Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) technology is a widely used method for the biological treatment of the wastewater. This technology combines biological treatment with membrane filtration, resulting in high-quality effluent.
Here, we will discuss the percentage of BOD and COD removal that can be achieved using MBR technology, as well as the different processes in this technology that contribute to the reduction of BOD and COD.
Percentage of BOD and COD removal in MBR technology:
MBR technology can achieve significant reductions in both BOD and COD levels in wastewater. The percentage of removal depends on several factors, such as:
· The characteristics of the wastewater,
· The design of the MBR system, and
· The operating conditions.
Typically, MBR technology can achieve a BOD removal of up to 99% and a COD removal of up to 90%. However, these percentages can vary depending on the factors which were mentioned above.
Difference between MBR, MBBR and FBR: An Overview
The MBR process is extremely sensitive, cannot handle overloading, and has very high operation and maintenance expenses when compared to other biological processes like Fixed Bed Bio Reactor (FBBR). Chemicals are also necessary for cleaning membranes.
A membrane bioreactor (MBR) plant makes use of physical separation and biological disintegration. The upstream apparatus includes a screen for removing grit and oil in order to prevent the membrane from clogging.
In comparison to FBBR and MBBR systems, an MBR system (Membrane Bio Reactor) is a filtering system that has a high concentration of bacteria (held within the membrane). Even microorganisms can be isolated from the water depending on the membrane's pore diameter.
Figure 1 shows the comparison in process between MBR and Activated Sludge Process (ASP).
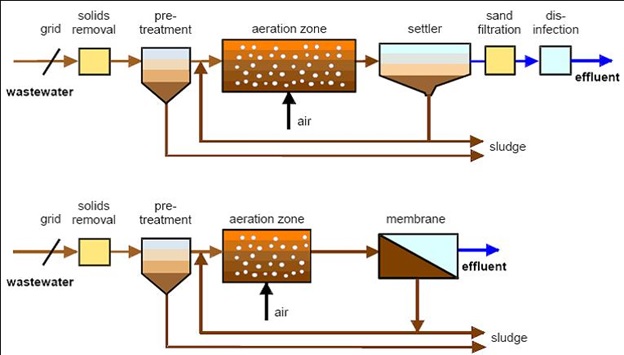
Figure 1: Comparison between ASP and MBR.
To sustain the wastewater flow across the membrane, negative pressure is needed, which is a labor- and energy-intensive procedure.
Moreover, the membrane must be backwashed at predetermined intervals and occasionally replaced. Regular expert maintenance and servicing are required for this system.
An upstream activated sludge buffer is part of the MBR system. As a result, there is less sludge produced than in FBBRs and MBBRs, and there is no need for sludge settlement, which saves space.
MBR Technology and BOD and COD reduction at various Steps of Treatment:
Membrane Bio Reactor technology uses several processes to control and reduce Biological Oxygen Demand and Chemical Oxygen Demand in wastewater. These processes include:
· Physical treatment,
· Primary treatment,
· Secondary treatment, and
· Tertiary treatment.
Physical Treatment:
Physical treatment is the first step in MBR technology and involves removing large debris, solids, and other materials that may clog the system. This is typically done through screening and grit removal. Physical treatment does not contribute significantly to BOD and COD removal, but it is an essential step in preparing the wastewater for further treatment.
Primary Treatment:
Primary treatment is the next step in MBR technology and involves the removal of settleable solids and organic matter that can be easily degraded. This process is achieved through sedimentation and the use of chemical coagulants.
Primary treatment can contribute up to 30% to BOD and COD removal.
Secondary Treatment:
Secondary treatment is the most critical process in MBR technology and involves the use of microorganisms to remove dissolved organic matter from the wastewater. In MBR technology, microorganisms grow in a suspended growth system. As the wastewater flows through the system, the microorganisms break down the organic matter, reducing the BOD and COD levels.
Secondary treatment can contribute up to 70% to BOD and COD removal, and the level of removal depends on several factors, including the type of microorganisms used, the operating conditions, and the design of the MBR system.
Tertiary Treatment:
Tertiary treatment in MBR technology involves the use of membrane filtration to remove any remaining contaminants in the wastewater after the primary and secondary treatment processes. The membrane filtration process is carried out using a membrane module, which consists of several small membrane fibers or sheets. The membrane module is usually made from materials such as polymeric or ceramic materials.
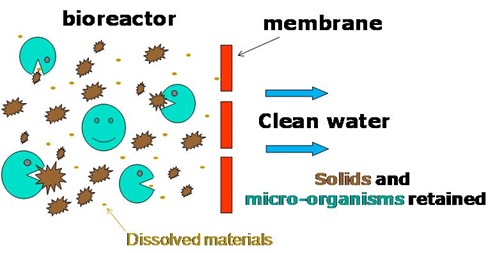
Figure 2: Diagram showing easy working of Membrane in MBR
The wastewater is pumped through the membrane module, and the membranes act as a physical barrier that separates the treated water from the remaining contaminants, including suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, as shown in Figure 2.
The membrane pore size varies from a few nanometers to several microns, depending on the type of membrane used.
The membrane filtration process is very effective in removing contaminants, and it can achieve a BOD and COD reduction of up to 99%.
The effluent produced from the membrane filtration process is of high quality and can be reused for various purposes, including irrigation, industrial processes, and even drinking water.
Advantage of MBR:
One of the significant advantages of using MBR technology for tertiary treatment is that it eliminates the need for additional treatment processes, such as sand filtration or activated carbon treatment, which are commonly used in traditional wastewater treatment plants. This makes the process more cost-effective and easier to maintain.
Challenges of MBR:
Challenges associated with MBR technology is the fouling of the membrane surface. Fouling occurs when the contaminants accumulate on the membrane surface, reducing the permeability of the membrane and decreasing the efficiency of the system. To overcome this challenge, regular cleaning of the membrane is required, which can be done through physical cleaning, chemical cleaning, or a combination of both.
Conclusion:
MBR technology is an effective method for reducing BOD and COD levels in wastewater. It can achieve up to 99% BOD removal and up to 90% COD removal. The control and reduction of BOD and COD in MBR technology are achieved through several processes, including physical treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, and tertiary treatment.
Physical treatment and primary treatment do not contribute significantly to BOD and COD removal, but they are essential steps in preparing the wastewater for further treatment. Secondary treatment is the most critical process in MBR technology and involves the use of microorganisms to remove dissolved organic matter from the wastewater. Tertiary treatment is the final step and involves the use of membrane filtration to remove any remaining contaminants.
Leading manufacturer of sewage treatment plants in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information