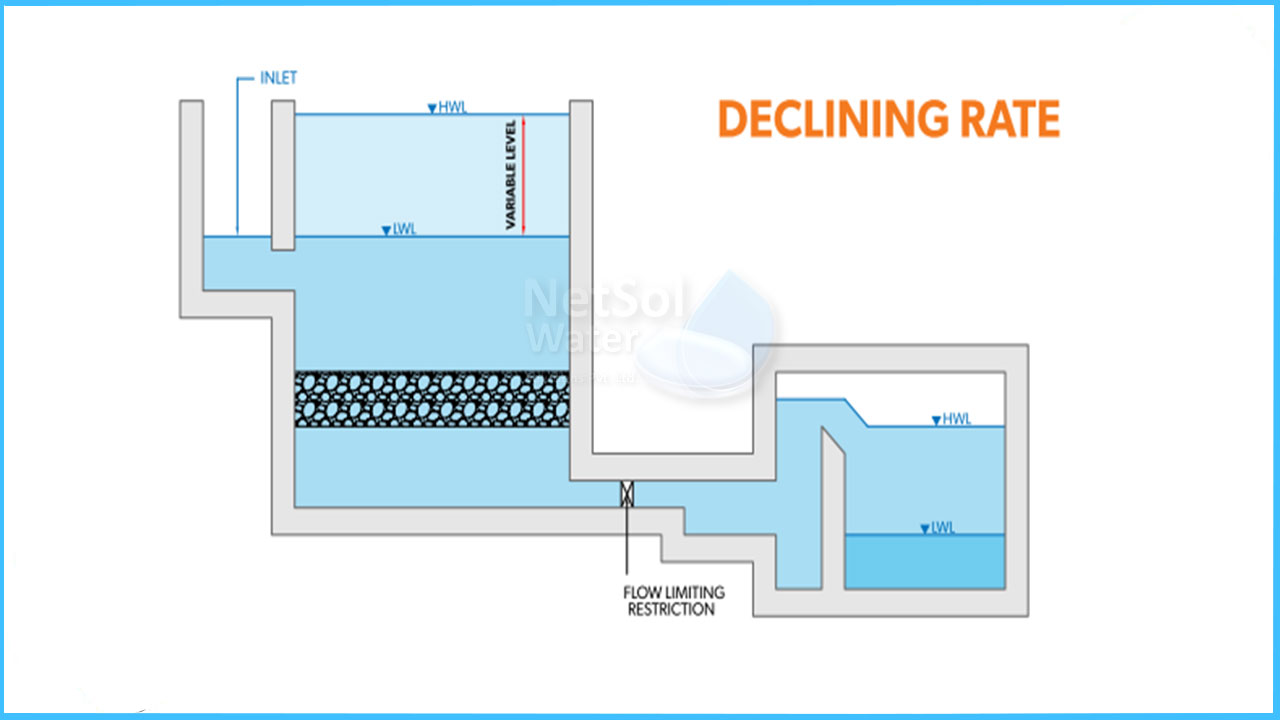
Operational Control System for Gravity Filter - Declining Flow Type
One of the simplest and oldest ways of filter management is descending-rate filtration. It is employed with a large number of filter cells - the more cells, the better the performance. The filter medium is the most important part of the system. A flow restriction can be placed in the effluent pipe or, in some situations, on the influent side to limit the maximum rate of filtration through a cell. An orifice plate could be the flow restriction.
A two-position control valve, which is partially closed immediately after a backwash to restrict flow of the cleanest cell, can also be used.To limit the maximum rate of filtration through a cell, a flow-restriction device, such as an orifice plate or partially opened valve, is frequently fitted in the effluent line. This flow limitation is used to control the amount of initial flow that passes through the filter - it's effectively a filter speed limit.
Pros
- Decreasing-rate systems are simple to operate since they only require a few control components.
- Filtration with a decreasing rate makes better use of the filter media depth. The greater filtration rate sends particulates deeper into the bed when the media is cleanest. Filtration rate reduces as dirt head loss increases to reduce shearing forces within the bed.
- Because the differences are spread out among more filter cells through the common influent system, the system manages fluctuating influent flow rates better than most other control systems.
Cons
- If not restricted or limited to a maximum rate, there is a risk of turbidity breakthrough in clean cells. Most regulatory authorities demand the use of a maximum filtration rate, so this can be a problem.
- When there are several filter cells present, the development of individual filter cell head loss is not visible. The fact that one unit may have more head loss than another is hidden by the influent flow, which is shared by all of the cells. Fortunately, today's electrical monitoring systems can easily measure cell run duration in order to properly sequence backwash events.