What is Onsite sanitation, Bore Hole and Dug well Latrine?
There may be insufficient population and infrastructure in rural areas and on the outskirts of cities to support the sewer system and central treatment plant. As a result, on-site sanitation is required to maintain sanitary living conditions.
Satisfactory wastewater management techniques should ensure that: water bodies used for water supplies are not contaminated; flies and vermin do not have access to excreta; surface water bodies are not polluted by runoff; and nuisance conditions such as odour are minimized for environmentally safe onsite sanitation.
Septic tanks and surface percolation are acceptable sites sanitation techniques, depending on the conditions; prolonged aeration, alone or in conjunction with a septic tank; and pit privies are still utilized in some areas without running water.
Onsite sanitation
On-site sanitation is commonly referred to as a "home latrine," but it can also refer to facilities used by numerous households living on the same property. On-site sanitation refers to facilities that are self-contained inside the site, as opposed to sewerage, which involves removing sewage from the site.
Some industry specialists believe that on-site sanitation is best suited for rural regions and is inappropriate in metropolitan settings. In actuality, given the continuing development of urban populations and the significant prevalence of low-income persons in slums and periurban regions, delivering sewers to all urban residents is impossible. On-site/plot systems that are well-maintained and developed are a viable alternative to sewage networks.
Bore-hole latrine
A bored-hole latrine is a hole in the ground that receives and stores excrement. Pit is a hole dug in a dirt auger, either manually or automatically, comparable to a basic pit latrine (Figure below). It works best on soil that is stable, porous, and devoid of stones, with groundwater that is deep under the surface. Bore-hole latrines, on the other hand, pose sanitary and health risks, and specialist advice should be obtained before they are built.
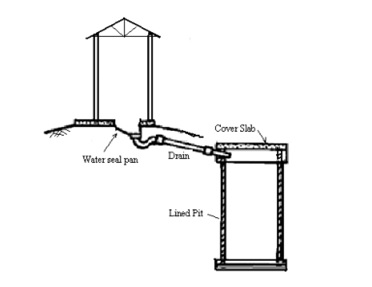
It is made up of a pit and a one-seat toilet box. Borehole latrines feature an augured hole rather than an excavated pit and may be lowered to a depth of 10 meters or more, however most are 4 to 6 meters deep. In regions where the soil is strong, stable, and devoid of boulders or big stones, augured holes of 300-500 mm in diameter can be excavated swiftly by hand or machine. While a tiny diameter makes it easier to drill, the pit's life is limited. For example, a 300-mm diameter hole that is 5 m deep will last roughly two years for a family of five.
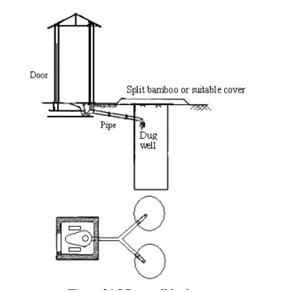
Dug well Latrine
To absorb liquid waste, a 75 cm x 75 cm x 360 cm hole is constructed in a dug well privy, which is lined with honey comb brickwork or stonework (Figure below). Human excreta from un- sewered areas are collected in dug well type latrines under the conservancy system.
If you need help designing an efficient onsite sewage treatment system, contact Netsol Water. We can help you with design calculations, budgetary expenses, preliminary layouts, and a lifetime cost analysis.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.



