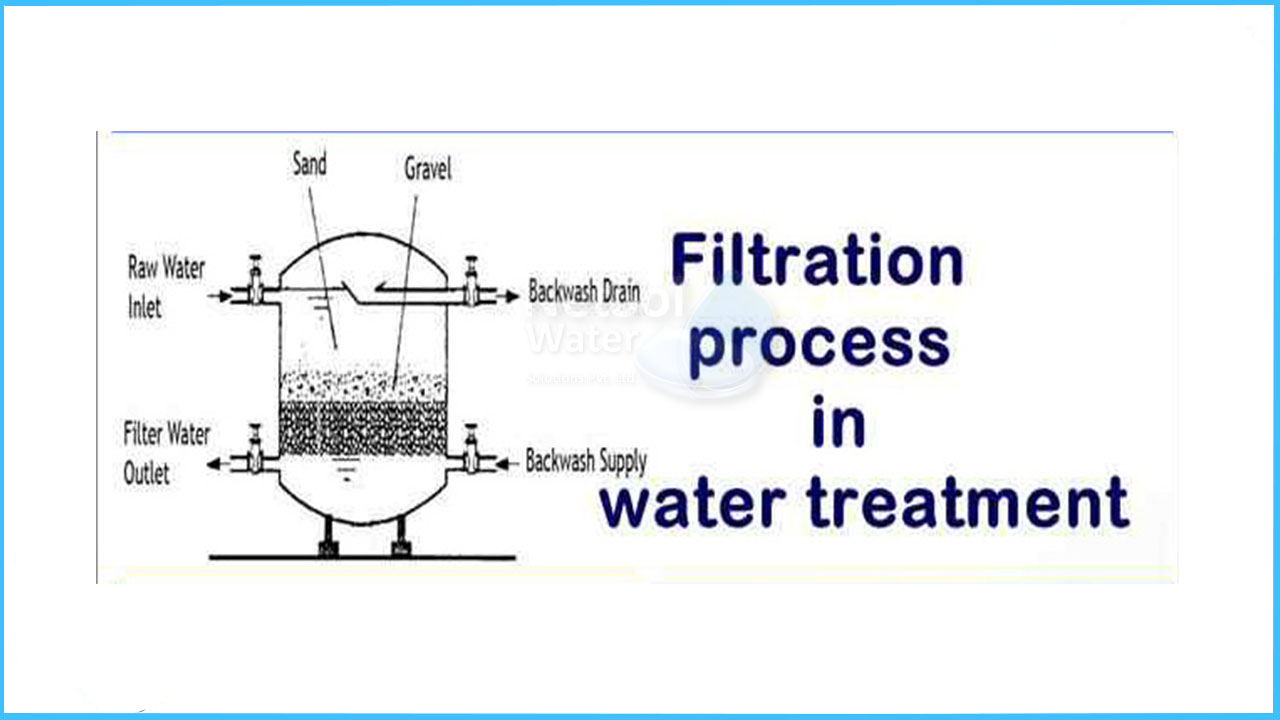
FILTRATION PROCESSES
Filtration is a process that removes particles from suspension in water. Removal takes place by a number of mechanisms that include straining, flocculation, sedimentation and surface capture. Filters can be categorised by the main method of capture, i.e. exclusion of particles at the surface of the filter media i.e. straining, or deposition within the media i.e. in-depth filtration.
Filters, as commonly understood in water treatment generally consist of a medium within which it is intended most of the particles in the water will be captured. Such filters might be manufactured as disposable cartridge filters, which can be suitable for domestic (i.e. point-of-use treatment) and small-scale industrial applications. Larger forms of cartridge filters exist which can be cleaned.
Granular media filters are used in either of two distinct ways which are commonly called slow-sand filtration and rapid gravity or pressure filtration. When the filters are used as the final means of particle removal from the water, then the filters may need to be preceded by another stage of solid-liquid separation (clarification) such as sedimentation (Sedimentation Processes), dissolved-air-flotation (Flotation Processes) or possibly a preliminary stage of filtration
Other processes take place in vessels similar to those used for granular media filtration, and in some respects the processes do have similarities with filtration but filtration is not their sole or primary purpose.
IMPORTANCE OF FILITRATION IN INDUSTRY
- 1. Contaminants that are present during the manufacturing process can be extremely damaging to equipment. One of the most important roles of industrial filtration is to capture and remove these contaminants and contain them for proper removal and disposal.
- 2. Air and gas filtration must be thorough and measurable to ensure that harmful or undesirable contaminants are removed. The outputs for many processes in industrial manufacturing must be clean and pure; any slight variations in the contaminant level could result in unusable products.
- 3. Industrial filtration is crucial in industrial manufacturing applications including, pneumatic conveying, additive manufacturing, and landfill gas collection. It helps to keep the air and gas free from contaminants during operations, helping to ensure purity of the process outputs.
- 4. Many vacuum manufacturing processes require a highly efficient separation of solids, liquids and vapours. This is not only to keep the systems functioning properly, but also to capture valuable process outputs and minimize waste. This can be accomplished using specialty filtration and separation products/systems that separate product from an air/gas stream under vacuum conditions.
COMMON INDUSTRIAL FILTRATION APPLICATIONS
While nearly all industries can benefit from filtration systems, below are some of the most common applications:
- Medical, pharmaceutical, and dental vacuum and compressed air systems.
- Oil mist elimination from the exhaust or discharge of vacuum pumps.
- Oil mist elimination from the vents of rotating equipment: turbines, compressors, lube oil systems, coupling guards and gearboxes
- Crankcase ventilation: Protect the surrounding environment by capturing oil mist vapours created by reciprocating engines and gen-sets-
- Industrial Processes using Vacuum Pumps and Blowers: Pneumatic conveying, wastewater treatment, steel degassing, chemical vapour deposition (CVD), CNC routing.
- Hydraulic tank breathers